The principle of the coating cupping test is similar to the sub-bending test, which is also the ability to detect the deformation of the coating layer with the substrate, and evaluate whether the de-coating bonding force is qualified by the situation of opening or peeling after the coating is deformed.
The sample is tested on a cupping testing machine. The test conditions are that the diameter of the steel ball is 20mm, the diameter of the cup mouth is 27.5mm, and the steel ball is moved from the back of the sample (uncoated surface) to the coated Press in the direction of the surface, and the depth of the indentation varies with the substrate and the coating surface, generally 7 M. Observe the opening of the coating on the protruding deformed part. If the coating deforms like the substrate without cracks, peeling and peeling, It means that the coating adhesion is qualified. (Related instrument: cupping Tester)
Heating and cooling test method (thermal shock test)
The heating and cooling test method, also known as the thermal shock test method, is to heat the tested sample at a certain temperature, then quench it, and use the different deformation coefficients of the coating layer and the substrate to evaluate the bonding of the coating. Whether the force is qualified. When the force between the coating and the substrate due to temperature deformation is greater than its bonding force, the coating will peel off. This test is applicable to the situation where the linear shadow coefficient of the coating and the substrate is significantly different.
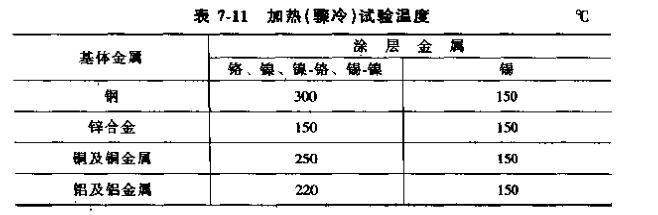
The specific test method is: heat the sample to the predetermined temperature with a constant temperature box-type resistance furnace, and the holding time is generally 0.5-1 h, depending on the specific situation. After the sample is heated and kept warm, the sample is naturally cooled in the air , or put it directly into cold water for ring cooling. Observe the surface layer of the sample, and if it does not peel or fall off, it means that the binding force is qualified.
The heating temperature of the sample is required to be the temperature specified in Table 7-11, and the temperature error is 1°C. Some easily oxidized metals should be heated in an inert gas or in a suitable liquid.