Abstract: Cupping test is a method used to evaluate the ductility, adhesion and flexibility of coatings when the substrate is deformed. This article describes the scope, instruments and materials of the Cupping test, as well as the measurement method and result representation. This test is an indispensable test item for Coatings that require post-forming processing in industrial manufacturing. National standard GB/T 9753 and international standard ISO 1520 also provide relevant specifications and guidance.
1. Introduction
In the Coatings industry, evaluating the performance and suitability of coatings is critical. Cupping test is a commonly used method to assess the ductility, adhesion and flexibility of coatings when deformed on substrates. This article will introduce the relevant content of Cupping test in detail.
2. Instruments and materials
The instruments and materials required to perform the Cupping test are as follows:
Cupping test machine: can be manual or hydraulic. The key part includes a hard and smooth spherical punch and a circular sample holder. The test process can be observed by binocular stereo Microscope or magnifying glass.
Steel plate: The thickness is 0.30~ 1.25mm, and the width and length are not less than 70mm.
Magnifying glass: 10 times magnification.
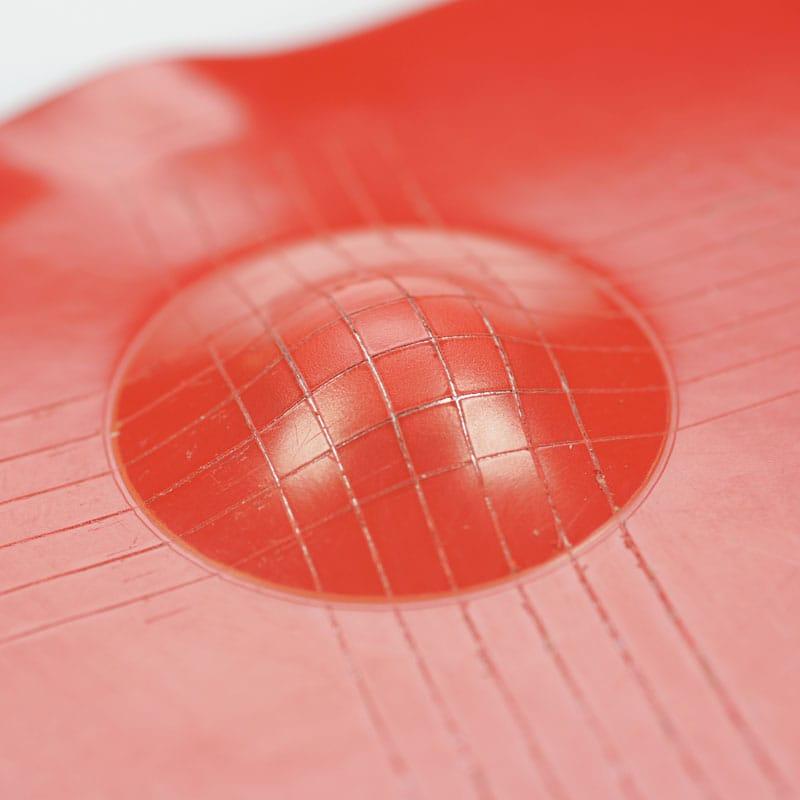
3. Determination method
3.1 Preparation Before the test, it is necessary to paint and dry the painting test plate, and adjust the state at a temperature of (23 +/- 2) ℃ and a relative humidity of (50 +/- 5) % for at least 16 hours.
3.2 Test steps
Fix the test plate between the fixing ring and the die so that the coating faces the die. Adjust the test plate so that the intersection between the central axis of the punch and the test plate is not less than 35mm from each side of the test plate.
The testing machine is turned on, and the punch is pushed towards the test plate at a constant speed, so that the test plate forms a dome shape with the coating facing outward until the specified depth is reached or the coating is cracked or separated from the substrate.
4. Presentation of results
Depending on the test situation, the results can be expressed as follows:
When the test is carried out according to the specified stamping depth, when the specified depth is reached, observe whether the coating is cracked or separated from the substrate, and determine whether it passes or fails according to the evaluation criteria.
When the test is performed at the minimum depth causing failure, the stamping depth is gradually increased to the minimum depth at which the coating begins to crack or separate from the substrate as a result.
5. Reference standard
This test method refers to the following national and international standards:
National standard GB/T 9753 "Paints and varnishes Cupping test".
International standard ISO 1520 "Paints and varnishes Cupping test (Second Edition) ".
Conclusion
As a commonly used Coating performance evaluation method, Cupping test can assess the ductility, adhesion and flexibility of coatings when the substrate is deformed. By performing this test on Coatings, you can better understand the performance of coatings in actual use, so as to guide subsequent processing and application processes in industrial manufacturing.










