1. Thermal insulation of the coating
The main factor that determines the thermal insulation performance of the coating is the thermal conductivity of the coating material itself. The lower the thermal conductivity, the better the thermal insulation performance. In addition, the thermal insulation performance of the coating is also related to the size and shape of the pores and oxides distributed in the coating. , the quantity is related, and it is also related to the thickness of the coating and the structure of the coating and the surface of the substrate. If the coating is porous, its thermal insulation will be improved, but at the same time its heat resistance and oxidation resistance will be reduced. ;If the thickness of the coating is increased (relevant instrument: Thickness Gauge), the thermal insulation effect of the coating can be improved, but at the same time, the bonding performance between the coating and the substrate surface will be reduced. Therefore, in actual application, according to different purposes, Correct control and use of these interrelated and contradictory properties, as thermal insulation materials, ceramics and cermets are effective.
2. Inspection of thermal insulation of coating
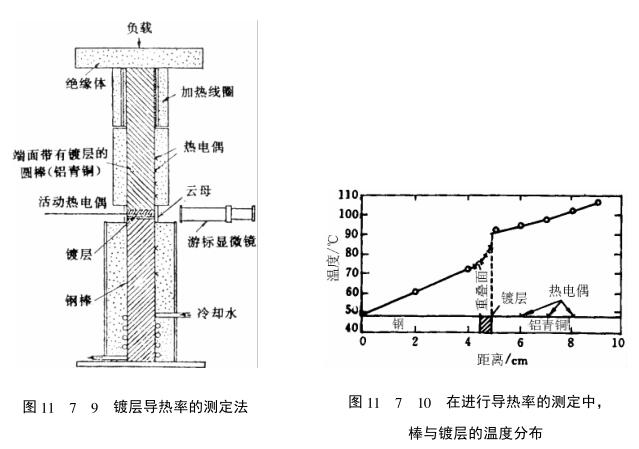
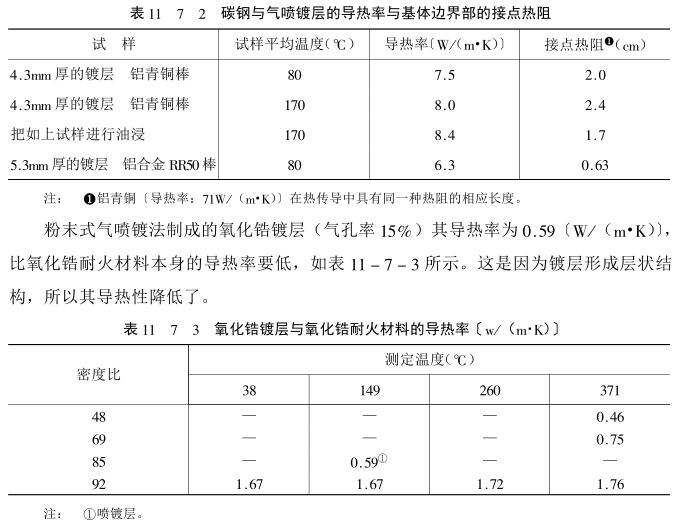
Determination of the thermal conductivity of the coating and the boundary between the coating and the substrate can evaluate and test the thermal insulation of the coating. The determination of the thermal conductivity of the coating requires a set of special test equipment, including several parts: a heat source device for heating the sample; The device for measuring the heat flow of the heated sample; the moving mechanism of the sample and the temperature measurement and automatic recording device of the sample. There are many methods for measuring the thermal conductivity of the coating, the following are two of them, (1) such as As shown in Figure 11_7_9, the coating sprayed on the end of the round rod (aluminum bronze material can be used) is ground, and then the end face of the quenched steel rod with the same diameter after grinding is used to fit the end face of the round rod, and the vertical pressure Then heat one end of the rod through the heating coil, measure the temperature of each point on the rod with a thermocouple assembled at each position of the round rod, and measure the temperature of the coating part by moving the joint angle of the thermocouple. The position of the exit point is determined by a vernier microscope. The measured temperature of each point on the rods on both sides of the coating and the temperature of each point of the coating can give a temperature change curve, thereby obtaining the thermal conductivity of the coating, and by This is used to evaluate the thermal insulation of the coating. Figure 11_7_10 shows the temperature measurement results at each position of a quenched steel rod-carbon steel coating (4.3mm thick)-aluminum bronze rod. The coating can be obtained from the curve in the figure. The temperature gradient in the coating and the discontinuity of the temperature at the boundary between the coating and the substrate, the final measurement results are shown in Table 11_7_2. From the results in the table, it can be seen that the thermal conductivity of the coating is only the thermal conductivity of carbon steel (0.46J/cm· a fraction of s·K).
(2) In addition to the above-mentioned method of using the energized coil as the heating heat source, the high-temperature flame generated by the plasma Spray Gun or the oxygen-b rapid flame Spray Gun can also be used as the heating heat source. The sample is placed at a distance of 50-100 mm from the nozzle. It is perpendicular to the center of the flame, and can also form an angle of 40°. During the test, keep the operating conditions constant and regularly detect the heat flow. The detection of the temperature change of the sample is to spot weld or place a thermocouple with a bottom on the back of the sample. , the temperature can be continuously recorded on the millivolt meter and drawn as a curve. During the heating process of the sample by the flame, the change of the sample temperature with time is measured. Once a stable equilibrium is reached, the test is stopped. Generally, it takes about 5 minutes. Compare the curve of sample temperature with time to evaluate the thermal insulation of the coating. (Related instrument: furnace temperature tracker)