Guide:If you want to know about viscosity testing, please check the following in detail, if you need to buy viscosity testing equipment, pleaseClick here
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance experienced by some liquids as they move over another part of the liquid, and is a property within a fluid that hinders its relative flow. In coatings, except for powder coatings, other coatings are relatively viscous liquids. Viscosity is an important technical index of coating products, and in the process of coating production, the relative molecular weight of polymers in the paint base can be controlled by measuring the viscosity. Viscosity is also an important process parameter in coating construction, in brushing, roller coating, spraying, dipping and other coating construction, by adjusting the viscosity of the coating, the coating thickness can be controlled, and the coating appearance can be improved to a certain extent. The unit of viscosity is Pascal· Seconds (Pa·s), i.e. [dynamic] viscosity, indicates the amount of internal friction of a liquid when it flows; The concept of kinematic viscosity needs to be introduced when viscosity is determined using so-called kinematic viscometers, such as pore and bubble type viscometers, or when designing piping installations for transporting paints or paints. Kinematic viscosity is defined as the ratio of the viscosity of the liquid to the density of the liquid.This can be expressed by:
ν=η/ρ
Where: ν represents kinematic viscosity; η indicates dynamic viscosity; ρ denotes the density of the liquid
For paint production and coating application, it is a simple and easy way to control the process parameters by using a paint cup and a falling ball viscometer to test its conditional viscosity. The condition for determining viscosity with a paint cup refers to the time that a certain amount of sample flows out of a hole of a specified diameter at a certain temperature, expressed in seconds (s). The domestic paint cup is divided into two specifications: -1 cup and -4 cup, and the outflow time of the test can be converted into kinematic viscosity value (mm2/s) according to the following formula:
Tu-1 cup: t = 0.053v+ 1.0
Tu - 4 cups: t﹤60; t = 0.154V + 11 23s≤60 at 235; At t 150s, t = 0.223v+ 6.0
where t- outflow time(s) ; v- kinematic viscosity (m2/s).
Conditional viscosity as determined with a falling ball viscometerYes: the time required for a steel ball of a certain specification to pass through the upper and lower two scale marks of the glass tube containing the sample at a certain temperature, so the measured sample should be transparent. In addition, there is also a kind of bubble viscometer or gahrop tube commonly used in the industry, which is mainly used for intermediate control of the production process to determine the viscosity of semi-finished products such as paint and resin liquid.
Foreign countries also usually use the method of determining the conditional viscosity to control the production and coating construction of coatings, such as the international standard (ISO) Viscosity Cup (the equivalent standard GB6753. 4-1986), British Standard (BS) No. 4 Cup, French Standard (NFT) No. 4 Cup, American (ASTM) Standard Ford Cup, German Standard (DIN) 4mm Cup, German Standard (DIN) 6mm Cup, etc., bubble viscometer can be used to determine the viscosity of varnish. This section will introduce the test methods for Tu-1 Viscometer, Tu-4 Viscometer, Falling Ball Viscometer, Ford Cup, and Bubble Viscometer.
Tu-1 viscometer method
It is used to measure the outflow time of not less than 20s (based on this viscometer).
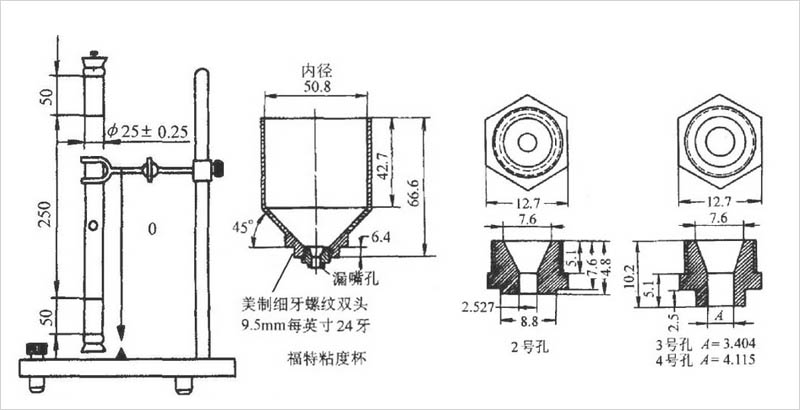
l) Instruments The instrument is shown in Figure 4.1-1, the upper part is cylindrical, the lower part is conical metal container, and the roughness of the inner wall is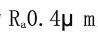 There is a line on the inner wall, there is a leaky mouth at the bottom of the cone, there are two holes in the lid of the container, one hole is for plugging rods, the other hole is for inserting a thermometer, the container is fixed in a circular Water Bath, and the viscometer is installed on a rack with two adjusting level screws. Basic dimensions: The inner diameter of the cylinder is
There is a line on the inner wall, there is a leaky mouth at the bottom of the cone, there are two holes in the lid of the container, one hole is for plugging rods, the other hole is for inserting a thermometer, the container is fixed in a circular Water Bath, and the viscometer is installed on a rack with two adjusting level screws. Basic dimensions: The inner diameter of the cylinder is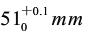 , the cone is high from the bottom to the engraved line
, the cone is high from the bottom to the engraved line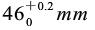 , the angle inside the cone of the viscometer is
, the angle inside the cone of the viscometer is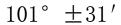 。 The drain is high
。 The drain is high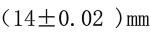 , the diameter of the drain
, the diameter of the drain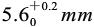
2) Test method Before each test, the inside of the viscometer must be wiped clean with gauze dipped in solvent, dried in air or dried with cold air, and the leak of the viscometer should be cleaned for light observation, and then the viscometer should be placed in a Water Bath sleeve and plugged into the stick. Stir the sample evenly, and use the pore size when there are crusts and particles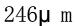 filter through a metal sieve and adjust the temperature to
filter through a metal sieve and adjust the temperature to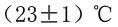 ; or
; or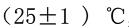 ; Then pour the sample into the viscometer, adjust the level screw to make the liquid level coincide with the engraved line, in order to let the bubbles escape in the sample should stand for a while, close the lid and insert the thermometer, the sample is kept in
; Then pour the sample into the viscometer, adjust the level screw to make the liquid level coincide with the engraved line, in order to let the bubbles escape in the sample should stand for a while, close the lid and insert the thermometer, the sample is kept in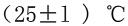 。 Place a 50mL measuring cup under the leaky nozzle of the viscometer, and when the temperature of the sample meets the requirements, quickly lift the stopper, and when the sample flows out of the leaky nozzle and drops to the bottom of the cup, the stopwatch is immediately activated. When the sample in the cup reaches the 50mL scale line, stop the stopwatch immediately, and the time required for the sample to flow into the cup for 50mL (s) is the outflow time of the sample, and the difference between the two measured values should not be greater than 3% of the average value.
。 Place a 50mL measuring cup under the leaky nozzle of the viscometer, and when the temperature of the sample meets the requirements, quickly lift the stopper, and when the sample flows out of the leaky nozzle and drops to the bottom of the cup, the stopwatch is immediately activated. When the sample in the cup reaches the 50mL scale line, stop the stopwatch immediately, and the time required for the sample to flow into the cup for 50mL (s) is the outflow time of the sample, and the difference between the two measured values should not be greater than 3% of the average value.
Tu-4 viscometer method
This viscosity testing methodIt is used to measure paint products with an outflow time of less than 150s (based on this viscometer).
l) The instrument is shown in Figure 4.1-2, the upper part is cylindrical, the lower part is conical, there is a replaceable leak at the bottom of the cone, and there is a groove in the upper part of the container for overflowing excess samples. The viscometer is mounted on a rack with two leveling screws. Tu-4 viscometer is made of plastic and metal, and its inner wall roughness is Ra0.4μm, but the metal viscometer shall prevail. Basic Dimensions:
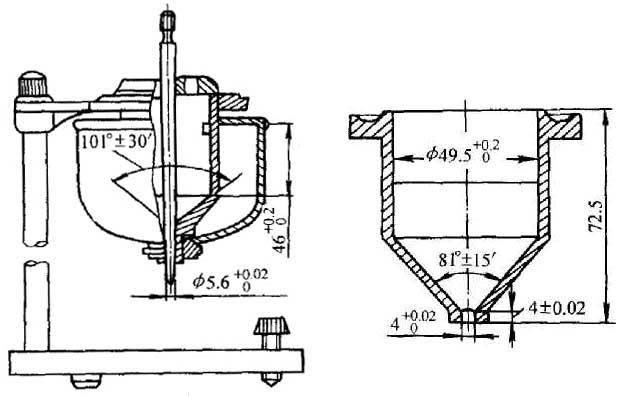
Figure 4.1-1 Tu-1 Viscometer
Figure 4.1-2 Tu-4 Viscometer
The viscometer capacity is:![]() The drain is made of stainless steel and has a high hole
The drain is made of stainless steel and has a high hole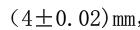 , bore inner diameter
, bore inner diameter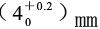 , the angle inside the cone of the viscometer is 81°±15′, the total height is 72.5mm, and the inner diameter of the cylinder
, the angle inside the cone of the viscometer is 81°±15′, the total height is 72.5mm, and the inner diameter of the cylinder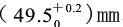 。
。
2) Test method The cleaning treatment of the viscometer and the preparation of the sample are coated with the -1 viscometer test method, adjust the horizontal screw to make the viscometer in a horizontal position, place a 150mm enamel cup under the leaky mouth of the viscometer, plug the leaky hole with your hand, pour the sample into the viscometer, scrape the bubbles and excess samples with a glass rod and scrape the grooves, and then release the fingers to make the sample flow out, and at the same time immediately start the stopwatch, stop the stopwatch when the sample flow (wire) is just interrupted, and the whole time that the sample flows out of the viscometer (s), This is the conditional viscosity of the specimen. The difference between the two measurements should not be greater than 3 % of the mean value, and the specimen temperature should be (25±l) °C or (23±l) °C.
Falling ball viscometer method
This viscosity testing methodIt is used for the determination of transparent coating products with high viscosity.
l) The instrument is shown in Figure 4.1-3. It is composed of glass tube and steel ball, the length of the glass tube is 350mm, and the inner diameter is (25±0.25) mm; There are graduation lines at 50mm from the edge of the nozzle at both ends, the distance between the two lines is 250mm, there is a cork stopper on the nozzle and the lower end, there is an iron nail in the middle of the cork plug at the upper end, the pipe is vertically fixed on the frame (measured by a plumb weight), the diameter of the steel ball is (8±0.03) mm, and the weight is 2.091g.
2) Test method The transparent sample is poured into the tube, so that the sample is 4cm higher than the scale mark, and the steel ball is also released together, plugged with the cork with iron nails, placed on the cork with iron nails with a long-term magnet, the tube is reversed to make the iron nails absorb the steel ball, and then flip it over, fix it on the frame, and adjust it vertically with a plumb weight, and then remove the long-term magnet to make the steel ball fall freely, start the stopwatch immediately when the steel ball passes through the upper scale mark, stop the stopwatch when the steel ball falls to the lower scale line, and record the time when the steel ball passes the two scale lines (s), This is the conditional viscosity of the specimen. The difference between the two measurements should not be greater than 3 % of the mean value.
Ford Cup Law
This viscosity testing methodIt is suitable for measuring the viscosity of paint, varnish and related fluid materials with Ford type Viscosity Cups, and the combined cup mouth (Ford No. 2, No. 3 or No. 4) is used to determine the outflow time within 20-100s.
1) Instruments
The Ford Cup is made of corrosion-resistant, solvent-resistant material and is assembled as a single unit according to the dimensional requirements shown in Figure 4.1-4.
2) Test method Before and after each test, wash the cups with an appropriate solvent and a soft-bristled brush, never with metal
The tool is in contact with the instrument and needs to be cleaned with special care when cleaning the leaky hole to avoid any film deposition on the inner wall or notching the inner wall.
The test should be performed in a room without ventilation and without sharp temperature changes, and in order to achieve high accuracy, the room temperature should be 20-30°C, the temperature of the measurement should be above the dew point of the atmosphere around the instrument, and the sample temperature should be (25±0.1)°C.For materials with an outflow time between 20-100s, Ford No. 3 cups and Ford No. 4 cups should be used, and materials with an outflow time between 40-100s should be Ford No. 2 cups. Adjust the instrument to make it in a horizontal position, plug the leaky hole with your fingers, pour the material that is stirred evenly in advance and without any foreign matter or bubbles into the cup, it is better to make it excessive, and then scrape the excess with a ruler, release your finger, press the stopwatch, and measure the time from the beginning of the material to the first interruption of the liquid (silk), and the number of seconds obtained is the viscosity of the material.
Bubble timekeeping
This viscosity testing methodIt is suitable for determining the viscosity of transparent liquids without crystals or colloidal particles by means of seconds of air bubbles or contrast。 For most liquids, the number of bubble seconds is approximately equal to its number of s, a unit of kinematic viscosity. lSt =10-4 m2/s 。
1) Instruments
Thermostatic Baths are suitable for any bath that can maintain a temperature of (25±0.1) °C and use water as a medium.
a. Standard viscosity tube is a flat bottom transparent glass tube with an inner diameter of (10.65 ±O.025 ) mm and an outer length of (114±l ) mm. It should be self-tube bottom-up in (27±0. 5 ) mm, (100 ± 0.5) mm, (l08±0.5) mm engraved with obvious standard line. The distance between the first and second reticules should be (73±0.5) mm.
b. Reference standards are a set of standard viscous tubes, filled with a clear liquid with a pre-measured viscosity expressed in terms and bubble seconds, and in a logarithmic series of 26% according to Table 4.1-2 (log1. 260 = 0.100), these standards should be marked with numerical marks independent of Si or bubble time as shown in Table 4.1-2. A long series of Gordner-Holder alphabet standards are also listed in Table 4.1-2 for general and historical information purposes only. Gahrops do not have the three reticles on standard viscosity tubing and are shorter than standard viscosity tubing. For convenience, the reference standard can be divided into three series, 15 tubes from 0.22-8.0 for the lean series, 14 tubes from 10 to 200 for the high viscosity series, and 7 tubes from 250 to 1000 for the ultra-high viscosity series. The chronograph mechanism is capable of reading a stopwatch or electronic alarm clock with an accuracy of 0.1s.
c. Pipe rack It can invert 1 or more viscous tubes 180°, accurate to 1° upright movable frame, and can immerse the tube in a constant temperature bath. Viscous tube cork - NO.2 short stopper.
2) Test method
The viscosity of the material to be measured is placed in a standard viscosity tube, about 108mm marking. Shift the viscosity tube into a thermostatic bath at 25 °C and gently plug the viscosity tube with a cork to keep it warm for 10 min at this temperature. It is important to control the temperature of the thermostatic bath, as a temperature change of 0.1°C in the thermostatic bath will cause a 1% change in the timing of the bubbles.After 10min, adjust the liquid level so that the bottom of the meniscus is on the 100mm line, and plug the plug tightly so that the bottom surface of the plug is on the 108mm line, which will ensure that the bubble is stable and the size is appropriate.Insert the viscosity tube into the tube rack and immerse the tube rack in a 25°C Water Bath. If the measurement is performed by the contrast method, the appropriate standard tube is inserted into the tube rack next to the viscosity tube to be tested. The tube with the cork should be kept in a Water Bath for at least 20 min before reading the viscosity value. For liquids with a viscosity of 4 s or less according to the bubble lift time, in order to obtain more accurate results, the viscosity can be measured by comparing the method with a reference standard that has measured the viscosity in advance or measured the bubble time (see the reference standard above).
During the reading, the viscosity tube is quickly inverted and the number of seconds it takes for the air bubble to rise or the result compared to the standard is measured. When the top of the bubble is tangent to the 27mm line, the timer is started to read the number of seconds, and when the top of the bubble is tangent to the 100mm line, the timing is ended, and the bubble time of the 73mm lift is measured. All timing and comparison processes should be carried out in such a way that the viscosity tube is kept in a vertical position. If the viscosity tube deviates from its vertical direction by a radius of one distance, it will cause an error of about 10 % of the bubble travel time.
The provisional calculation standards for comparative viscosity tubing are shown in Table 4.1-2.
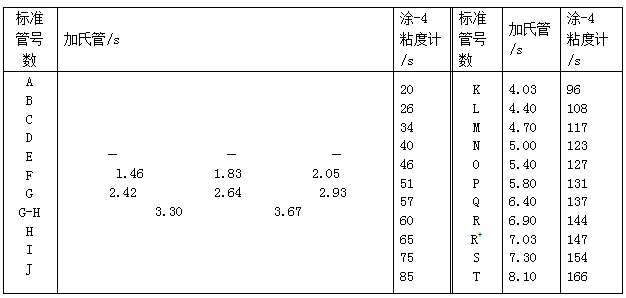
The viscosity of the Gahris tube and the Tu-4 cup is shown in Table 4.1-3.
The viscosity of a fluid varies with temperature. For example, near room temperature, the temperature changes by 1°C, the viscosity change rate is about (2-10) %, and the change rate is also related to the viscosity of the fluid itself. When measuring, it is necessary to avoid illumination in the surroundings that exceeds the necessary illumination, as the radiant heat generated by excessive illumination will cause the correct indication of the thermometer or the temperature of the measured fluid to change, and the measurement test should be completed as soon as possible due to the high volatility of the paint.After long-term use, some viscometers need to be calibrated with a viscosity standard solution (such as distilled water, etc.) with a guaranteed viscosity value, and the viscosity and density of distilled water at various temperatures are shown in Table 4.1-4.
The commonly used viscosity conversion table of coatings is shown in 4.1-5.Table 4.1-2 Provisional calculation standards for comparative viscosity tubing
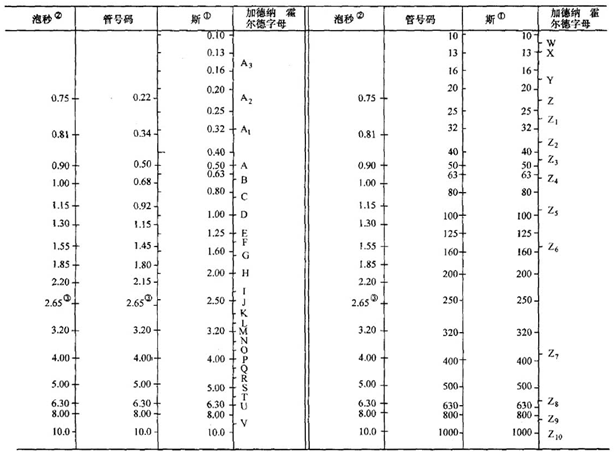
(1) Arranged by the relationship between the Si, the bubble seconds, and the Gardner-Züld letters, the Si is arranged by its logarithmic value.
(2) The bubble time (in seconds) of the viscosity tube marked with a number of less than 4s was measured by photographic technology.
(3) When the bubble seconds are above 2.65, for most products, it is roughly equivalent to the value measured by the power method, and when it is lower than 2.65, this relationship is no longer maintained.
Galdor tube vs. Tu-4 cup viscosity comparison table
Viscosity, kinematic viscosity and density of swallow distilled water at various temperatures
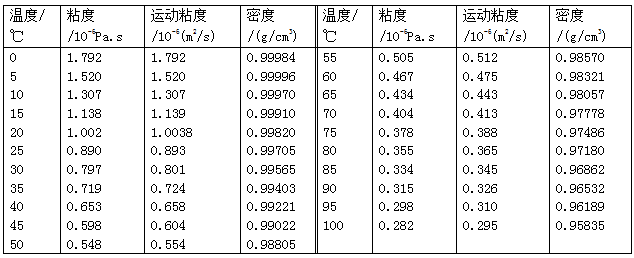
Note: The viscosity and kinematic viscosity values in the table are relatively measured based on the value of 1.0038×10-6m2/s at 20°C.
A conversion table of commonly used viscosities for coatings
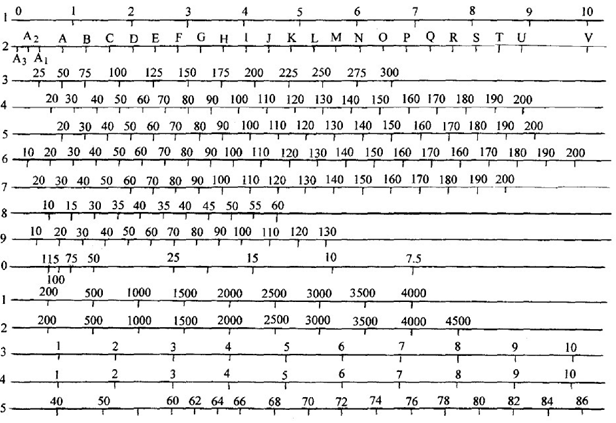
Note: 1. Kinematic viscosity: 1, 13 tow, 2. Grignard tube, 3. International standard (ISO) Viscosity Cup, 4. British standard (BS) No. 4 cup, 5. French standard (NFT) No. 4 cup, 6. American standard (ASTM) Ford No. 4 cup, 7. German standard (DIN) 4mm cup, 8. German standard (DIN) 6mm cup, 9. Engela viscometer, 10. Barbi viscometer, 11. Hodwood sharp hole viscometer, 12. Sepot universal viscometer.
2. Dynamic viscosity: 14. Pois, 15. Krebs unit.