As a common experimental instrument, the rotational rheometer plays a vital role in the study of the rheological properties of various samples such as liquids, solids, and colloids. This article will introduce the classification, measurement principle, instrument structure and environmental conditions of rotational rheometers, aiming to gain a deeper understanding of the importance of this key instrument in scientific research and engineering applications.
Rotational rheometer classification
According to different control methods, rotational rheometers can be divided into two types: stress control type and strain control type. The stress-controlled rotational rheometer produces normal stress on the sample by controlling the drive motor, while the strain-controlled rotational rheometer produces a certain strain on the sample by controlling the rotation of the drive motor. Each of these two classifications has its applicable scenarios and characteristics.
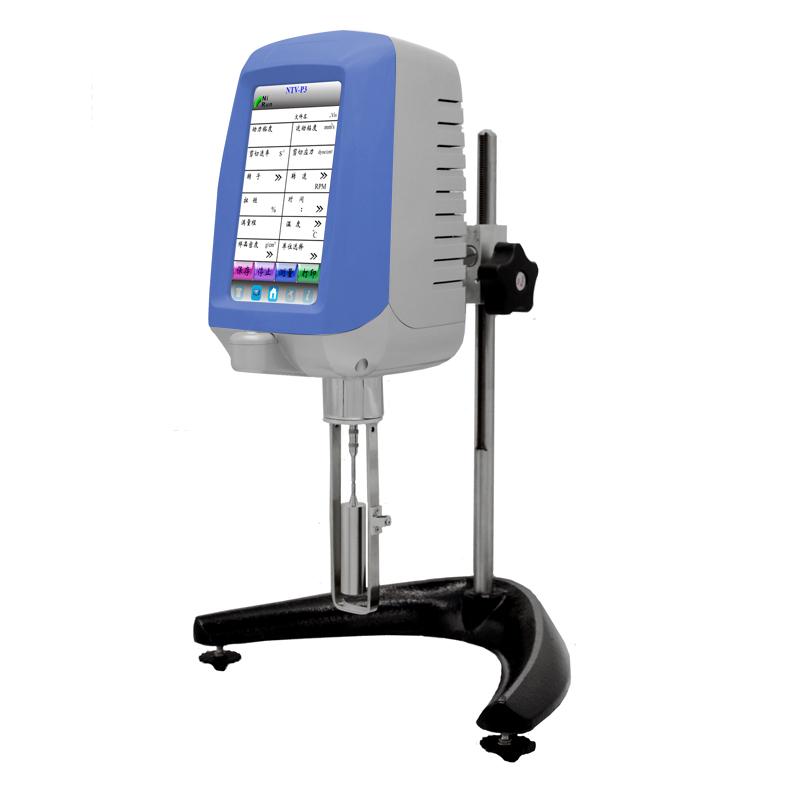
Measurement principle
Stress controlled rotational rheometer
The drive motor and torque sensor of the stress-controlled rotational rheometer are located above the sample. By directly controlling the drive motor, the sample reaches a certain torque and generates normal stress. This type of rheometer continuously adjusts the strain until a preset stress is reached. The measuring principle is based on producing normal stress on the sample by controlling the drive motor. In this type of rheometer, the drive motor and torque sensor are located above the sample. By directly controlling the rotation of the drive motor, the sample generates a certain torque, thereby generating normal stress. During the measurement process, the stress-controlled rotational rheometer uses stress control instructions to continuously feedback the stress magnitude to the control center and adjust the rotation speed of the drive motor until the preset stress is reached. This type of rheometer has precise control capabilities and can accurately measure the rheological properties of samples under different stress levels. Therefore, it is widely used in experimental research that requires precise control of stress in the fields of materials science and engineering. value
Strain controlled rotational rheometer
The drive motor of the strain-controlled rotational rheometer is below the sample, and the torque sensor is above the sample. By directly controlling the rotation of the drive motor, the sample produces a certain strain and generates torque and normal stress. In this type of rheometer, the strain control command accurately achieves the desired strain. The measurement principle is based on producing a certain strain on the sample by controlling the rotation of the drive motor and measuring the resulting torque and normal stress. In this type of rheometer, the drive motor is located below the sample and the torque sensor is located above the sample. During the measurement process, by setting strain control instructions, the rheometer can directly and accurately reach the required strain level. This type of rheometer has a high degree of flexibility and accuracy, can quickly and accurately control the strain of the sample according to experimental needs, and measure the torque and normal stress generated by the sample in real time, so it is widely used in materials science, biomedicine, food It has been widely used in the study of rheological properties in engineering and other fields.
Instrument structure
The structure of the rotational rheometer mainly includes rheological measurement system, Air Compressor, temperature control system, data processing system and other components. The rheological measurement system is the core component, including deformation drive motors, bearings, torque sensors, optical encoders, normal force sensors and measurement rotor systems. Among them, the deformation drive motor applies deformation, the bearing fixes the drive shaft and ensures its free rotation, the torque sensor is used to measure the torque generated under the deformation of the sample, the optical encoder is used to read the displacement data of the drive shaft, and the normal force sensor is used to measure The force exerted by the sample on the bearing is measured, and the measuring rotor system is used to place the test sample. Common sample stages include parallel flat plate, flat plate-cone plate and concentric cylinder.
Deformation drive motor: applies intermittent or continuous deformation to the sample.
Bearing: secures the drive shaft and ensures its free rotation.
Optical encoder: used to read the displacement data of the drive shaft, with high accuracy and able to resolve angular displacement down to nanoradians.
Normal force sensor: used to measure the force exerted by the sample on the bearing.
Torque sensor: used to measure the torque generated by sample deformation.
Measuring rotor system: a component used to place test samples. Common ones include parallel flat plates, flat plates-cones and plates, and concentric cylinders.
How to operate
To operate a rotational rheometer, you need to follow the instrument's instruction manual. In the measurement preparation stage, the measuring rotor system needs to be installed, and the measurement parameters and temperature control methods need to be set. In the measurement step, select the corresponding measurement mode according to the experimental needs, such as steady-state measurement mode, dynamic measurement mode or transient measurement mode, and set the measurement parameters. Finally, start the experiment through the operating software, and clean the sample stage and other components in time after the experiment.
environmental conditions
The ambient temperature and humidity in which the instrument works should comply with the requirements of the instruction manual of each instrument. Avoid interference from external vibrations on the instrument and maintain good ventilation. During the experiment, volatile solvents or high-temperature decomposed components should be eliminated in time to ensure the accuracy of the experimental results.
Here's how to do it in detail:
Measurement preparation phase:
Select the appropriate measurement rotor system according to the experimental requirements and ensure that it is installed securely.
Set measurement parameters according to the purpose of the experiment, including strain control mode, temperature, shear rate, strain or stress range, etc.
Before starting the experiment, calibrate the instrument to ensure that the instrument is in normal working condition and the parameters are accurate.
According to the experimental needs, prepare the required samples, such as liquid samples, melt samples or solid samples, and load them into the measuring rotor system.
Measurement steps:
Select the temperature control method and set the starting temperature. After the temperature stabilizes, confirm that there is no sample on the sample stage, and adjust the upper and lower sample stages (clamps) to zero position manually or automatically.
Select the corresponding measurement mode according to the experimental requirements, and turn on the motor for measurement. During this process, the rheometer will cause a certain strain in the sample according to the set strain control instructions.
Load the prepared sample into the sample stage and adjust the spacing to ensure that the sample is completely filled in the gap of the measurement system. For solution samples, low-viscosity, high-boiling-point silicone oil and other substances that are immiscible and non-reactive with the sample can be coated on the edge of the sample to reduce solvent volatilization.
Set measurement parameters according to experimental requirements, including temperature, shear rate, strain, stress, frequency, etc., and select the corresponding sampling method.
Start the experiment by operating the software, monitor the measurement process, and save the experimental data in time.
End of experiment:
After the experiment is completed, turn off the motor to stop measurement. Remove the test sample from the sample stage and perform necessary cleaning work to ensure that the sample stage is clean. Turn off the rheometer host and perform the necessary shutdown steps according to the instrument's instruction manual. Through the above steps, the operation of the strain-controlled rotational rheometer can be completed, the required rheological property data can be obtained, and the accuracy and reliability of the experimental process can be ensured.
As an important experimental instrument, rotational rheometer plays an irreplaceable role in research and application in materials science, chemical industry, biomedicine and other fields. An accurate understanding of its measurement principles, structural composition and operating methods is of great significance to ensure the accuracy and reliability of experimental results.