1 Definitions, Purpose and Significance

2 Relevant Standards
GB/T 1771_1991 Determination of neutral salt resistance of colorcoats and varnishes
IS07253: 1996 Determination of the resistance of color paints and varnishes to neutral salt spray
ASTM B117-2003 Salt Multi-test
ASTM B287-74 Acetic Acid Salt Spray Test
ASTMB368-97 Copper-accelerated acetate multiple-salt test (CASS test)
3 Introduction to test methods
3.1 Test principle
Although outdoor salt corrosion (specific test environment) can more truly reflect the impact of environmental conditions on the product at a certain stage, due to the uncontrollable outdoor uncertainties and the need to shorten the test time, many industrial product standards stipulate that the salt spray resistance test is used to evaluate the salt corrosion resistance of the paint film. The test is based on the results of a large number of outdoor salt corrosion tests, and finds out the relationship between outdoor environment and paint film damage, the purpose is to simulate the salt spray corrosion environment in nature in the laboratory, and evaluate the salt corrosion resistance of the paint film through the observation of the sample during and after the test.
3.2 Test equipment
At present, the test equipment commonly used at home and abroad is a salt spray corrosion chamber. The equipment is mainly composed of a box (spray multi-chamber), a salt solution storage tank,It consists of a level controller, a properly treated compressed air system, a central jet tower for one or more nozzles, an adjustable baffle, a model bracket, an air saturator, a box immersion heater and the necessary temperature and humidity controllers. When the salt solution is exported from the solution storage tank and flows through the liquid level controller into the bottom of the spray tower, under the action of the air flow (pressure difference) of a certain pressure, it is sucked in and atomized by the self-priming nozzle to form dense salts, which are evenly settled on the test model in the mist chamber after being sprayed out through the baffle guide at the upper part of the spray tower. (Related Instruments: Constant Temperature and Humidity Test Chamber)
3.3 Operational Points
3, 3.1 temperature control
The temperature in the salt spray chamber used for the neutral salt resistance test and the acetic acid/salt spray test should be kept at (35±2) °C, and the temperature of the air saturator should be higher than the temperature in the chamber (5-10) °C. The temperature in the salt spray chamber for the cool acid/copper acceleration one-salt multi-salt test should be kept at (49±1) °C. (Related Instruments: Constant Temperature and Humidity Test Chamber)
3.3.2 Preparation of salt spray test solution
3.3.2.1 Neutral salt resistance should be prepared with test solution
The chemically pure grade sodium chloride in accordance with GB1266 conditions is fully dissolved in the tertiary water in accordance with GB6682., with a concentration of (50i 10) g/L. The pH of the solution measured with a precision pH meter (accuracy 0.1 pH) at 25 °C should be in the range of (6.5-7.2). When the range is exceeded, pure hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide solution can be added for adjustment, and the prepared solution can be used only after transition.
3.3,2.2 Acetic acid is prepared with a salt spray solution
First, the chemically pure grade sodium cyanide that meets the conditions of GB1266 is fully dissolved in the tertiary water that meets the conditions of GB6682 at a concentration of (50i 10)g/L. Then use glacial acetic acid to adjust the pH value of the solution, so that the pH value of one salt and multiple solutions of acetic acid is in the range of (3.1-3.3), and the prepared solution can be used only after filtration.
3.3.2.3 Preparation of copper-accelerated acetic acid and salt spray solution
In the first step, the chemically pure grade chloride that meets the conditions of GB1266 is fully dissolved in the tertiary water with GB6682 in a concentration of (50±10) g/L. In the second step, 0.25g of human reagent-grade dicyide 1 (Cu Cl2 2H20) is added to each liter of saline, and dissolved and mixed thoroughly. The third step is to adjust the pH value of the solution with glacial acetic acid at 25 °C to make it in the range of (3.1~3.3), and the prepared solution can be used only after transition. (RELATED INSTRUMENTS: PH METER)
3.3.3 Control of salt spray sedimentation
There should be at least two dry 1 salt spray collectors made of glass or other temperamental materials in the salt spray exposure area, one of which should be installed near the spray outlet and the other at a much higher spray outlet, and the location of which requires that only the settled salt spray be collected, and not the liquid dripping from the specimen or other parts of the chamber. Salt sedimentation: After a minimum of 24 h cycles, the collected solution is calculated, and each 80 cm2 collector per unit area should collect (1-2) ml of salt solution with a concentration of (50i 10) g/L and a pH of (6.5-7.2). The collected sodium chloride solution is not reusable.
3.3.4 Preparation, maintenance and pretreatment of test samples
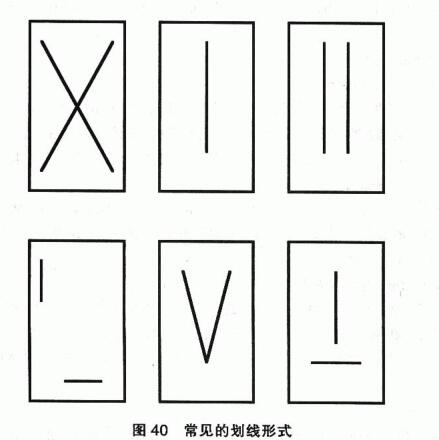
The selection, treatment, preparation method and curing time of the salt spray test sample substrate are generally required in the relevant product standards, and can also be prepared and cured with reference to the provisions of GB/T 1765-89 "Paint Film Preparation Method for Determining Damp Heat Resistance, Salt Resistance and Weather Resistance (Artificial Acceleration)", or agreed between the entrusting test party and the inspection agency. The back and perimeter of the plate to be tested can be applied with the test sample or a coating system known to have better corrosion resistance. If it is necessary to do the marking (cutting through line, scratching, scratching and scratching) test, a marking tool with a carbide crane (cemented carbide) tip (such as the single-edged cutter in GB9286 recommended by GB/T1771-91 and type E in ANSI B94.50 recommended by ASTMD1654-2005) but similar tools such as blades, needles, uncutting knives, scissors and other similar tools are not allowed. On the surface of the sample, a bright V-shaped line without burrs is carved evenly across all coatings on the substrate. If it is necessary to do the test of cutting through the metal plating, the degree of marking shall be agreed between the commissioning test party and the inspection agency. If necessary, several lines can be drawn as agreed, and the quality of the lines can be observed with the help of a low-magnification glass. Common forms of crossing: two crossed lines, a straight line parallel to the long side, two straight lines parallel to the long side of the hand, two vertical lines, a V-shape, etc., as shown in Figure 40:
3.3.5 Testing, testing, inspection and evaluation of test samples
When the curing period of the test plate is over, except for one of the standard plates, the remaining three pieces should be put into the testing machine immediately
Trial. The template should be placed on the template bracket in the box with the surface facing up, and no contact between the samples and between the samples and the box is allowed, and the templates are not allowed to be stacked. In addition, the sample should be changed at regular intervals on the test plate rack, such as the exchange of the front, middle and rear rows.
During the test, you can refer to the provisions of the relevant product standards, or entrust the test party and the inspection agency to agree on a damage index as the end point of the test, such as: the width of one-way rust, the level of blistering, rust and falling off in the unmarked area, etc. Common test times are multiples of 24 hours, such as: the recommended exposure cycles in the American ASTM B117-1997 standard are 24, 48, 96, 200, 500, 720 hours.
When the sample is inspected, the test sample can be taken out of the box and compared with the standard board in sufficient light or under light. The evaluation can be carried out with reference to the requirements of relevant product standards, or with reference to GB/T1740-89 "Determination of Paint Film Resistance to Damp Heat", ASTM D1654-92 "Evaluation of Specimens Coated with Pigment or Paint after Subjecting to Corrosive Environment" and other evaluation standards, and the unidirectional direction of the marked and unmarked area of the sample: the degree of TF erosion and direct extension and blistering, rusting, falling off, and discoloration are inspected and graded. The periphery of the model and the hole Zhouguo within 5mm are not assessed, and the final result is subject to the same level of the three test plates.
The common methods for the evaluation of the marking of the test sample are: air blowing method, rinsing and scraping method, and tape removal method.
Air puffing means that after the dew cycle is completed, each specimen is rinsed with a slow stream of water at a temperature of 110°F (45°C) or less. The hand-held nozzle is sprayed along the entire scribing line at an angle of about 45°, the air pressure is 550kPa, and the diameter of the TL nozzle is 3mm. The near-scribing surface of the mechanical disturbance part of the air nozzle is used to ensure the passage of air jet. The air injection is completed within 15 minutes of removing the specimen from the blast chamber. If air spraying cannot be completed within the specified time, the test plate is immersed in room temperature water or stored in a plastic bag to avoid any effects of dry manipulation.
The rinse and squeegee method involves rinsing each specimen with a slow stream of water at a temperature of 110°F (45°C) or less after the exposure cycle is completed. With a scraper that conforms to the ASTMD1654_924,5, under a slow stream of rinse water, scrape the specimen strongly. Holding the scraper, the scraper surface is perpendicular to the specimen face and parallel to the scribing line, scraping back and forth across the scribing line to remove the coating that has rotted on the substrate and the coating that has lost adhesion, but should not scrape off the coating that still has adhesion. The scraping operation is completed within 15 minutes of removing the specimen from the exposure box. If the scraping operation cannot be completed within the specified time, the specimen is immersed in room temperature water or stored in a plastic bag to avoid any effects caused by dry manipulation. (Related Instruments: Adhesion Tester)
The tape removal method means that after the exposure cycle is completed, the test board is washed with clean water and dried at (23±2) °C, and a piece of tape paper with a size of about 25mmx150mm is glued to the cutting line, and then quickly pulled away in the direction perpendicular to the test plate.
It is worth noting that whether it is the air blowing method, the elaboration method or the tape removal method, it is generally only applicable to the final result evaluation and not the evaluation of the test results of the middle L division in the continuous test by hand, that is to say, the same group of test samples can not be repeatedly processed above, but the test results of different test stages can be met by increasing the number of test plates and taking out the evaluation at different stages. If necessary, the manufacturer and the testing institute may also agree to adopt other applicable assessment methods.
After the above treatment, the measurement is taken from the width of the corrosion or paint layer damaged by the line Wangyan, and the one-way rust is evaluated. For the measurement of unidirectional corrosion, the representative maximum, minimum and average value should be taken, and the average of the representative F erosion distance should be taken unless otherwise specified. Value.
The assessment of the unmarked area of the opponent can be recorded and rated, or it can be rated using ASTM D714. If it is necessary to assess the formation of decay under the paint film, the coating can be carefully peeled off with a neutral paint stripper.
3.4 Factors influencing the results of salt spray test
3.4.1 The salt spray chamber and all parts in contact with the salt solution or salt spray should be made of emotional, breathable materials, otherwise the simultaneous corrosion of the parts will affect the test results of the test plate.
3.42 The angle of the baffle of the spray tower should be adjusted to the appropriate position to avoid the impact of external force due to the direct alignment of the spray direction of the nozzle with the test sample, which will affect the test effect of free sedimentation of salt.
3.4.3 The emptying pipe of the salt multi-box should be of sufficient size to reduce the back pressure in the box and empty the pipe. There should also be a shielding wrench at the end, otherwise there will be pressure or vacuum fluctuations in the box and have a certain impact on the inspection results.
3.4.4 The compressed air that provides spray for the salt spray chamber should be degreased, dewatered and dusted, otherwise it is easy to block the nozzle or directly affect the test results.