The physical and chemical properties of matter, such as refractive index, viscosity, density, surface tension, vapor pressure, flat art constant, rate constant, etc., are all related to temperature. Quality determination needs to be carried out under constant temperature conditions. To control the temperature of the studied system, Western methods are usually used: one is to control the temperature by using the t day qualitative of the phase transition temperature of the substance. For example, a mixture of water and ice (0°C), boiling point water (l00°C), liquid nitrogen (-l95.9°C), etc. Although this method is simple, it has certain restrictions on the choice of temperature; the second is to use the electronic regulation system to automatically adjust the working state of the heater or refrigerator, so that the controlled object is below the temperature set by f. The constant temperature tank with liquid as the medium introduced in this section is the temperature control device of this type, which automatically adjusts the heater through the electronic relay to achieve daily temperature adjustment. When the t direct temperature bath makes the system temperature lower than the set value due to the outward diffusion of heat, etc., the relay will chase the heater to work, and when the system reaches the set temperature again, it will automatically stop heating. remain constant within a certain range,
The following liquid media can be used according to the temperature control range:
-60-30°C with ethanol or ethanol aqueous solution;
0~90℃ water;
80-160 ℃ with glycerin or glycerin aqueous solution;
70-300 ℃ with liquid paraffin, silicone oil, cylinder lubricating oil.
The schematic diagram of the constant temperature bath device at room temperature (room temperature - 250°C) is shown in the figure
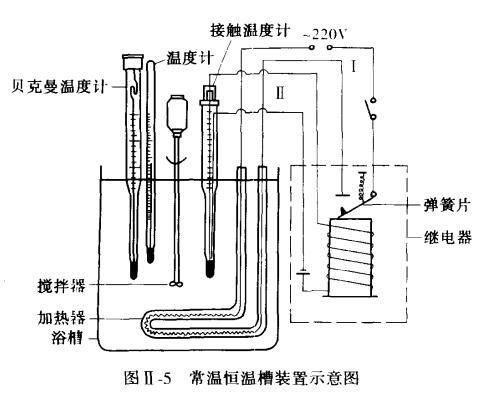
Assembly of the constant temperature bath
Take the constant temperature Water Bath as an example to illustrate the assembly method of the constant temperature tank.
Take a container of a certain volume, and wait for distilled water to fill the container to 4/5 of the volume. Install the heater first, and then install the agitator, contact thermometer, thermometer, relay, and wire according to Figure ll-5. Attention should be paid to the layout of each device during installation, because the accuracy of the temperature declared by the constant temperature structure is high. In addition to the sensitivity of the contact thermometer, the performance of the stirrer, the heating condition of the heater, the quality of the relay, and the speed of heat dissipation in the bath, it is also related to the layout of the equipment in the constant temperature bath. Even if each part is very sensitive, without a good layout, the purpose of constant temperature cannot be achieved_
In t buy warm bad, the heater and the stirrer should be placed closer. Contact thermometers should be placed near them, not far away. The measuring system should not be placed on the edge, and the thermometer should be as close as possible to the measured system.
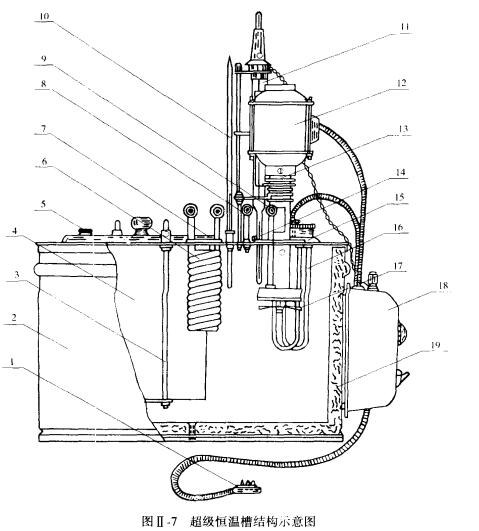
In addition to the general constant temperature tank assembled above, a Super Constant Temperature Bath is commonly used in the laboratory, and its structure is shown in Figure 117. The principle of constant temperature is the same as above, the difference in structure is that it is equipped with a circulating water pump, which can circulate the constant temperature water in the bath structure through the system to keep the system constant temperature without immersing the system in the bath.
To measure the quality of the constant temperature tank, it can be measured by the good sensitivity of the constant temperature tank. The determination of the sensitivity of the constant temperature bath is to use a sensitive thermometer (such as a Beckman thermometer) to record the change of temperature over time at a specified temperature (such as 30°C), and record the reading of the thermometer every 1 minute for 30 minutes. Then take the temperature as the longitudinal standard. Time is drawn as a temperature-time curve on the abscissa, as shown in Figure ll-8. Figure (a) represents a constant temperature bath. Higher sensitivity; (b) indicates poor sensitivity; (c) indicates that the heater power is too large; (d) indicates that the heater power is too small or the heat dissipation is too fast
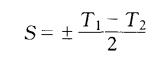
In the formula, T1 is the highest temperature read when heating is stopped; T2 is the lowest temperature read when heating is started. Obviously, the smaller S is, the better the performance of the constant temperature bath will be.
How to use the constant temperature bath
First assemble the constant temperature tank, and then adjust the constant temperature Water Bath to the set temperature. If the room temperature is assumed to be 20°C, and the experimental temperature is to be set at 30°C, the adjustment method is as follows: first loosen the locking screw that touches the magnetic screw adjustment range on the upper end of the thermometer, and then turn the magnetic screw adjustment cap to make the upper edge of the temperature indicator nut Located at about 29°C, turn on the power, turn on the heater and stirrer to make it work, observe the reading of the l/l0 scale thermometer, when the heater stops heating and the thermometer reading does not reach 30°C, turn it clockwise The magnetic screw adjustment cap makes the contact and the mercury column in the state of just contacting and disconnecting (whether the contact and the mercury column are disconnected or in contact can be passed; the switch of the traffic light of the relay is judged). Continue heating so slowly until the temperature rises to 30°C, at which point the heater just stops heating, then tighten the locking screw c















