Adhesion refers to the sum of the physical and chemical binding force of the coating film on the surface of the substrate. The wettability of the material removed during painting and the roughness of the substrate surface also affect its adhesion. The test methods are divided into direct method and indirect method. The direct method is mainly the pull-off method (GB5210-85), which measures the pulling force required to peel the paint film from the surface of the substrate. The indirect method, such as scratch hardness, impact strength, flexibility, etc. Adhesion, but the circle method and the cross-cut method are generally used to test the adhesion of the coating film, which is quick and convenient to operate.
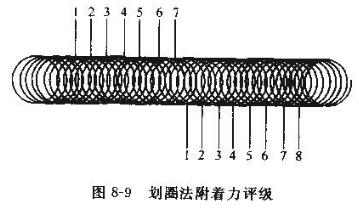
The circle-drawing method (GB/T172o-89) is to use a circle-drawing adhesion Tester, apply a cutting load until the needle can cut through the paint film, and evenly draw a circular rolling line (length 7.5cm ± 0.5 cm), as shown in Figure 8 -9 marks the parts 1~7 respectively, and the grids of the marked parts are regarded as intact if more than 70% of the paint film is preserved, then the smallest grid part with a good paint film is the corresponding ship stress level, 1 is better, and 7 is the worst.
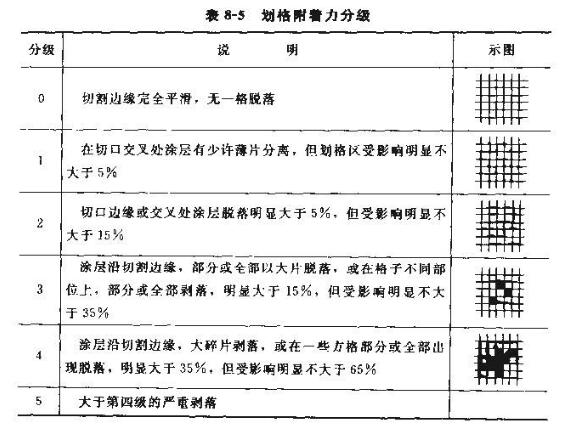
The cross-cut method (GB/T9286--88) is to use a high-alloy steel cross-cut tool to cut vertically and horizontally at the same distance of 1 mm. The rating method for the number of cuts is 6, see Table 8-5, the better is Gt0, the most The difference is Gt5 grade, and the grading ranking of European and American countries is 5B is better. OB is the worst. If the number of cuts is 11, it is expressed as a percentage of intact grids.