Different methods of determining the degree of adhesion of a paint film to a painted surface are proposed in Diria.
 For example, in order to measure the adhesion of oil base to paper (relevant instrument: viscometer), two methods have been proposed based on the determination of the work done by the static phase division method and the dynamic new division method. When using the static method, press a 10 mm wide paper strip on the zinc plate of the color paint to be tested in advance;
For example, in order to measure the adhesion of oil base to paper (relevant instrument: viscometer), two methods have been proposed based on the determination of the work done by the static phase division method and the dynamic new division method. When using the static method, press a 10 mm wide paper strip on the zinc plate of the color paint to be tested in advance;
The paper strip is then slowly torn off together with the lacquer layer affixed to the paper strip in a special machine.
In the case of the dynamic tear-off method, a pendulum-type instrument is used, the principle of which is to apply the paint to be tested on a paper strip close to the pendulum; press the paper strip against the zinc plate and vibrate the pendulum, As a result, the paper strip falls off the board at random, and the pendulum consumes some work when the paper strip falls off the board, and the pendulum makes a smaller angle than when it is freely swinging.
The inclination angle of the pendulum can be measured on the arc dial (scale gauge) by the cursor reflected from the lamp by the concave mirror.
The work (adhesion) of the peeling off of the paint film can be represented by the number of ergs per square centimeter.
It should be pointed out that these methods are only suitable for paint materials with small values of adhesion, but not suitable for most paint materials with high adhesion.
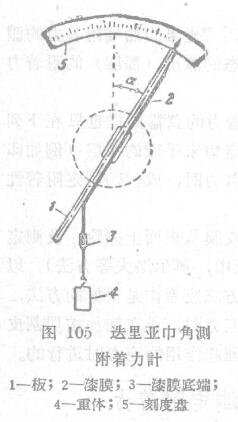
In order to measure the adhesion of the paint film, Dieli has proposed a disk adhesIon Meter and an angle adhesIon Meter.
Disadvantages of the disc adhesIon Meter are that the tear-off speed is not constant, and in the case of a large-scale test, a large number of plates must be prepared. In addition, it is almost impossible to use this kind of Tester to test the paint film with strong adhesion.
The Angular Adhesion Tester is suitable for determining the adhesion of certain paint materials.
Apparatus As shown in Figure 105, the paint sample is applied to a plate 1 that can rotate around a horizontal axis. When the sample is dry, cut the paint film 2 into small strips with a certain width; then use the weight 4 to tighten the bottom 3 of the small strips that are lightly separated from the board with a knife edge.
The plate coated with the paint film is initially in a vertical position; at this time, there is no peeling off of the paint film,
At the beginning, the board is carefully rotated around the firing axis; when the board reaches a certain angle a with the vertical surface, the brittle falling of the paint film from the bottom surface (test board) occurs.
The work A of the peeling off of the paint film can be calculated by the following formula:

This method of determining the adhesion of paint films is simple and, under fixed conditions, gives good results when testing different paint materials, above all when testing clear and pigmented paints made of polymeric resins. the result of. Like other methods of depositing paint films from surfaces, the Derial method is not suitable for testing those paint films whose adhesion exceeds the molecular cohesion of the paint film (such as most resin paint films). In addition, the disadvantage of this method is that the result depends on the speed of tearing (shedding), which in turn varies with the weight of the load and the size of the expected chamfer.
It should be noted that the work done by the paint film measured by this method does not include the work of stretching the paint film under the load during the running period, because the aforementioned formula assumes that the paint film has no stretchability. Also does not take into account the work of the torn paint film; bending strain. However, as pointed out by Su Liajin, the correction of the work of strain is not of great significance, and the value A calculated by the formula is basically consistent with the true work done by the peeling of the paint film.