Relative viscosity is an abstract number, that is, a known quantity at a certain temperature. The ratio of the outflow time of the sample to the outflow time of the standard liquid (water) at the standard temperature of the well under the same conditions. The Engler's viscometer is used to determine the relative viscosity of liquids, the most common method, which is not widely used in the surface paint industry.
In order to determine the relative viscosity of paint materials when testing them, a number of instruments were used, and the viscosity of the material could be measured by the time (seconds) of the material flowed out, or by the silver method.
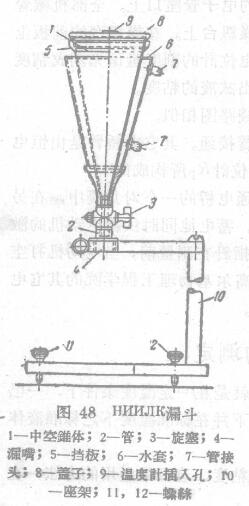

The relative viscosity was determined with a HHHJIEG funnel
In order to determine the viscosity of varnishes, oils, and enamels, C.B. Yakubo Funaki proposed a so-called HIMJIK funnel. (Related Instrument: Viscosity Cup)
This funnel has a large outlet diameter, which allows the funnel to be used to determine the viscosity of heavy oils, clearing speeds, etc., and secondly, to make this determination very fast.
The HHHJIK bucket is used in the test viscosity of the sample not lower than 100 centipoise, and the result obtained is not accurate when the viscosity is less than 100 centipoise, because the liquid flows out very quickly through the funnel mouth of the wide close, so it loses the sensitivity of the measurement.
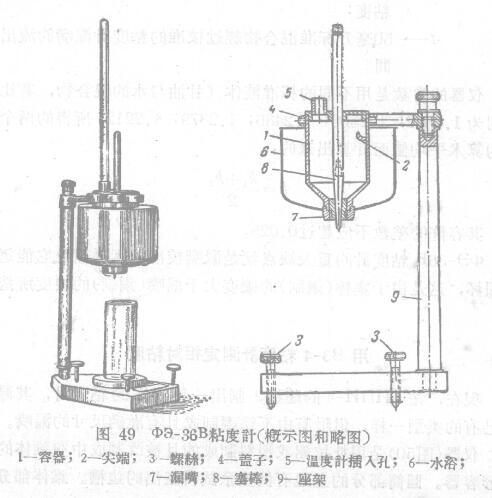

Relative viscosity was determined with a 36B viscometer
In the aviation industry, in order to determine the viscosity of the oil depth material, widely lI1l with 〇3-36B type viscometer, this kind of junctIon Meter was proposed by the Disco paint factory, and then reformed by JlnAM, the sketch and general diagram of the instrument are shown in Figure 49, this junctIon Meter - and the general industrial viscometer (funnel) is not much different, this kind of messenger is dedicated to the determination of the relative junction of the varnish and magnetic paint of the oil-based and nitrate micro-ki, this boat gauge has three replaceable nozzles (No. 1, No. 2, No. 3); One of the most widely used is the No. 2 nozzle (5 mm diameter)
Before the determination of the junction, the viscometer, especially the leaky nozzle, should be cleaned 1 first well to make it dry, before the measurement, the sample must be carefully lifted, and then let stand for about 15 minutes to remove bubbles.
The assay is performed as follows. In the container 1 of the ship gauge, the depth of the calibration test is compensated, and the well makes the horizontal plane of the liquid and the tip 2 nearly equal in height, and then uses the screw 3 to adjust the instrument to make the speed straight. The adjustment is carried out as follows: by adjusting the spiral until all three ends 2 are equally convex on the liquid water surface in the container 1, the thermometer is inserted into the hole 5 of the difference in the well of the certificate 4 in the container, the temperature of the tested varnish is adjusted to 20C by using the hot or cold water flowing into the Water Bath 6, and this temperature should be maintained throughout the test time, and thereafter, the measuring cancer with a volume of 50 ml and with a scale is placed under the mouth of the leaky mouth 7 and the plug rod 8 is extracted, Using a stopwatch, the stroke can be measured by the time when 50 ml of liquid flows out of the drain (shift').
The moment the liquid appears from the mouth of the leak, it can be regarded as the beginning of the outflow, and when the body reaches the meniscus mark of the IL1 measuring flask, the liquid can be considered to have flowed out.
Multiply the number obtained by the outflow time of 50 milliliters of varnish expressed in seconds by the special coefficient (i.e., constant, which is contained in the instruction manual of the instrument) used in the measurement, and the coefficient is used to turn the obtained result into the relative outflow time of the same varnish flowing through the No. 2 nozzle of the standard viscometer, and its product is the viscosity of the varnish obtained, and the calibration and determination of the viscometer constant can be used; The junction and specific gravity have been measured in 1 liquid. A mixture of oil and water is usually used as this liquid,
Determine the relative viscosity with a B3-4 viscometer
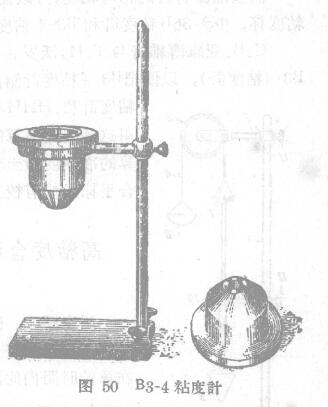
Now, as suggested by THHH-4, a simple viscometer has been produced with the same funnel as the existing type, but with a slitter made of stainless steel with an exactly-sized nozzle, and the feeder (Fig. 50) is a high-back container made of dura pins or plastic and modified into a hollow cone. The upper part of the national simple part has a side rot for the overflow of excess sample, and the end of the cone part is non-sticky. Its drain nozzle '(diameter 4 + 0.02 mm, height 4±0.02 mm), the volume of the B3-4 viscometer is equal to 100±0.5 ml.
Before the measurement, the sample is carefully batched, the temperature is adjusted to 20-C (-t2 °C), and the well is allowed to stand to eliminate air bubbles (generally stand for 5~10 minutes).
The viscometer should be carefully cleaned with solventsWashing, the well is dry, special attention should be paid to the cleanliness of the warm nozzle,,, the junctIon Meter is installed on the seat frame, the leakage mouth is blocked with a ball or finger, the sample is loaded into the container to make the liquid level and the container side of the same height, the excess part of the sample flows into the side structure, and the bubbles in the liquid rise to the surface; Use a ruler or glass to dial the foam into the side of the mess, the viscometer is placed under the bearing vessel, and then the ball or finger is removed from the mouth of the leak, and at the same time start the tableshift, when the continuous flow of the sample is finally broken, stop the stopwatch, the measurement should not be less than twice, the accuracy of the outflow time is determined to 0.2 seconds, if the maximum is 100%, the difference between the determination shall not exceed 5%. The meter must be cleaned with an appropriate drop agent and wiped with a cheerful and dry material, and the phase of the paint material should be measured: the degree of dissipation can be used in the above 1 degree meter (HnnaK viscometer cups, 03-36B viscometer and 113-4 viscometer)
C.B. Jakubovich and T.N. Vorogushin developed a comparison chart (for the B3-4 viscometer) in order to put the . When using this chart, it is important to note that the conversion accuracy of the varnish measured by the B3-4 viscometer is ±o% at the same temperature, and that the viscometer should conform to the standard correction factor.