1 Definitions, Purpose and Significance
The ability of the paint film to resist environmental damage such as sunlight, air, water (acid rain), and microorganisms while maintaining its original properties is called the weather resistance of the paint film. Hand paint film, like plastic and other polymer materials, will inevitably be affected by the interaction of internal factors and external environmental factors over time, and some irreversible damage phenomena such as discoloration, loss of light, chalking, cracking, rust, peeling, spots, staining, etc. Therefore, for the quality of the coating, in addition to its appearance, physical, chemical and mechanical properties, it is more important to investigate its service life, that is, the durability of the paint film itself. It is obviously very important and necessary to carry out the weather resistance test and the comprehensive evaluation after the test of the paint film, which can not only objectively investigate the advantages and disadvantages of the comprehensive technical performance of the paint film, but also evaluate its real use value.
2. The causes and main mechanisms of paint film aging
2.1 The internal factors of paint film aging
The internal causes of paint film aging are generally related to the type and quality of raw materials such as tree J fingers, curing agents, pigments, fillers, additives and other raw materials used in the production of coatings, and are also inseparable from the matching of the coating formula system, rationality, film-forming conditions, coating methods, substrate selection, treatment methods and other factors. Common examples: the amount of paint often leaves some trace impurities in the polymerization process or the polymer itself contains some special chemical structure. When the coating encounters the radiation of ultraviolet rays during use, assuming that the molecular structure of the paint tree contains some ultraviolet absorbing groups, the aging defect of the resin will be easily highlighted, and the degradation of the surface of the paint film is inevitable after the resulting photochemical reaction. Another example: the common rutile titanium dioxide pigment has stable lattice and small photochemical activity, and its resistance to ultraviolet radiation is significantly better than that of Ruiqin titanium dioxide pigment. It shows that there are differences in the photochemical activity, hue, particle size and crystal form of different pigments, and it is these differences that will directly or indirectly affect the lightfastness and chalking resistance of the paint film.
2.2 External factors of paint film aging
The external causes of paint film aging refer to the combination of physical, chemical, biological and other damaging factors caused by the outdoor environment.
2.2.1 Light:
Sunlight is one of the main external causes of the aging of paint films for outdoor use. The spectrum of sunlight can be divided into three regions: ultraviolet, visible and infrared. The spectrum and energy of solar emissions in the atmosphere are shown in Table 9:
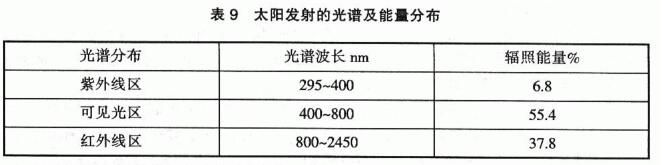
As shown in Table 9, although the spectral distribution of the ultraviolet region is very narrow, and the irradiation energy only accounts for about 7% of the total energy of the sun, the shorter the wavelength, the stronger the energy, and the greater the damage to many polymer materials. After the paint film is exposed to ultraviolet radiation with high energy, it will produce photo-induced oxidation reaction, which will directly lead to the gradual fracture of the polymer chain structure and chemical degradation, resulting in discoloration (darkening or fading), loss of light, chalking and other aging phenomena.
2.2.2 Water
In the outdoor environment, the role of water on the paint film is mainly manifested in various forms such as rainfall, humidity, and condensation. The paint film is kept under high humidity conditions for a long time, especially the water film formed during condensation, and the moisture can easily penetrate into the inside of the paint film. If the sunlight is fully irradiated, it will be easier to promote some water-soluble substances and substances containing hydrophilic groups in the paint film system to be dissolved and absorbed by water, thereby changing the composition and proportion of the paint film, and accelerating the water degradation of the paint film. When the moisture reaches the surface of the metal substrate, the moisture and the metal substrate will react with the electrodes, resulting in bubbles in the paint film and rust in the substrate.
2.2.3 Temperature
In the outdoor environment, the infrared rays in the sunlight are absorbed by the paint film and converted into heat energy, and the temperature of the paint film surface will increase accordingly. The photochemical reaction is always accelerated with an increase in temperature. Therefore, under the action of ultraviolet rays, the thermochemical reaction generated by heat energy accelerates the breaking rate of the polymer molecular chains in the paint film, resulting in the degradation of the surface layer of the paint film and the formation of free radicals, making the paint film hard, brittle, soft and sticky. The higher temperature also destroys the pigment in the paint film, and when the surface temperature of the paint film is high, when it rains, it will cause a certain temperature difference, which will cause the expansion and contraction between the paint film and the substrate, resulting in alternating internal stress. It is easy to cause blistering, opening, pulverization, peeling and other aging damage phenomena of paint film after the adhesion of the paint film decreases. (Related Instruments: Standard Light Source Box)
2.2.4 Oxygen
The interaction between the air and sunlight greatly promotes the speed of photo-oxidation and thermal oxidation of polymers in the paint film, and the paint film will produce pores. Tiny porosity can cause the film to lose its resistance to staining and cause spots. In severe cases, it will cause cracks, peeling, discoloration, loss of light and other damage to the paint film.
2.2.5 Combination of factors
The destructive force generated when a variety of destructive factors occur at the same time is the resultant force formed by the interaction and superposition of various destructive factors, and its power will far exceed the sum of the single factors, that is, the (1+1) big hand 2 effect, which is usually called the comprehensive destructive factor.
2.2.6 Miscellaneous
Other factors are: ozone, high-energy radiation, acid rain, mold, etc.
3. The main method of paint film aging test
The methods of paint film aging test are widely used in atmospheric aging test and artificial climate aging test. (Related Instruments: Aging Test Chamber)
3.1 Atmospheric aging test
3.1.1 Relevant standards: GB/T 9276-1996 Test method for natural climate exposure of coatings
Atmospheric aging test, also known as natural climate exposure test, refers to the study of the aging and damage effect of various atmospheric factors on the paint film in various natural environments, and evaluates its durability through the appearance inspection of the sample during the test period and after the test is completed, and the physical and mechanical properties of the paint film can also be tested during the exposure process or after the end of the exposure. According to the type of atmosphere, the atmospheric aging test can be divided into ordinary atmosphere, industrial atmosphere and oceanic atmosphere. According to the climatic characteristics, it can be divided into cold climate, cold and temperate plateau climate, sub-humid hot climate, sub-humid hot industrial climate, humid hot climate, dry hot climate, etc. The exposure methods can be divided into 45° south, local knot, vertical latitude and horizontal exposure.
3.1.2 Establishment of natural exposure sites
The natural exposure site should be established in a flat and open place, with no tall reservoirs and obstructions around, so that the model can fully be affected by various atmospheric factors in the area, and there should be no factory chimneys and facilities that can emit a large number of corrosive gases nearby, so as to avoid the impact of local serious pollution. Salt spray climate exposure sites should be built on seashores or islands. The exposure site should have the necessary meteorological observation equipment and various model coating inspection instruments and lighting facilities. Meteorological data mainly include: temperature, humidity, sunshine hours, solar radiation, rainfall, wind speed, wind direction, etc. The exposure frame should be made of materials that do not affect the test results, such as wood, aluminum alloy, or steel coated with anticorrosive coatings, and its structure should be durable, withstand the maximum local wind, and can freely adjust the exposure angle.
3.1.3 Methods of inspection of the model
The inspection of the sample GB/T 9276-1996 stipulates that the time unit of the exposure test shall be taken as the year and month, and if there are no special provisions, the test shall be inspected every half a month within three months, and once a month from three months to one year, and once every three months after more than one year. Due to the different requirements of coating varieties and the different destruction rates in the exposed areas, the inspection cycle can be appropriately changed according to the situation. The prescribed inspection items include loss of light, discoloration, cracks, blistering, spots, rust, gold, staining, mildew and shedding. There are two main inspection methods: instrument method and visual inspection method, among which gloss and color tests can be carried out according to GB/T 9754, GB/T 9761 and GB/]1' 11186.2. The chalking evaluation of coatings is divided into (; BIT 9277.
The natural climate exposure test can truly reflect the degree of environmental damage to the product in a certain area and a certain period of time, but it will be affected by the changes of many uncertain factors in the test conditions. Generally speaking, the impact of natural climate exposure always varies with the natural environment (region, country, meteorology, season) of the exposure site. In addition, the natural climate exposure test period of coating products is longer (in multiples of years). In order to meet the needs of economy, competition and shorten the cycle of natural aging test, many product standards in our garden have selected artificial climate aging test to test the weather resistance of products.
3.2 Artificial climate aging test, instrument type, basic structure and test method
Artificial climate aging test, also known as artificial accelerated aging test, is a way to simulate the aging process of natural climate action or under broken glass in the laboratory based on the relationship between climate change factors and paint film damage found in the results of a large number of natural climate exposure tests. Compared with the natural climate exposure test, the artificial climate aging test only involves a few limited factors (variables), which are easy to control and moderately intensify, so as to accelerate the aging test. During the test, the durability of the sample can be evaluated by checking the appearance, physical, chemical, mechanical and other properties of the sample during and after the test.
Artificial climate aging testing machine is a large-scale instrument that can create the so-called artificial climate (simulating a variety of characteristic climatic factors in nature) in the laboratory and achieve the effect of accelerated aging test. The artificial climate testing machine can generally be selected and classified by digging the light source used in the test; Common types are: carbon arc ultraviolet lamp type, fluorescent ultraviolet lamp type, xenon arc lamp type and metal surface lamp type.
3.2.1 Carbon arc ultraviolet lamp type
The application history of carbon solitary ultraviolet lamp aging machine is relatively long, it is composed of fuselage, drum, rod, light cover, arc adjustment mechanism, humidifier, etc. Originally, 1if was used to evaluate the lightfastness and color rate of printing and dyeing fine fabrics and products, and later improved as a simulated outdoor light aging test equipment for coatings and other materials. The carbon arc ultraviolet lamp aging machine is divided into closed type and open type according to the structure, and is divided into ordinary type and sunlight type according to the composition of carbon rod. The device is usually equipped with multiple carbon rods at the upper and lower ends of the instrument, and when the appropriate voltage and current are applied between the two groups of broken rods, a large amount of ultraviolet light will be generated. The structure and type of carbon arc lamp are different, and the degree of simulation of sunlight is also different, such as the sunshine type carbon arc lamp because of the special metal elements contained in its carbon rod, the degree of simulation of sunlight will be better than that of ordinary type. However, no matter which kind of arc breaking lamp, the optical spectrum is quite different from the spectrum of outdoor sunlight, coupled with the cumbersome operation of the instrument, poor test continuity and other reasons, the test method can only be seen in the earlier standards. For example, AsTM G152 is an aging test method for open and closed arc breakers for non-metallic materials.
3.2.2 Fluorescent ultraviolet lamp type
The fluorescent ultraviolet lamp aging machine is composed of a fuselage, a fluorescent ultraviolet lamp (uV), a water spray system, a cold doubt system, and a detailed illumination controller. The energy distribution of the subfluorescent ultraviolet lamp depends on the emission spectrum produced by the phosphorus co-existence and the propagation of the glass tube, so the phosphorus co-existence is added to the lamp to convert it to a longer wavelength, and the common fluorescent ultraviolet lamp is divided into two types according to the specific spectral band: UVA (UVA-340, UVA-351) and UVB (UVB-313, F40). Fluorescent UV lamp equipment can provide simulation of day/night, different temperatures, indoor and outdoor environmental conditions by controlling the change of light/dark cycle, change of temperature, humidity and water spray, and change of lamp. The fluorescent ultraviolet lamp simulates the ultraviolet part of sunlight better than the arc breaking lamp, but it still artificially increases the spectral energy that deviates from the ultraviolet part. The comparison between fluorescent ultraviolet lamp and natural light is shown in Figure 36 and Figure 37.
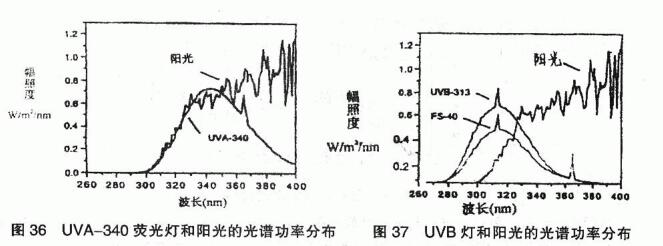
It can be seen from Figure 36 and Figure 37 that whether it is UVA-340 lamp or UVB-313 lamp, their spectral distribution map has a large difference with natural light, their energy is almost concentrated between 280~360m, there is almost no energy above 360nm, and a part of the ultraviolet spectral energy and most of the energy of the visible spectrum and infrared spectrum are missing. In other words, the light source used in this type of testing machine cannot effectively simulate the distribution of the full spectrum of energy of outdoor sunlight. It is worth mentioning that when the UVB-3 13 lamp is working, it will emit a large amount of radiation energy below 295nm (natural light cut-off wavelength), which will cause the aging phenomenon that will not occur outdoors, resulting in a large difference between the test data of the tested material and the outdoor natural aging test data. Although the "outdoor simulation" of the fluorescence ultraviolet accelerated aging test is poor, and the test data of some polymer materials will cause different degrees of deviation, the test method can be quickly assessed, compared in parallel, and screened for the aging resistance of some special materials, such as high-energy radiation resistance test, identification of degradable plastics, etc., so it is still used by some standards.
Relevant base indication: GB/T 16422.3-1997 Plastic laboratory light source exposure test method - Part 3 fluorescent ultraviolet lamp.
IS01 1507:1997 Artificial aging of coatings of pigments and varnishes - exposure to fluorescent ultraviolet rays and water.
3.2.3 Xenon arc lamp type
The xenon arc lamp aging machine is divided into two types: flat plate type and rotary type according to the structure, and is divided into two types: air cooling and water cooling according to the cooling method. The xenon arc lamp aging machine is composed of a fuselage, a xenon arc lamp system, a light crosser, a water spray system, a cooling system, a humidification system, an irradiance controller, a rotating drum, etc. Xenon arc lamp is an arc discharge light source filled with high-purity xenon gas, and when an appropriate voltage and current are applied between the metal electrodes at both ends of the lamp, a spectrum closer to sunlight will be generated, which can mimic natural light under various conditions. The power of air-cooled xenon arc lamp is generally small, and there is more energy concentrated in the (800-1000) nm near-infrared wavelength range, which is easy to make the sample accept more heat, and this cooling method will have a certain impact on the optical system and overall performance of the instrument. The water-cooled xenon arc lamp is equipped with two tubular transparent glass fervers with the same axle, and the deionized water for cooling can flow between the surface of the lamp and the inner and outer filters. In addition to cooling the lamp, the water can also absorb some of the excessive infrared energy. The main function of the combined filter is that the desired energy spectrum distribution can be obtained by matching the properties of two different glasses. Commonly used filters are: quartz glass, measuring glass, high borosilicate glass, soda lime glass and coated infrared absorbing quartz glass. Figure 38 shows the spectrum of xenon lamp and natural light
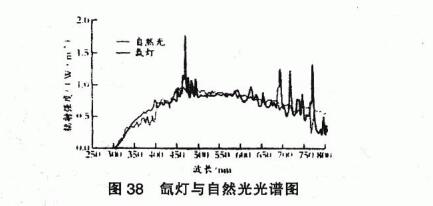
As can be seen from Figure 38, the spectrum of xenon lamp is the same as that of . The spectrum of natural light is similar in the ultraviolet and visible parts and simulates natural light well. In addition, by using different combinations of internal and external filters of xenon lamps, and by changing the parameters such as temperature, humidity, rainfall cycle and irradiation intensity of xenon lamps in the Test Chamber, the use environment of different products can be simulated, such as: coatings, plastics, automotive interior and exterior trims, textiles, etc. At present, the use of water-cooled xenon lamp for artificial accelerated aging test has become a general, first consideration of weather resistance test method, and the corresponding xenon lamp aging test methods are also many, including 1S0, ASTM, sAE, JIs, GM, etc. The common standards are shown in Table 10 for artificial accelerated aging test methods

As can be seen from Figure 39, the spectral distribution of metal halide lamps is very close to the spectral distribution of sunlight received on the Earth's surface, especially in the infrared region. The metal surface lamp type test device is large-scale, and is mainly used in the steam rate and its zero partArtificial accelerated aging test of large equipment such as electrical and electronic products.
Related Standards: Aging of Automotive Components in DIN75220 Solar Simulation Equipment (Metal Halide Lamps)
3.3 Experimental elements of artificial climate aging
Regardless of the artificial climate aging test, the test parameters in the test method used should be thoroughly understood before the test. Such as: light source type, filter combination, black standard temperature/blackboard temperature, box temperature, rainfall cycle, light/dark cycle, condensation, irradiation intensity that imitates one sun or two suns, monitoring point, speed of the sample holder, conductivity, purity, pressure, etc. Strict implementation of the provisions of the corresponding standards during the test is the basis for ensuring the accuracy of the test data.
3.3.1 Preparation, maintenance and testing of test plates
The selection, treatment, preparation method and curing time of the substrate of the artificial climate aging test template are generally required in the relevant product standards, and can also be agreed between the entrusting test party and the inspection agency, and can also be prepared and cured in accordance with the provisions of GB/T 1765-89 "Preparation Method for Determining Paint Film for Moisture and Heat Resistance, Salt Resistance and Weather Resistance (Artificial Acceleration)". When the curing period of the test plate is over, in addition to leaving one of them as the standard board, the remaining 2-3 pieces are put into the testing machine for testing. The sample should be placed on the ground in the test plate frame to prevent it from falling during the test, the air in the box should be circulated, and the arrangement position of the sample on the test plate frame should be changed with a certain time interval, such as: the position of the upper row and the middle row and the lower row are exchanged regularly, so as to ensure the uniformity of the test plate under various conditions.
3.3.2 Artificial climate aging test time
The test time can be carried out with reference to the provisions of the relevant product standards, or it can be agreed with the entrusting test party, and the test can be terminated when some test parameters (discoloration, loss of light, chalking, blistering, rusting, etc.) reach a certain grade or comprehensive evaluation level. It is also possible to use the "reference material method" to put the sample (reference standard plate) with known aging resistance performance into the test together with the tested sample to determine the difference between the sample tested and the reference standard plate in a certain test stage or to determine the test endpoint. The chemical structure and aging condition of the reference standard plate should be similar to the test model as much as possible.
3.3.3 Inspection and rating of artificial climate aging test samples
During the artificial climate aging test and at the end of the test, the sample paint film should be inspected and graded. When the sample is inspected, the test sample can be taken out of the box and compared with the standard board. The main inspection items are: discoloration, loss of light, chalking, blistering, rusting, cracking, peeling, spots, gold, staining, mildew, etc. The evaluation can be carried out in accordance with the requirements of the relevant product standards, or in accordance with the provisions of GB/T1766-1995 "Rating Method for Aging Resistance of Pigment and Varnish Coatings". There are two types of ratings: individual rating and comprehensive evaluation. The comprehensive assessment is divided into two types of products, decorative paint and protective paint, according to the degree of sample damage: excellent, good, medium, can, poor, inferior six levels. The damage phenomenon caused by the 5mm around the sample and the hole and external factors is not assessed, and the final result is subject to the two pieces with the same level in the = test board.
3.3.4 Factors influencing the results of artificial climate aging tests
3.3.4.1 Test instrument calibration
After the artificial climate aging testing machine has been running for a period of time, it is very important to verify the monitoring parameters of the testing machine, mainly including: standard light source, relative humidity, black mark temperature, box temperature, irradiance, irradiation, water purity, etc. Otherwise, the reproducibility of the test results will be reduced.
3.3,4.2 Combination and cleaning of light crossers
In the aging test of water-cooled xenon arc lamp, attention should be paid to the combination of internal and external light crossers according to different test standards, otherwise abnormal spectral and emission intensities will be generated, causing deviations in test results. In addition, deposits and other residues on the filter can also affect the light transmittance of the filter, so the filter should be cleaned or replaced regularly.
3.3.4.3 Test water
The water quality of the deionized water used for the cooling of the lamp in the instrument, simulating outdoor deterioration, condensation and humidification should meet the requirements of GB6682 laboratory water secondary water, otherwise evaporation residues will be formed on the surface of the lamp, which will affect the radiation intensity and service life of the lamp, and the sediment on the surface of the test plate will also produce unreliable test results.
3.2.5.4 Compressed air
The compressed air used for humidification in the instrument should be dehydrated, deoiled, filtered dust and constant pressure before it can be supplied to the instrument, otherwise it will cause poor humidification effect and test plate pollution.

