In the actual use of coatings, one of the most widely used and most effective properties is the wear resistance of the coating. When the coating is mainly used in wear-resistant applications, it is even more necessary to understand and evaluate the wear-resistant performance of the coating, which is important for the selection of spraying materials, the design of the spraying process, and the performance of the predicted coating. very necessary.
1. Coating wear resistance
Since the coating is a flat stack of sprayed material particles on the surface of the substrate, the particles that make up the coating are harder than the original sprayed material. Because pores are distributed between the particles of this stack, the macroscopic hardness of the coating is not high. Very high, but the particles themselves have the unique property of being hard. Moreover, compared with the original sprayed material, the sprayed coating has more oxides in different forms (such as granular) in the sprayed structure, or as a thin film interposed between the coating and the particles, forming a hard material dispersed. This is the reason why the coating can be used as an excellent wear-resistant material. In addition, if two kinds of wire materials with different properties are used during spraying, a mixture of two materials or a pseudo-alloy coating can be made. This is another reason why coatings can be used as wear resistant materials. There are many wear-resistant materials for spraying, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, molybdenum, self-fluxing alloy or self-fluxing alloy mixed with superhard powder, and various ceramics (alumina, chromium oxide, etc.). A strong wear-resistant coating can be obtained by adding superhard powder such as tungsten carbide to the spraying material.
2. Inspection of coating wear resistance
The wear resistance test of the coating is generally to simulate the working conditions of wear, and conduct a comparative friction and wear test to evaluate and test the wear resistance of the coating. In practical applications, there are many types of wear, and there are many corresponding wear test methods.
Commonly used are the following.
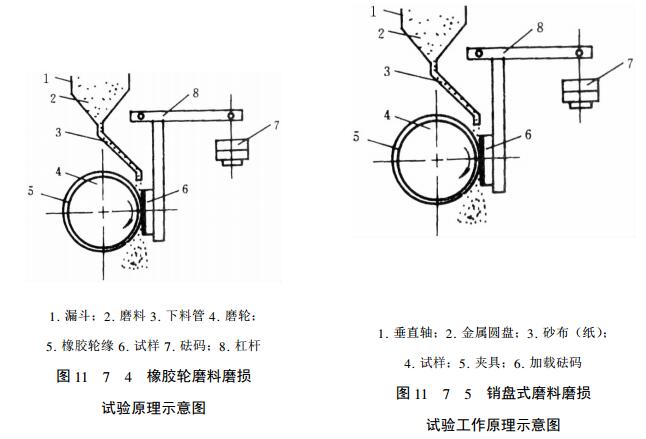
1) Abrasive wear test There are generally two types of abrasive wear test, one is rubber wheel abrasive wear test, and the other is pin-on-disk abrasive wear test.
2) The diagram of rubber wheel abrasive wear test is a schematic diagram of the test principle. Abrasives with a certain particle size fall between the rotating grinding wheel and the square sample through the feeding tube at a fixed rate. The rim of the grinding wheel is rubber with a specified hardness. The sample is pressed against the rotating grinding wheel with a certain pressure by means of a lever system, and the coated surface of the sample is in contact with the rubber wheel surface. The direction of rotation of the rubber wheel should make the direction of movement of the contact surface consistent with the direction of abrasive flow. During abrasive rotation, the abrasive produces low stress abrasive wear on the specimen. After a certain friction stroke, measure the weight loss of the sample, that is, the reduction of the coating, and use this to evaluate the wear resistance of the coating (related instruments: wear testing machine).
A typical sample is a rectangular test piece of 50mm×75mm, with a thickness of 10mm. Prepare a coating on its plane, and use a surface Grinder to grind the coating. The grinding direction should be parallel to the length of the sample. Make the coating surface free of any attachments or defects. Generally, the test parameters are
| rubber wheel material | Neoprene |
| abrasive | 50-70 mesh natural quartz sand |
| Rim speed | 140m/min |
| friction stroke | 1000 turns, that is, 550-560m |
| load (pressure) | 130N |
(2) Pin-on-disk abrasive wear test Figure 11-7-5 is a schematic diagram of the working principle of the pin-on-disk abrasive wear test. Use sandpaper or emery cloth on the disc as the abrasive for the testing machine. The sample is made into a pin type, which is pressed on the disc sandpaper under a certain load pressure, and the coating surface of the sample is in contact with the disc sandpaper. The disc rotates, and the sample moves linearly along the radial direction of the disc. After a certain friction stroke, measure the weight loss of the sample, that is, the wear amount of the coating, so as to evaluate the wear resistance of the coating. The test equipment is a domestic pin-disc type 01.!# abrasive wear Tester. The sample adopts a cylindrical shape with a diameter of "$$. The coating is prepared on one plane end of the test, and the coating is ground and cleaned to make the surface free of any defects and attachments. The end surface of the sample should be perpendicular to its axis. The suggested test parameters are as follows
Disc speed: 60r/min
Abrasive : 150-mesh silicon carbide sandpaper with a hardness of about Hm2 600; or 140-180 mesh artificial quartz sandpaper with a hardness of about Hm840.
Sample feed rate : 4mm/rs
Test load : 24N
Friction stroke : 9m
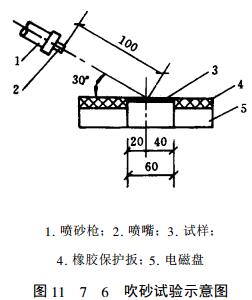
2) Sand blowing test The wear caused by the surface of the painted part being scoured by sharp hard particles is erosion wear, and these particles can be carried by gas or liquid and impact the surface of the painted part at a certain speed. The erosion and wear resistance of the coating can be evaluated by sand blowing test.
The test principle is shown in Figure 11-7-6. The sample is placed in the sandblasting chamber with the coating upward, fixed on the electromagnet, and protected by rubber plates around it. Then use a jet-suction sandblasting gun to blow the sand. The sandblasting gun is fixed with a clamp to keep the sandblasting angle and distance constant. And maintain a certain blasting air pressure and sand supply rate. Abrasives generally use corundum sand. During the blasting process, the abrasive will cause erosion and wear to the coating. Sand blowing time is generally set at 1 minute.
After the test, the weight loss of the sample is measured, that is, the amount of coating mass reduction. It is used to evaluate the erosion and wear resistance of coatings. Generally used test parameters are as follows:
Sample length 60mm, width 50mm, thickness 5mm, coating thickness ≥ 0.6mm.
Sandblasting gun: jet-suction type.
Nozzle hole diameter ø10mm
Sand blasting air pressure 0.54MPa
Sand blasting angle 30°
Sandblasting distance 100mm
Sandblasting time 1min
3) Friction and wear test
The relative movement of various friction pairs produces wear, and there are many factors that affect the wear, such as the material, surface shape, movement form, working conditions and lubrication methods of the accessories. Therefore, it is difficult to evaluate the wear resistance of this type of coating. Generally, the wear resistance of the coating should be tested by simulating the actual working conditions as much as possible. Generally, the domestic MM-200 wear testing machine can be used in the laboratory. Make the sample into a ring of ø40mm×10mm
Pre-process a ring groove with a width of 9 mm and a depth of 0.5 mm on the ring surface, and then prepare a coating on the ring groove, and grind the ring surface to the sample size on a grinding machine, clean it and carry out the test. The accessories that form the friction pair are shown in Figure 11-7-7
Four kinds of contact and motion forms are formed with the sample coating respectively. The material of the accessories can be CCr 15 or cast iron, or the material of the accessories that meets the actual working conditions. During the test, dry friction or lubricated friction can be adopted respectively, and different friction speeds can also be adopted. After the test, determine the weight loss of the sample, that is, the reduction of the coating. According to the test results of each group of friction pairs and conditions, the wear resistance of the coatings was compared. Generally, the following test parameters can be used.

Lubrication conditions Dry friction or 20 # engine oil lubrication, 5-6 drops/min.
The friction speed is 200r/min (0.42m/s) or 400r/min (0.85m/s).










