The density of a material is one of the important properties that describes its physical state. In materials engineering, density, apparent density, and bulk density are commonly used parameters to evaluate the structure, properties, and applications of materials.
1. Density
Density is the mass per unit volume of a material in an absolutely dense state. In an absolutely dense state, the density of the material is calculated without considering pores, that is, excluding internal voids. The common calculation formula is:
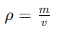
in,
Ï represents the density of the material (unit: g/cm³),
m represents the mass of the material in the dry state (unit: g),
v represents the volume of the material in an absolutely dense state (unit: cm³).
2. Apparent density and bulk density
Apparent density (also known as apparent density, approximate density) and bulk density (also known as bulk density, apparent gross density, bulk density) are used to express the mass per unit volume of the material, taking into account the internal closed pores and open pores.
The apparent density represents the mass of the material per unit microscopic appearance volume (including internal closed pores). The calculation formula is:
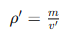
in,
â² Ï â² represents the apparent density of the material (unit: g/cm³),
m represents the mass of the material in the dry state (unit: g),
Ⲡv Ⲡrepresents the volume of the material without open pores (unit: cm³).
3. Bulk density
Packing density refers to the mass per unit volume of granular materials or powdered materials in a naturally stacked state. In packing density, the volume of the pores inside the particles and the volume of the spaces between the particles are taken into account. The calculation formula is:
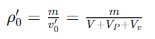
in,
Ï â² 0 represents the bulk density of the material (unit: kg/m³),
V represents the volume of the container (unit: m³),
V P represents the volume of pores inside the particle (unit: m³),
V v represents the volume of the space between particles (unit: m³).
To sum up, density, apparent density and packing density are important parameters to describe the density and structural characteristics of materials. Their difference lies in the consideration of pores and void volumes under different circumstances, which is of great significance for the structure and performance evaluation of materials.







