In the method of measuring the hardness of the paint film by the scratch method, methods such as scratching with pin pens of different hardness and scratching with various blades (penetrators) can be proposed.
Determination of Hardness of Paint Film by Pencil Scratch Method
This method uses a set of pencils (with graphite cores of different hardness) to determine the hardness of the paint film. The hardness of the paint film can be indicated by the number of pencils that can penetrate the thickness of the paint film and reach the bottom surface. (Related instrument: Hardness Tester)
More objective results can be measured as follows. The paint film to be tested is placed on a balance pan, and weights of different weights are placed on the other pan. Use a pencil of a certain hardness to scratch the paint film until it is scratched, at this time find out the weight that balances the balance pan. This method can be used with a standard pencil and graphite sharpened to some extent.
Determination of Hardness of Paint Film by HNNJIK Instrument Scratch Method
CH, Xie Lie Bryannikov once designed an instrument with an automatic device that makes the movable surface of the instrument run at a constant speed (Figure 118), and used the scratch method to measure the hardness of the paint film.
The pillar 2 of the upper balance beam 3 is fixed on the pedestal 1 . One end of the balance beam has a movable load 4, and on the other end there is a hole in which a tool 5 is fixed. Use the stop screw to fix the tool in the position shown in the figure. The top of cutter has the axle journal 6 of putting load 7. Place two boards—fixed board 8 and movable board 9 on the movable surface 10---the template of painting is fixed on these two boards. Pressing the lever 11 can release the brake to move the plane 10, which may move the slide block connected with the movable plane by means of an elastic spring. In order to ease the initial vibration and make the movement more uniform, a shock absorber is installed on the movable surface.
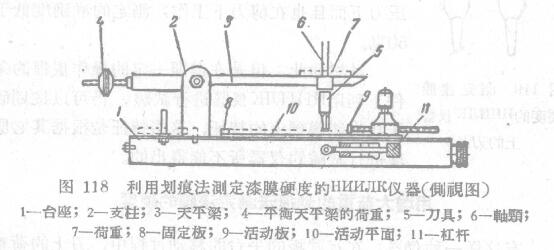
 When carrying out the test, a glass plate with a size of 90 x 120 mm is coated with a sample with a thickness of 40 (± 4) µ. When the sample is dry, or after the time specified in the technical conditions, place the sample on the movable plane 0 and sandwich it between plates 8 and 9. The movement of the load 7 can balance the balance bar 3 with the cutter 5 fixed thereon. Thereafter, a load 7 of 50 grams is placed on the journal 6 of the tool; the tool is carefully placed on the paint film and the lever 11 is pressed to start the movement of the movable surface 10. Then observe the marks left by the knife on the paint film. If the paint film has been completely cut through to the broken glass surface along the path of the knife movement, the test can be considered as completed in this case. The first 3 mm that the tool passes when moving is not taken into account. If the knife does not cut through the paint film to reach the broken glass surface, add 50 grams of load and repeat the test.
When carrying out the test, a glass plate with a size of 90 x 120 mm is coated with a sample with a thickness of 40 (± 4) µ. When the sample is dry, or after the time specified in the technical conditions, place the sample on the movable plane 0 and sandwich it between plates 8 and 9. The movement of the load 7 can balance the balance bar 3 with the cutter 5 fixed thereon. Thereafter, a load 7 of 50 grams is placed on the journal 6 of the tool; the tool is carefully placed on the paint film and the lever 11 is pressed to start the movement of the movable surface 10. Then observe the marks left by the knife on the paint film. If the paint film has been completely cut through to the broken glass surface along the path of the knife movement, the test can be considered as completed in this case. The first 3 mm that the tool passes when moving is not taken into account. If the knife does not cut through the paint film to reach the broken glass surface, add 50 grams of load and repeat the test.
Repeat the test under the condition of increasing load (50 grams each time) until the paint film is completely cut through to the glass plate in the whole process of knife cutting. At this point the test is complete.
The load (in grams) placed on the tool journal when the measurement is over is the standard for the hardness of the tested paint film.
The shape of the cutter on the HnnJIK instrument is shown in Figure 119. The tip of the knife is facing the pillar, the sharpness of the knife needs to be checked , the hardness of this standard film should be 150 grams after 72 hours of drying. (Related instrument: drying time Tester)
Although the first method provides a practical concept of the hardness of the paint film, it also has some major disadvantages: this is that the knife gradually becomes blunt and requires regular sharpening.
The results obtained for the film appear to be too low, this is because the knife is not working under pressure and also under shear; the accuracy of the determination is as low as 50 grams.
Even so, under the condition of complying with certain operating procedures, the HNNJIK instrument can still be used to find out the characteristics of the hardness of the paint film according to the scratch method. These characteristics cannot be obtained by instruments based on other principles.
Determination of Hardness of Paint Films by Scratch Method with Increasing Load
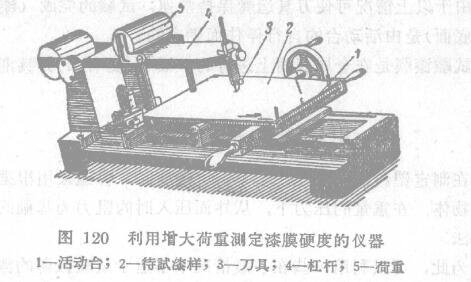
There is such an instrument: during the movement of the platform with the test plate, the load on the knife can gradually increase. It is very convenient to use this instrument to test by scratching. For this purpose, the instrument shown in Figure 120 can be utilized. (Related Instruments: Scratch Hardness Tester)
The instrument has a movable platform 1 on which a paint sample 2 to be tested is placed. The knives shown in Figure] 19, as well as hard minerals with a certain sharpening angle, phonograph needles, etc., can all be used as scratch knives. When using phono needles, it is recommended that the needle tip be ground to a 0.2 mm diameter area.
The cutter 3 should be fixed on the movable balance red rod 4, and the lever is installed on the movable table. The load (rotor) 5 moves along the red rod. The movement of the load is connected with the movement of the table. Therefore, when the test plate moves, the load also moves to the tool. When it is close to the tool, ll exerts a lot of pressure on the tool.
While adjusting the load, the pressure on the tool can be increased evenly from zero up to the full weight of the load while moving the template. Depending on the hardness of the paint film, different loads are used.
In order to calculate the weight of the scratch, put a measuring ruler on the paint film to measure the scale of the paint film being scratched (starting from 0), and multiply the obtained value by the weight of the load.
Determination of the hardness of the paint film by the scratch method on an instrument designed by the Institute of Industrial Science and Technology of the Estonian Academy of Sciences
Ritso and Landra (Academy of Sciences of the Estonian Soviet Social Democratic Republic, Institute of Industrial Problems) once designed an instrument that uses an electric motor to drive a movable table based on the aforementioned principles (see Figure 121).
Due to the above conditions, the tool can be kept running at a constant speed; the completion of the test (the paint film is scratched to the bottom) is determined by the self-stopping of the movable table.
The test paint film is carried out on the metal substrate, and the cutting tool used is a record player needle.

