pH meter, also known as acidity meter, is a commonly used physical and chemical analysis instrument, mainly used to measure the pH value of the solution, but also to measure the potential difference between the two electrodes, in environmental protection, health and epidemic prevention, quality control, safety protection and other fields. The accuracy of the measured values directly reflects the physical and chemical properties of the samples to be tested. Therefore, it is of great significance to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the pH meter correctly to ensure the quality of the product.

Structure and principle of a pH meter
Structural composition
The pH meter we use consists of two parts: an electrometer and an electrode. Electrodes can be divided into glass electrodes (measuring electrodes) and calomel electrodes (reference electrodes), and the commonly used composite electrodes today are composite glass electrodes and calomel electrodes. In addition, a pH meter may also contain a temperature compensation device, a signal amplification and display device, etc.
How it works
The pH value is used to express the pH of a solution and is the negative logarithm of the concentration of H ions in the solution, i.e., pH = -lg [H⁺]. During the measurement, the electrode is immersed in the solution to be measured, and the concentration of H ions in the solution is converted into a mV voltage signal and sent to the electric meter. The signal is amplified by an electric meter and logarithmically converted to pH, which is finally displayed by a millivolt level display. The change in hydrogen ion concentration causes a change in the potential of the glass electrode, which in turn causes a change in the potential between it and the calomel electrode, which is consistent with the Nernst equation: E = E₀ - 2.3026 RT/F. where R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, F is the Faraday constant, and E₀ is the standard electromotive force of the electrode. It can be seen that temperature is a key influencing factor when measuring pH, and it is necessary to pay attention to temperature changes and take them into account when measuring them.
Selection and preparation of standard buffer solutions
Standard buffer solutions are commonly used
1. B4-0.05mol/kg potassium hydrogen phthalate solution, pH value of 4.003 at 25 °C.
2. B6-0.025mol/kg mixed phosphate solution, pH value at 25°C is 6.864.
3. B9-0.01mol/kg borax solution, pH value of 9.182 at 25 °C.
Preparation of standard buffer solutions
To ensure that the standard buffer solution is accurate, it needs to be prepared correctly. The potassium hydrogen phthalate pH reference material (GBW(E)130070), mixed phosphate pH reference material (GBW(E)130071), and borax pH reference material (GBW(E)130072) developed by the National Reference Materials Research Center can be used. The standard deviation of the measurements for these reference materials is 0.002 pH and the total uncertainty is 0.01 pH.
Preparation steps
1. Take one reference material at a time and dilute it at 25°C with twice distilled water or deionized water with a conductivity of less than 2 μS/cm.
2. Pour the diluent into a 250ml volumetric flask, wash the container containing the reference material several times with distilled water, and pour all the washing solution into the volumetric flask.
3. Add distilled water to the scale mark so that the concave liquid level is level with the scale mark.
4. Shake the volumetric flask to fully dissolve the substance.
Calibration operations
As a measuring instrument, pH meters need to be regularly verified and calibrated to ensure accuracy. Calibration is usually performed with three standard buffer solutions (B4, B6, B9) in sequence, and some pH meters with 4/9 conversion are calibrated with B6 solution first; The alkaline solution was calibrated with B9 (adjusted to "9") and the acidic solution was calibrated with B4 (adjusted to "4"). During calibration, wash the electrode to absorb the water, immerse in the solution and adjust the knob after the reading is stable, so that the displayed value is consistent with the standard pH value, and the calibration value should be within the allowable error range. If the calibration value is out of tolerance, check the electrode fault first, replace the qualified electrode and try again, if it is still inaccurate, the electric meter needs to be sent to the metering department for maintenance.
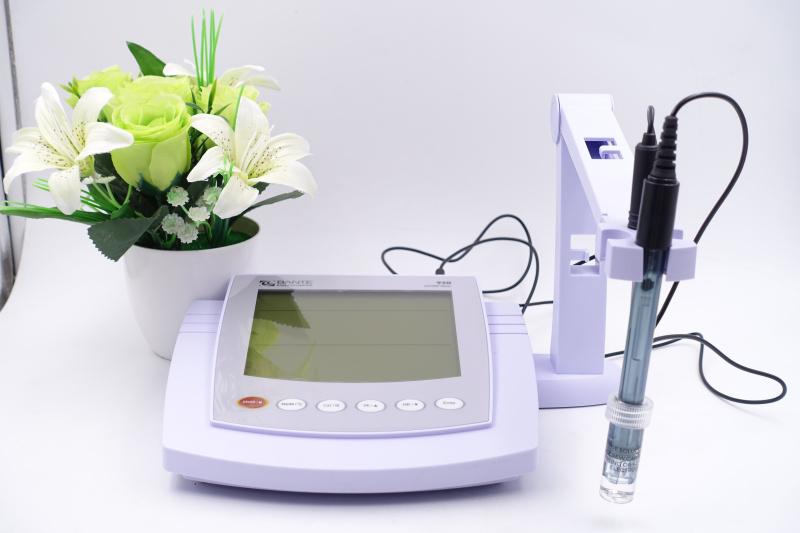
Measurement steps
To measure the pH value of a solution with a pH meter, the following operations need to be done in order: turn on the instrument first, measure the preheating for no less than 5 minutes for a short time, and measure the preheating for more than 20 minutes for a long time; After measuring the temperature of the solution with a thermometer, the corresponding value is set by the panel temperature compensator; In terms of electrode preparation, new electrodes or long-standing electrodes need to be soaked in advance, pay attention to protect the glass bulb when using, and standardize the handling of rubber sleeves and rinse electrodes before and after measurement; Finally, the electrode is immersed in the solution and stirred, and the record is read after the value is stable, and the wire is kept stationary during the measurement, and the measurement time is appropriately extended in case of special solution.
Maintenance points
The maintenance of the pH meter needs to be carried out in many aspects, during daily use, it is necessary to keep the socket of the instrument input clean, access the short wiring to prevent dust when not in use, and wipe the shell regularly; In terms of electrode maintenance, the glass electrode needs to avoid collision, when there are contaminants, clean with mild detergent and then rinse with distilled water, calomel electrode should keep the internal potassium chloride solution at about 2/3 and saturated, and if there is a blockage, it can be soaked in 0.1mol/L hydrochloric acid solution and ultrasonicated; In terms of calibration frequency, it is recommended to calibrate the pH meter every 48 hours for frequently used pH meters, and it is necessary to calibrate after measuring the extreme acid and alkali solution, after the electrode has been exposed for more than 0.5 hours, or before using it again after a long period of inactivity; When storing, the electrode should be removed and washed and dried, the glass electrode should be soaked in 3mol/L potassium chloride solution or special preservation solution, the calomel electrode should be covered with a rubber sleeve, and the instrument should be stored in a dry, clean and non-corrosive gas environment; At the same time, it is necessary to regularly check whether the electrode bulb is damaged, bubbles and cracks, as well as whether the functions of the instrument are normal, and repair and deal with the abnormalities in time.
To sum up, the correct use of pH meters covers many aspects such as understanding the structural principle, preparing standard solutions, accurate calibration and calibration, standardizing measurement operations, and comprehensive maintenance. Each step is crucial, and only by strictly following these requirements can we ensure the accuracy and reliability of the pH meter measurement results, give full play to its important role in various physical and chemical analysis, and provide solid data support for scientific research, production and other fields.
If you have any other questions or need further guidance during the use of pH meters, please feel free to contact us.
