Metallographic microscopy is one of the physical methods. Use the normal metallographic method to make a cross-section sample of the tested coating, and then observe the enlarged image of the cross-section of the tested coating on a metallographic microscope with a micrometer eyepiece, so as to directly measure the average of the local thickness of the coating. thickness. Because this method directly measures the section thickness of the coating under a certain magnification, it has the advantages of high measurement accuracy, sufficient basis, and intuitive discrimination. Or use other thickness measurement methods to verify and arbitrate painted parts with disputed results.
1) Principle of the method
Metallographic thickness measurement is a method of observing and measuring the cross-sectional thickness of the coating to be tested by using a special metallographic microscope with a certain magnification and a micrometer eyepiece. In order to make the profile of the coating conform to the requirements of the metallographic microscope inspection, the coating to be tested should be cut, edge protected, inlaid, ground, polished and chemically etched in advance during thickness measurement, and then a sample that meets the requirements should be prepared. conduct.
2) Test instrument
It is allowed to use various types of metallographic microscopes with calibrated micrometer eyepieces. The magnification series of metallographic microscopes should be more than 200~500 times, and 200 times when the coating thickness is more than 20 μm, and the coating thickness is 20 μm. Use more than 500 times when it is below. (Related Instruments: Thickness Gauge)
3) Sampling and cutting
The sampling methods and quantities of various inspected coatings are based on the technical conditions and regulations of the coatings. Generally, the samples can be cut from one or several places on the main surface with a special cutting machine. Unless otherwise specified, Cuts should be made at areas representative of the coating thickness and prone to blemishes. Care should be taken not to damage the coating when cutting the sample, so as to prevent the coating from bursting and falling off during cutting and affecting the accuracy of thickness measurement.
4) Sample making
Sample preparation is the key to metallographic thickness measurement. It is more difficult to prepare metal-coated samples than ordinary metal samples. Because the thickness of the coating or chemical protective layer is generally not large, there are pores, and it is easy to crack, etc. Therefore, the following steps must be strictly followed:
( 1 ) Edge protection
In order to improve the interface clarity of the coating surface during microscopic inspection, and to protect the coating from damage during grinding, the cut coating should be coated with other coatings with a coating thickness of not less than 10 μm before mounting to protect the test surface. kind of edge. The hardness of the thickened protective coating should be similar to that of the coating to be tested, but the color should also be different. For example, the copper layer is used for protection when measuring the nickel layer, and the nickel layer is used for protection when measuring the copper layer. The zinc layer and the cadmium layer can protect each other, but the copper layer cannot be used for protection, so as not to produce a replacement copper layer during immersion. , making the interface of the coating under test unclear.
(2) Mosaic
To make the cross-section of the sample coating after edge protection perpendicular to the coating surface, it is necessary to make the sample into a mosaic. When inlaying, the coating section should be as vertical as possible to the coating (perpendicularity deviation 1o°, the apparent thickness is 1.5% higher than the real thickness).
Mounting materials vary depending on the coating or protective layer.

When making an inlay, the inlay material should be close to the corner of the coating, and the distance between the coating to be tested and the edge of the inlay should be kept more than 5mm, so as to prevent the verticality of the coating profile and the coating from being affected by the inclination when the inlay is polished. , resulting in errors in coating thickness measurement.
(3) Grinding and polishing
The thickness of the coating is measured with a metallographic microscope. The coating profile must reach a mirror state to meet the requirements of the microscope inspection. Therefore, the coating profile after inlaying should be fully ground and polished.
In order to improve the resolution of the coating section of the sample when the thickness is detected by the mirror, it is necessary to grind and polish the coating section together with the inlay. Specimen grinding and polishing can be carried out by hand or special metallographic grinding and polishing machine. Regardless of whether it is done manually or mechanically, the following aspects need to be paid attention to:
① When grinding, choose abrasive materials, which should be carried out in order from coarse to fine, and the final sandpaper used should be above 280.
②The grinding operation direction should be at an angle of 45° to the coating surface. Every time the sand paper is replaced, the previous sand grains on the sample surface should be wiped off and the grinding direction should be 90° to the previous direction.
③ The material covered on the throwing plate during polishing can generally be fine canvas, woolen cloth, silk or artificial fiber fabric, and the polishing abrasive is chromium oxide or aluminum oxide fine powder. In the pre-polishing stage, a thicker polishing solution can be used (the polishing solution is put into water and stirred when used); in the later stage, a thinner polishing solution can be used (without stirring); finally, clean water is used. In this way, the polished sample does not need to be cleaned, but can be dried directly.
(4) Dipping
The purpose of dipping is to expose the respective color and surface features of the coating of the sample section and the profile of the base metal, and further improve the accuracy of microscopic examination.
For different substrates and coatings, different etching solutions should be used, and the commonly used etching solutions are shown in Table 11_2_12.
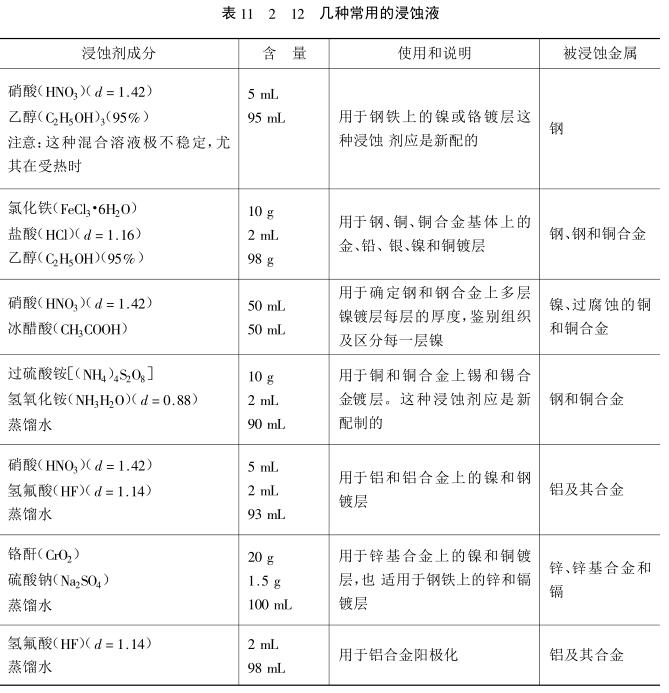
Note: d in the table represents density.
After etching, the sample was first rinsed with water, then washed with absolute alcohol, and finally dried quickly with hot air.
Note: The chemical protection layer does not need to be etched after polishing.
5) Test methods and steps
(1) The inspection and calibration of the metallographic microscope shall be carried out according to the instructions.
(2) According to the coating thickness range, select the appropriate eyepiece and objective lens magnification, and adjust the microscope focal length.
(3) Place the sample at an appropriate position on the stage of the metallographic microscope, further adjust the focus, and carefully measure the thickness of the coating section with a micrometer eyepiece. Each measurement is the average of at least three readings at the same location.
If it is necessary to measure the average thickness, measure the coating thickness at five points on the entire length of the sample section, and take the arithmetic mean value.








