To test the weather resistance of the paint film, according to CB1767-79 "Determination of Weather Resistance of Paint Films", it can be exposed outdoors in the open air, or it can be carried out in an artificial test climate room. The latter can accelerate the aging test to shorten the cycle of the coating film durability test, but it is not as economical as the outdoor exposure test.
The outdoor exposure test method is as follows
Before the test, polish the two white iron plates used to make the sample with fine emery cloth, and polish the four corners and four sides of the sample for exposure to the sun, then apply the anti-rust primer, and then coat the paint to be tested. Aluminum powder paint or other different color paint with good weather resistance is used for edge sealing, and each coat must be fully dried. Two samples should be made, one is called the exposure sample, the size is 150x250x(0.8~1.5)mm, used for testing; the other is called the standard sample, the size is 70x150x(0.8~1.5)mm, and it is properly stored indoors. for use in comparison. The sample should be maintained indoors for 5-7 days before being put into test. Before the sample is put into test, the appearance state and physical and mechanical properties of the paint film should be observed in advance and recorded.
During the test, place the sample on a steel or wooden exposure rack. The cycle of checking the sample is generally stipulated as: within the first to three months of exposure, check every 15 days. From the fourth month onwards, check once a month, and check quarterly after one year. In the rainy season or when the weather changes suddenly, check it at any time, and record it if there is any abnormal phenomenon. When inspecting, take the model indoors, first use a soft brush to sweep off the dust on the surface of the model, and check for pulverization. Then wipe the model with a soft cloth or sponge in water, and then check the loss of light, discoloration and other items after drying.
During normal inspection, individual ratings can be carried out to assess the damage of each index of the paint film, and at each stage of the test or at the end of the test, a comprehensive rating can be carried out, that is, the aging of each individual item is combined to give the coating film. The overall evaluation is expressed in terms of excellent, good, medium, poor, poor or a 5-point system.
Durability testing items include loss of light, discoloration, chalking, cracks, blisters, rust spots, shedding, etc.
1. Lost light
In the weather resistance test, as time goes by, the gloss of the paint film will gradually decrease, which is called gloss loss. Gloss loss can be measured with a photoelectric gloss meter, expressed as a percentage of loss of light (compared with the original gloss of the paint film). Table 8_3 is the coating gloss loss evaluation table. (Related instrument: gloss meter)

2. Discoloration
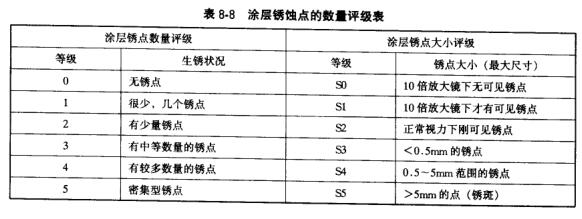
Refers to the phenomenon that the color of the paint film decreases or becomes darker or lighter due to aging in the atmosphere. The color change can be quantitatively measured with a photoelectric Colorimeter. Table 8-4 is the evaluation table of coating color change grade. (Related instrument: Colorimeter)
3. Pulverization
Chalking is the phenomenon that the surface of the paint film is damaged by ultraviolet rays, water vapor, oxygen, etc. after being exposed to the sun for a long time, and the pigment on the surface cannot remain firmly in the paint film, and falls off to form a powder layer. The powdering method can be determined by powdering Tester, gravimetric method, gloss method and finger method. Figure 8-31 is the Tester for coating powdering rate. During the inspection, the paint film is bonded to the smooth surface of the photo paper. After applying a specified uniform load, take out the photo paper, observe the print of the photo paper and compare it with the standard powdering rate grade. Compare the samples and evaluate the grade of the chalking rate of the paint film. Table 8-5 is the rating table for the powdering degree of the coating.


4. Crack
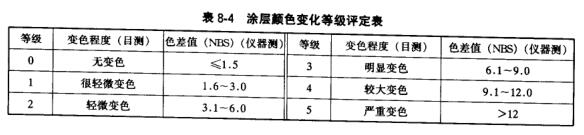
It is a representative damage phenomenon of paint film in weathering test. When specifically evaluating cracks, the depth, percentage and density of cracks are mainly recorded. Table 8-6 is the rating table for coating crack degree.
5. Blistering
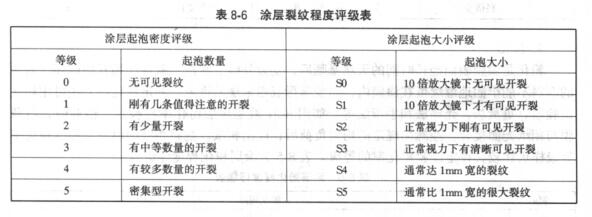
It is a phenomenon in which there are bubbles in the paint film due to the presence of gas and liquid. The evaluation of foaming is generally based on the size, density and distribution area of the bubbles, as shown in Table 8_7.
6. Rust
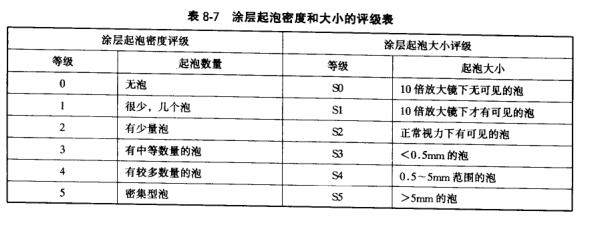
It refers to the phenomenon that compounds mainly composed of iron hydroxides and oxides are formed on the surface of steel after painting. The evaluation of corrosion is mainly based on the number and size of corrosion spots on the test area of the model, as shown in Table 8_8.