Conductive coatings refer to coatings with conductive or semiconducting properties. The characteristics of conductive coatings are convenient construction, simple equipment, low cost, and wide application. They are mainly used for surface coatings of non-conductive materials, such as the elimination of charges on the surface of electronic components, and are especially suitable for coating various complex shapes of surfaces.
According to conductive materials, conductive coatings can be divided into intrinsic conductive coatings and blended isoelectric coatings. For their definition, composition and characteristics, see Table 1-64.

Curing conditions, conductive coatings can be divided into room temperature curing type, heating nationalization type, high temperature sintering type, and external line curing type. The naming of conductive coatings is often combined with two classifications, such as carbon-based conductive coatings-heating curing type, Wire-based conductive coatings - normal temperature curing type, etc. The main factors affecting the conductive properties of conductive coatings are the conductivity and conductivity of the base material; l the shape and size of the real material, and the nature of the solvent.
①The conductivity of the base material is shown in Table 1-65
②Shape and size of conductive filler
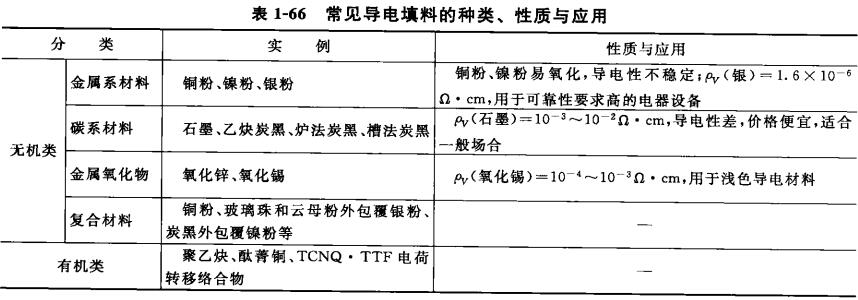
Flake or technological fillers can promote the contact between materials and have good electrical properties, while spherical materials will reduce the chance of contact between materials, and the conductivity is slightly worse. The more particles there are, the better the conductivity. Conductive materials can be divided into inorganic and organic, as shown in Table 1-66.
③Solvent
Common solvents include water, alcohol, aromatics, etc. The type of solvent selected for conductive coatings must be able to dissolve the base resin and not make the conductivity of the conductive material unstable. The coating conditions and the solvent's dissolution of the base resin must be met. The better the conductivity, the better the conductivity; the higher the boiling point of the solvent, the higher the conductivity. If some organic substances containing buildingine and cohesive groups are used as additives, the workability of conductive coatings can be improved, such as titanate coupling agent .The amount of solvent should be a small amount, not too much, otherwise its conductivity will be reduced. Common types of conductive coatings include electrostatic conductive coatings, printed circuit board coatings, electrothermal coatings, anti-fouling conductive polyester materials for ship bottoms, and electromagnetic wave screen coatings. , electrochromic coatings, photoconductive coatings, aviation conductive coatings, anti-corrosion coatings for metal oil tanks, etc.,
