Types of surface defects and their characteristics
1) Pinholes refer to a type of pores on the surface of the coating that are similar to those drilled by a needle tip. Although their density and distribution are different, they are generally similar in size and shape when viewed under a magnifying glass. For example, pinholes in the electroplating layer are usually defects caused by the adsorption of hydrogen bubbles during the electroplating process.
2) Pitting refers to a type of irregular concave hole on the surface of the coating, which is characterized by different shapes, sizes, and depths. Pockmarks are generally caused by defects in the substrate or adhesion of foreign matter during electroplating.
3) Burrs refer to a kind of raised and prickly foreign matter on the surface of the coating, usually characterized by being more prominent in the upper plating or high current density areas.
4) Bubbles refer to a type of raised vesicles on the surface of the coating, which are characterized by varying sizes and densities, and are separated from the substrate. Bubbling is generally more obvious on zinc alloy and aluminum alloy coatings.
5) Peeling refers to the cracking or non-cracking defect in which the coating and the substrate (or undercoat) peel off. Peeling (recommended detection instrument: scratcher) is usually caused by poor treatment before coating.
6) Spots refer to a type of stains, dark spots and other defects on the surface of the coating. It is caused by poor deposition, adhesion of foreign matter or unclean passivation solution during electroplating .
7) Fog means that there are cloud-like coverings of varying degrees on the surface of the coating, most of which are generated on the surface of the bright coating.
8) The yin and yang side refers to the defects of uneven brightness or uneven color on the surface of the coating. In most cases, it shows certain regularity in similar products.
In addition to the above-mentioned surface defects, the surface of the coating sometimes has defects such as silk flow, scratches, water marks, and tree-like and spongy coatings , which should be strictly inspected.
Test Conditions
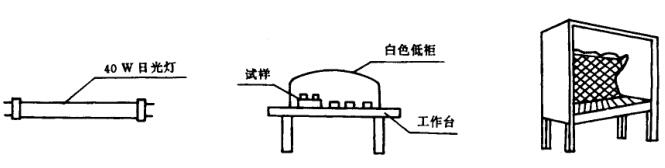
In order to clearly observe the surface defects of the coating and prevent the interference of external factors, the visual inspection of the surface defects of the coating should be carried out on the specified appearance inspection workbench or appearance inspection box (also known as the standard light source box, north-south tide note) (as shown in the figure)
When natural lighting is used for visual inspection, the sample should be placed on a white platform without reflection and inspected under natural .
When artificial lighting is used for the appearance inspection workbench and appearance inspection box, the illuminance should be 300lx (approximately natural light (equivalent to the illuminance at 500mm of a 40w fluorescent lamp), and a white typing paper cabinet should be placed under the lighting for visual inspection . The distance of the naked eye is not less than 300mm. For important coatings and painted parts with special requirements , a 2-5 times magnifying glass is allowed to be used for inspection.
Test Methods
For the coated parts to be inspected for coating appearance defects, the oil stain on the surface of the sample should be wiped off with a clean soft cloth or cotton gauze before inspection , but care should be taken not to scratch the coating. During the inspection, the operator should concentrate his attention, carefully observe whether there are various unacceptable defects on the coating surface, and make a correct assessment according to product quality and technical standards. The degree of malpractice should be explained in words, and the appearance should be sealed if necessary .
In general, the coating on the surface of the product to be coated should meet the requirements of fineness, uniformity, completeness and smoothness. The following surface defects are not allowed on the part where the product is specified to be coated:
(1) Obvious pores, air bubbles, pile flow and wrinkling;
(2) There are pitting, ash, dirt and obvious unevenness of the coating film on the main surface (it is recommended to use a wire rod coater for coating film preparation);
(3) There are serious defects such as missing coating, shedding, abrasion and stickiness;
(4) For the surface of products with color and gloss requirements, there are color differences and uneven gloss.

