I. Introduction
Electromagnetic stirrer is one of the indispensable equipment in the laboratory, which is widely used in various experimental processes in chemistry, biology, materials science and other fields. Its main role is to achieve homogeneous mixing of solutions through stirring, which is essential for the uniformity of the reaction and the accuracy of the experimental results. The electromagnetic stirrer not only improves the efficiency of the experiment, but also reduces the error of human operation, especially in the experiment that requires long-term and stable stirring, the electromagnetic stirrer can maintain a constant stirring effect to ensure the repeatability and reliability of the experiment. In addition, the heating and temperature control function of the electromagnetic stirrer makes it play an important role in experiments that require precise temperature control.
Magnetic stirrers are multi-functional to meet the needs of different types of experiments in the laboratory. First of all, its core function is to drive the stirring magnet to rotate in the container by electromagnetic force to achieve uniform mixing of the solution. Secondly, the heating function allows the electromagnetic stirrer to control the temperature of the liquid while mixing the solution, which is important for reactions that need to be carried out at specific temperature conditions. The temperature control function further refines the temperature adjustment, making the experimental process more stable and controllable. In addition, magnetic stirrers are often equipped with a speed control function that allows the stirring speed to be adjusted according to the needs of the experiment, so as to accommodate liquids with different viscosity and mixing requirements. Some advanced models are also equipped with a timer function that automatically stops the operation after a set time, further enhancing the convenience and safety of the experiment.
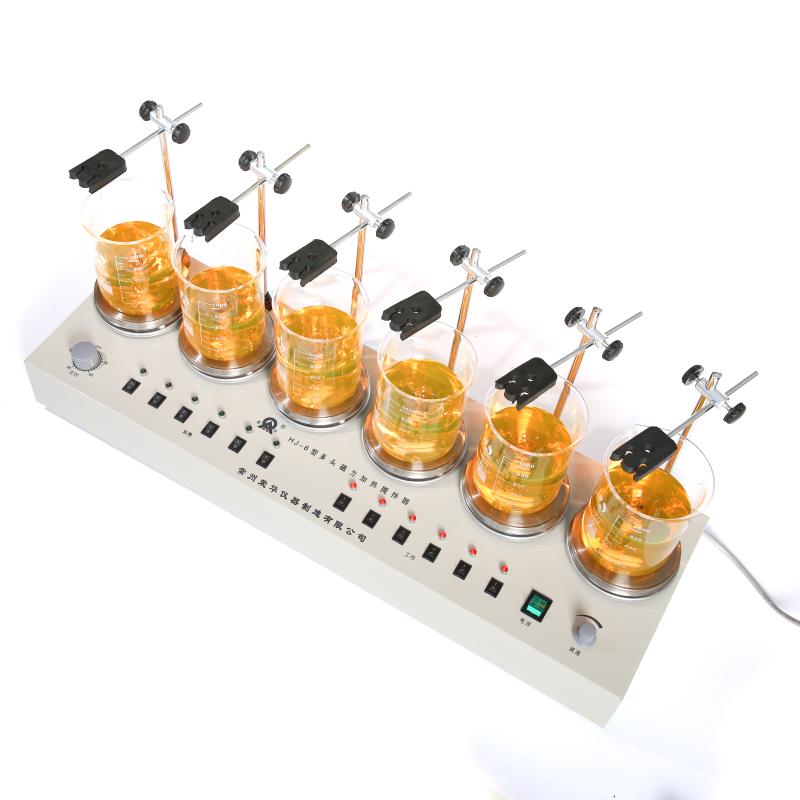

Second, the basic structure and working principle
1. Structural composition
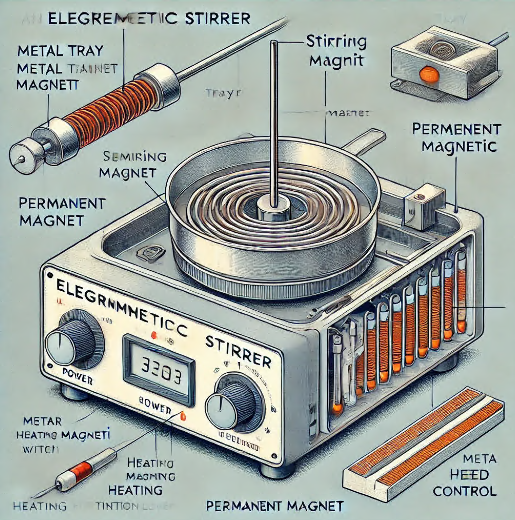
Introduce the main components of the stirrer: metal tray, stirring magnet, rotating motor, permanent magnet, heating elements (such as metal heating wire and mica insulation), control panel (power switch, heating switch, speed adjustment knob, indicator light).
(1) Metal pallets
Function: The metal tray is the main support platform of the electromagnetic stirrer, which is used to place the containers to be stirred, such as beakers, Erlenmeyer flasks, etc. Trays are often designed with a non-slip surface to ensure that the container remains stable during the mixing process and is not easy to slip. The metal tray conducts heat and heats the solution evenly in the container.
(2) Stirring magnets
Function: A stirring magnet is a small iron rod, usually encapsulated by a glass or plastic tube, that is used for liquid stirring in a container. The stirring magnet is driven by electromagnetic force and rotates at the bottom of the container, generating eddy currents, thus achieving the stirring effect. The size and shape of the stirring magnet can be selected according to the experimental needs to accommodate the stirring requirements of different vessels and liquids.
(3) Rotate the motor
Function: The motor is the core component that drives the stirring magnet to rotate. By connecting a permanent magnet, the motor generates a rotating magnetic field that drives the stirring magnet for stirring. The speed of the motor can be adjusted to meet the mixing needs of liquids of different viscosities and ensure the stability of the mixing effect.
(4) Permanent magnets
Function: The permanent magnet is fixed on the shaft of the rotating motor, and a magnetic field is generated through the rotation of the motor, which attracts stirring magnets to rotate in the container. The magnetic field strength of the magnet and the rotational speed of the motor together determine the rotation speed and stirring effect of the stirring magnet. The use of permanent magnets guarantees the stability and reliability of the stirring process.
(5) Heating element
Function: The heating element usually consists of a metal heating wire and mica insulation, embedded under the metal tray. The heating element is heated by an electric current and conducts it to the tray, which in turn heats the liquid in the container. Mica insulation is used to isolate the electrical contact between the heating element and the tray for safety. The heating function is essential for experiments that require temperature control, such as chemical reactions or dissolution experiments.
(6) Control panel
Function: The control panel is the interface for operating the electromagnetic stirrer, which usually includes a power switch, a heating switch, a speed adjustment knob, and an indicator light. The power switch controls the power supply of the whole machine, the heating switch is used to turn on or off the heating function, the speed adjustment knob is used to adjust the speed of the stirring magnet, and the indicator light shows the working status of the current equipment. The control panel is designed to be simple and easy to operate, allowing the experimenter to easily adjust the various functions of the agitator.
2. Working principle
In an electromagnetic stirrer, the motor rotates by driving a permanent magnet to rotate, creating a rotating magnetic field. This magnetic field is conducted through the bottom of the container to the stirred magnet inside the container (usually a small iron rod encased in a glass or plastic tube). The stirring magnets rotate synchronously under the action of the magnetic field, which creates eddy currents inside the container, resulting in the agitation of the liquid. The stirring speed can be controlled by adjusting the speed of the motor, so that the stirring intensity needs of different experiments can be adapted.
The working mechanism of the heating and temperature control function
Magnetic stirrers are usually equipped with heating elements that are embedded underneath the metal tray. The heating element is made of a metal heating wire, which is heated by an electric current to generate heat, and the heat is conducted through the metal tray to the bottom of the container, so that the liquid in the container gradually heats up. The heating process is monitored by a temperature control system, and the experimenter can set the desired temperature via the adjustment knob on the control panel. The temperature control system monitors the temperature of the tray or container in real time through sensors, and automatically adjusts the heating power according to the set value to maintain the stability of the liquid temperature and ensure the accuracy and repeatability of the experiment.
3. The main functions of the electromagnetic stirrer
(1) Stirring function
The core function of the electromagnetic stirrer is to stir the liquid, and different speeds have a significant impact on the mixing effect. Higher speeds are typically used for rapid mixing of low-viscosity liquids, while lower speeds are suitable for higher-viscosity solutions to avoid turbulence or bubble formation caused by over-agitation. Precise control of the rotational speed is critical to the success of the experiment, as too fast can cause the stirring magnet to run out of control, affecting the uniformity of the stirring, while too slow may not adequately mix the solution. By setting the rotational speed appropriately, the experimenter can ensure that the reaction species are stirred consistently and effectively throughout the experiment.
(2) Heating and temperature control
The heating function of the electromagnetic stirrer makes it also indispensable for experiments that require temperature control. In general, the temperature adjustment range of the heating function can be from room temperature to 300°C, or even higher, to accommodate a variety of different experimental needs, such as heating of chemical reactions, dissolution or evaporation of samples, etc. Uniform heating and temperature stability are important features of the heating function, which not only ensures that the temperature of the entire liquid sample is consistent during the heating process and avoids local overheating, but also maintains a constant temperature through a precise temperature control system to improve the reproducibility of experiments and the reliability of results. This is important for those temperature-sensitive experiments and can significantly reduce human error.
(3) Timing and speed regulation
The timing function greatly improves efficiency and convenience in experimental operation, especially in experiments that require long periods of agitation or heating. By setting the time, the magnetic stirrer can be automatically stopped after the scheduled task is completed, avoiding the need for long hours of manual monitoring by the experimenter. The speed control function provides more flexibility, and the stirring speed can be precisely adjusted according to the needs of different experiments. Whether it's low-speed stirring to prevent settling of suspended solids, or high-speed stirring to accelerate dissolution, the speed-regulating function adapts to a wide range of experimental conditions, making the magnetic stirrer a versatile and efficient tool in the lab.
Fourth, the field of application
(1) Chemical experiments
In chemical experiments, electromagnetic stirrers are widely used in potentiometric titration, pH determination, and ion-selective electrode determination. In potentiometric titration, the electromagnetic stirrer ensures the homogeneous mixing of the reaction substances by maintaining the continuous stirring of the solution, avoiding local concentration differences, thus improving the accuracy of the titration results. In pH determination, the stirrer helps to quickly and evenly distribute the acid-base solution, reducing measurement errors due to local concentration variations. In the ion selection electrode measurement, the stirrer avoids concentration polarization on the electrode surface by maintaining the movement of the solution, ensuring the stability and reliability of the measurement results. These experiments require the solution to be well mixed, and the electromagnetic stirrer greatly improves the accuracy and reproducibility of the experimental data through the controllable stirring speed and uniform stirring effect.
(2) Biological experiments
In biological experiments, electromagnetic stirrers are often used in operations such as biological cultivation and solution mixing. For example, during microbial culture, an electromagnetic stirrer can provide continuous agitation to evenly distribute nutrients and dissolved oxygen in the culture medium and promote uniform growth of microorganisms. For some biological reactions that require the addition of different reagents, the stirrer can efficiently mix the solution to ensure consistent reaction conditions. In addition, in biological experiments such as enzymatic reactions and protein extraction, the temperature control function of the electromagnetic stirrer can also provide a suitable reaction temperature to ensure the stability of bioactive substances and the smooth progress of the reaction. The application of electromagnetic stirrer in these biological experiments can effectively improve the stability and reproducibility of experimental results and ensure the success of experiments.
(3) Materials Science
In the field of materials science, electromagnetic stirrers are widely used in the synthesis and analysis of materials, especially in the preparation and dispersion of nanomaterials. The synthesis of nanomaterials usually needs to be carried out under strictly controlled conditions, and the electromagnetic stirrer can achieve uniform dispersion of nanoparticles and avoid agglomeration through precise stirring control, so as to obtain high-quality nanomaterials. In the preparation of polymer solutions, electromagnetic stirrers can also ensure the homogeneity of the solution, helping to improve the properties of the material. In addition, the temperature control function of the electromagnetic stirrer also plays an important role in the heat treatment process of the material, which can accurately control the reaction temperature of the material, so as to realize the control of the structure and properties of the material. Through these applications, the magnetic stirrer has become an indispensable tool in materials science research, helping to achieve the optimization of material properties and the development of new materials.

5. Use and precautions
1. Steps for use
(1) Start-up
Before using the magnetic stirrer, the speed adjustment knob should first be adjusted to the lowest position to prevent the stirring magnet from derailing due to sudden acceleration at start-up. After the 220V power is connected, press the power switch, and the power indicator will light up, indicating that the device has started to run.
(2) Speed regulation
Place the solution that needs to be stirred in the center of the tray and make sure that the bottom of the container is in good contact. Select the appropriate stirring magnet and put it in the container, confirm that the magnet is in the center of the container, and then gradually increase the speed knob to make the magnet start to rotate. When adjusting the rotational speed, it should be adjusted according to the viscosity of the solution and the experimental needs to avoid derailment of magnets or uneven stirring caused by too fast speed.
(3) Heating
If the experiment requires heating the solution, the heating switch can be turned on after the stirring starts. Set the desired temperature by adjusting the thermostat knob, and the device will automatically heat up and maintain the set temperature. At this point, the temperature indication should be closely observed to ensure that the temperature is stable within the desired range. During the heating process, avoid stirring too fast to prevent liquid splashing.
(4) Close
At the end of the experiment, gradually reduce the speed to the lowest level before turning off the heat switch (if in use). Finally, turn off the power switch, unplug the power supply, wait for the device and solution to cool down, and then remove the container and stirring magnet. After the equipment is cooled, the tray and magnet should be cleaned in time to prevent the residue from affecting the next use.
2. Precautions
Common problems and solutions in the mixing process:
(1) Magneton derailment
At high rotational speeds or when the liquid is viscous, the stirring magnet may derail due to not being able to keep up with the rotational speed, resulting in uneven agitation. To avoid this problem, start by lowering the speed and increasing it gradually, while choosing the right size and shape of the magnet to ensure that it can operate stably.
(2) Container displacement
Containers can be displaced due to vibration, especially when agitating at high speeds. To prevent this, a non-slip mat can be placed between the tray and the container or the stirring speed can be adjusted to reduce vibration. In addition, it should be ensured that the bottom of the container is flat and in good contact with the pallet.
The maintenance of the electromagnetic stirrer is directly related to the service life of the equipment and the safety of the experiment. The tray and stirring magnet should be cleaned in time after each use to avoid chemical residues corroding the equipment. In addition, the power cord and plug should be checked regularly to ensure that there is no damage or deterioration to avoid short circuits or electric shock accidents.During use, the operating procedures should be strictly followed, especially when heating, attention should be paid to prevent overheating or liquid splashing, and to prevent scalding or damage to the equipment. For equipment that is not used for a long time, the power supply should be disconnected to prevent the electrical components from being damp or damaged. Regular inspection and maintenance of the equipment can effectively extend the service life of the equipment and ensure the safety of the experiment.

6. Maintenance and maintenance
In daily use, the tray and stirring magnet of the magnetic stirrer should be cleaned in time after each experiment to prevent residual chemicals from corroding the equipment. Trays and magnets can be cleaned with a soft, damp cloth and avoid using strong acids, alkalis, or abrasive cleaners. Also, regularly inspect the appliance's power cord, plugs, and control panel to ensure there are no signs of damage, looseness, or aging. If any abnormality is found, it should be replaced or repaired in time to ensure the safe operation of the equipment.
Common faults include stirring magnet derailment, motor not turning, or heating function failure. Stirring magnet derailment is usually due to too high rotational speed or improper magnet selection, the workaround is to adjust the rotational speed and select the appropriate magnet. The motor does not rotate may be related to the power connection or motor failure, and the power cord, plug and internal connection of the motor should be checked. If the heating function fails, it may be a damaged heating element or a faulty temperature control system, and the relevant parts need to be inspected and replaced. In case of complex faults, it is recommended to contact professional and technical personnel for maintenance.

7. Purchase guide
Electromagnetic stirrers are available in a variety of types depending on their function and use. The basic type of magnetic stirrer is generally suitable for conventional solution stirring, without heating function, and is suitable for simple mixing operations. Magnetic stirrers with heating function are suitable for experiments that require simultaneous heating and stirring, such as chemical reactions or the dissolution of samples. The multi-head magnetic stirrer can stir multiple vessels at the same time, making it suitable for large-scale experiments or high-throughput needs. In addition, the digitally controlled magnetic stirrer has precise temperature control and timing functions, making it suitable for applications that require highly precise control of experimental conditions, such as biological culture and material synthesis.
Key factors to consider when making a purchase
When selecting an electromagnetic stirrer, the following key factors should be considered according to the specific experimental needs:
Power – The power determines the stirring capacity and heating efficiency of the agitator. For high-viscosity liquids or high-volume agitation, it is recommended to choose a model with higher power.
Stirring capacity – Different models of magnetic stirrer support different maximum stirring capacities. When purchasing, the appropriate volume range should be selected according to the volume of liquid required for the experiment to ensure the stirring effect.
Temperature control accuracy – For experiments that require precise temperature control, temperature control accuracy is an important consideration. High-end models typically offer higher temperature control accuracy and are suitable for temperature-sensitive experiments.
Material and durability – The material of the tray and stirring magnet affects its durability and resistance to chemicals. It is advisable to choose materials that are highly resistant to corrosion and easy to clean to prolong the life of the equipment.
Additional functions such as digital display, timing function and multi-head stirring, etc., can improve the convenience and efficiency of the experiment by selecting the appropriate additional functions according to the needs of the experiment.
All in all, as a common equipment in the laboratory, electromagnetic stirrer is widely used in many fields such as chemistry, biology, and materials science. Its core functions include stirring, heating and temperature control, speed regulation and timing, etc., which can meet the needs of various experiments. In chemical experiments, the electromagnetic stirrer improves the accuracy and reproducibility of experimental results through precise stirring and temperature control. In biological experiments, it helps in biological culture and solution mixing; In materials science, it is used in the synthesis and analysis of nanomaterials to ensure uniform distribution and optimal properties of materials.
When purchasing an electromagnetic stirrer, laboratories should consider the equipment's power, stirring capacity, temperature control accuracy, and additional functions according to the specific experimental needs. At the same time, regular maintenance and proper use of the magnetic stirrer are essential to extend the life of the equipment and ensure the safety of the experiment. Taking these factors into consideration, the experimenter can choose the appropriate electromagnetic stirrer to improve the efficiency and accuracy of the experimental operation and ensure the smooth progress of the experiment.














