Power balances are designed for studying the mechanical properties of polymers . The power balance can measure the interrelationship between polymer compression deformation and stress (applied force), time (duration of action) and temperature.
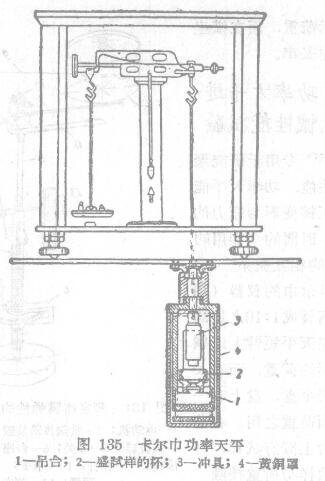
BA, the Messenger of Kalkin (Fig. '135) is an analytical balance with two arms in a ratio of 1:10. On the short arm of the balance, a cylindrical load is suspended by a steel wire, while on the long arm, a balance plate is hung, and there is an Orlov instrument group weight with membrane elasticity on the plate for balancing the load. A sample is placed on the stage under the load, and the screw is used to make the sample contact with the load. A part of the weight (balance weight) is removed from the balance plate, and the load that can cause pressure can be changed in a wide range. Its amplitude can be from zero degrees to the desired value.
The deformation of the sample is recorded by the altimeter according to the inclination of the mirror fixed at the end of the balance arm.
The movable carrier platform with the sample is placed in a simple brass cover, and the cover can be placed in a thermostat or a cryostat (related instruments: constant temperature and humidity Test Chamber). Assays can be performed over a wide temperature range (eg from -180° to +200°C). We now give as an example of a determination method based on the diagram in the work of BA Kalkin and T_H, Sogoro surname 7° (Fig. 136). The figure shows the relationship between deformation and temperature of polybutene with different molecular weight when the stress is constant.
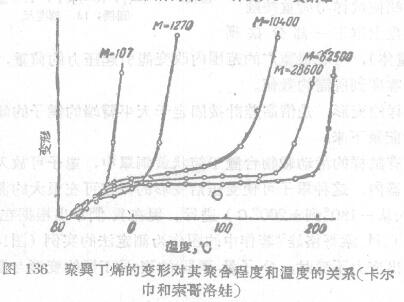
It can be seen from the figure that the high elastic state appears only when the molecular weight of the polymer is quite large.
The Karl towel power balance can undoubtedly be used to determine the mechanical properties of paint films. Therefore, it is necessary to try to formulate corresponding test methods.










