Fire retardant coatings (including flame retardant coatings) are important means of fire prevention. The meaning of fire retardant coatings and flame retardant coatings is different. Fire retardant coating means that the material not only does not burn or is difficult to burn, but also can prevent the burning of the substrate or have a retarding effect on the spread of its burning, and can play the role of heat and oxygen insulation. See Table 1-72.
Classification and characteristics of fire retardant coatings
| classification nature | Non-intumescent fire retardant coating | Intumescent fire retardant coating |
| fire prevention | ①The coating itself is difficult to burn or does not burn, and releases fire extinguishing gas under flame or high temperature; ②Forms an inorganic glaze film to isolate the air | ①The coating expands and carbonizes under flame or high temperature to form a uniform and dense honeycomb or spongy carbon foam layer, which can insulate oxygen and heat, and its thickness can be dozens or even hundreds of times thicker than the original film; ②The coating decomposes It emits non-combustible gas, which can dilute air or cool down. |
| Classification | Inorganic non-intumescent fire retardant coating (non-combustible) | Inorganic non-intumescent fire retardant coating (flame retardant) |
| Organic non-intumescent fire retardant coating (non-combustible) | Organic non-intumescent fire retardant coating (flame retardant) | |
| features | The heat insulation effect is poor, and it can only resist instantaneous high temperature or flame, but it has excellent water resistance and chemical resistance, high surface hardness, easy coloring, and is suitable for occasions with high decorative requirements. | Good fireproof effect, relatively thin coating, less inorganic pigment filler, poor strength, poor water resistance, large thickness, poor decoration, and the surface cannot be coated with finish paint. |
Flame retardant coating means that the material itself does not burn or is difficult to burn, and can self-extinguish from a high fire, but it cannot play the role of heat and oxygen insulation.
Fire-resistant coatings are mainly used in high-rise buildings, warehouses, stadiums, ancient buildings, etc. But it should be clear that if a fire spreads, it is impossible to extinguish the fire with only fire-resistant coatings.
Flame Retardant Mechanism of Fire Retardant Coatings
Combustion reactions are complex, mostly chain free radical reactions. Combustion needs to have three elements: combustibles, dynamic combustion agent (air, oxygen or oxidant) and ignition source (such as high temperature or fire), to prevent combustion, it is necessary to cut off any one of the three elements in the combustion process, and the coating of the fire retardant coating must be non-combustible or flame retardant, but its base material is generally a combustible or flammable organic polymer, which can be made flame retardant or a combination of the two, as follows, ① using a flame retardant organic polymer as the base material Introducing flame retardant elements into polymer molecules, such as Nansu, can also replace organic polymers with elemental film formers. ② Add flame retardants to coatings. Commonly used flame retardants are: aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, Halides, phosphate esters, etc.
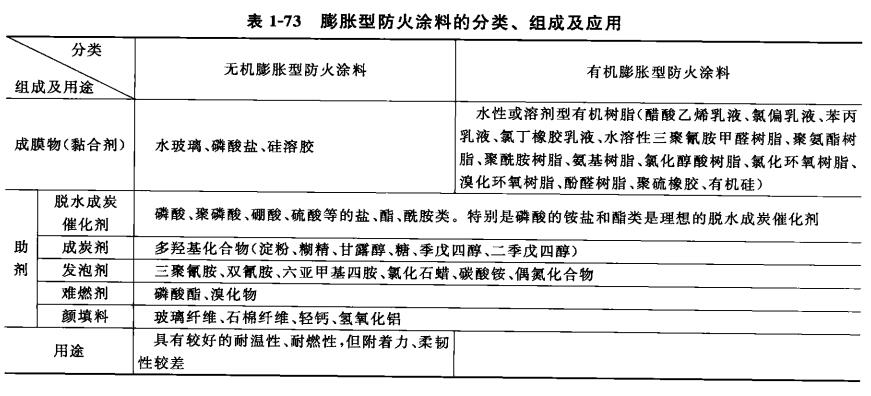
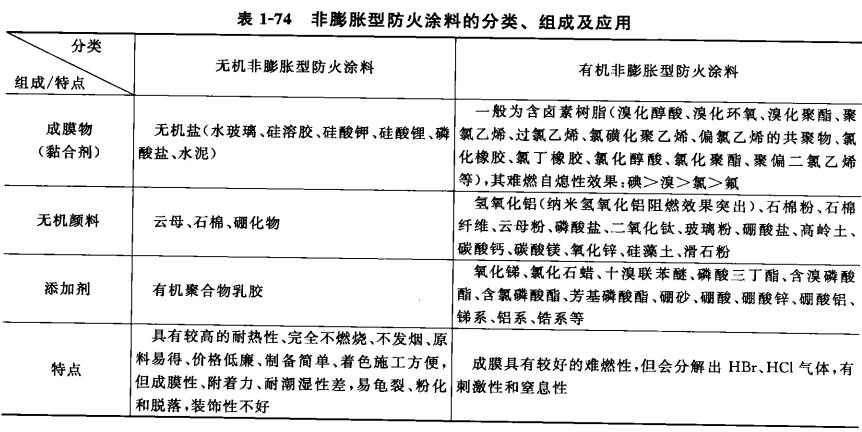
Fire retardant coatings can be divided into non-intumescent fire retardant coatings and intumescent fire retardant coatings
Please see the table below for the classification, composition and application of intumescent fire retardant coatings and non-intumescent fire retardant coatings