 (1) Structural features
(1) Structural features
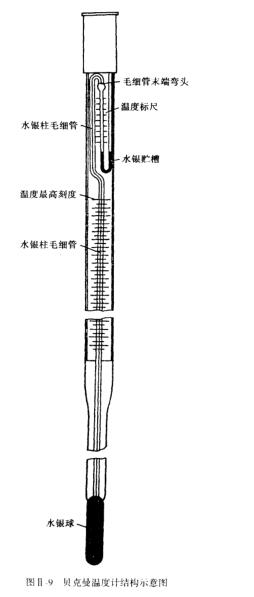
The Beckmann thermometer is a thermometer used to precisely measure temperature differences, and its structure is shown in Figure 11-9.
Its main features are as follows:
(l) The scale is fine, the interval between the marking lines is 0.01°C, and it can be estimated to 0.002°C with a magnifying glass, so the measurement accuracy is high.
(2) Since the amount of mercury in the mercury bulb is variable, it cannot be used to measure the absolute value of the system temperature. It can only measure the temperature difference ΔT of the system within the range of 5~6°C.
(3) It can be used in the range of -20---l50°C. This is because there is an auxiliary mercury storage tank at the upper end of its capillary , which can be used to adjust the amount of mercury in the mercury bulb, so it can be used in different temperature ranges.
(2) How to use
According to the needs of the experiment, the measurement range of the Beckmann thermometer is different, and the mercury level in the capillary needs to be adjusted to the appropriate range of the scale. Two adjustment methods are described below.
l. Constant temperature bath adjustment method
(1) Determine the temperature range used. For example, to measure the freezing point drop of an aqueous solution, it is necessary to be able to read a temperature reading below 1°C; to measure the boiling point rise of an aqueous solution, it is desirable to be able to read a temperature reading between 99 and 105°C; and for the determination of the heat of combustion, the mercury column at room temperature indicates that The most suitable temperature is between 2~3°C .
(2) According to the scope of use, estimate the temperature value when the mercury column rises to the elbow at the end of the capillary. For a general Beckmann thermometer, the mercury column rises from the highest point of the scale to the end of the capillary, and it needs to rise by about 2°C. According to this estimated value, the mercury in the mercury bulb is adjusted. For example, when measuring the freezing point depression value of an aqueous solution , it is planned to adjust the indication value of the mercury column on the scale of the Beckman thermometer in water at 1 °C to the highest temperature reading (that is, the indication value is around °C), then the value at the elbow The temperature corresponds to 3°C.
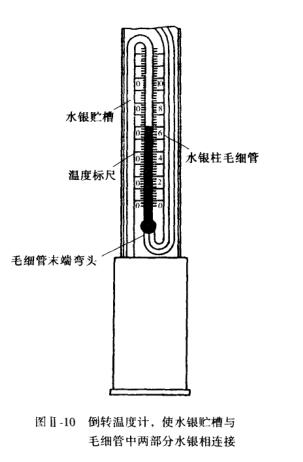
(3) Connect mercury. Immerse the Beckmann thermometer in a constant temperature bath with a high temperature, so that the mercury column in the capillary rises to the elbow and forms a drop at the spherical outlet, then take the thermometer turn it upside down to make it Connect with the mercury in the mercury tank. As shown in Figure 11-10.
(4) Adjust the amount of mercury in the mercury bulb. Use another constant temperature bath, adjust its temperature to the temperature that should be reached by the elbow at the end of the capillary, place the connected Beckmann thermometer in the constant temperature bath, and keep the temperature constant for more than 5 minutes.
(5) Take out the thermometer, hold the middle part of the capillary with your right hand tightly, make it perpendicular to the ground, tap the forearm of your right hand , then the mercury column will be broken at the elbow (this action should be brisk and quick).
(6) Inspection. Put the adjusted thermometer in the constant temperature bath where the temperature is to be measured, observe its reading, and check whether the measurement range meets the requirements. For example, in the experiment of measuring the freezing point depression, it can be checked with an ice-Water Bath at 0°C. If the temperature indication falls between 3 and 5°C, it means that the measuring range is suitable (if the deviation is too large, it needs to be readjusted according to the above steps.
 2. Scale reading adjustment method
2. Scale reading adjustment method
Figure II-l0 Invert the thermometer, so that the mercury reservoir is connected to the two parts of the mercury in the capillary . Those who are more skilled in the operation can use the scale reading adjustment method. This method directly uses the temperature scale on the upper part of the Beckman thermometer without additional adjustment by a constant temperature bath. The specific operation steps are as follows:
(1) Determine the temperature range used.
(2) Estimate the maximum use temperature value.
(3) Connect mercury. Hold the mercury bulb with the palm of your hand (or turn the thermometer upside down), so that the mercury rises to the elbow (if this method does not work, use the Water Bath force heating method used in the above method), then tilt the thermometer to make the storage tank The mercury in it is connected to it.
(4) Adjust the amount of mercury in the mercury bulb. If the estimated value is higher than the room temperature, you can use warm water or invert the thermometer to use gravity to let the mercury flow into the mercury storage tank. When the mercury surface at the temperature scale reaches the required temperature, proceed as in (5) in the above method 1. Cut off the mercury column at the elbow during the process ; if the estimated value is lower than room temperature, immerse the Beckman thermometer in a constant temperature bath with a lower temperature , let it be taken out of the Water Bath in the sink, and immediately cut off the mercury column.
(5) Inspection. with the above method
3. Precautions
(1) The Beckman thermometer is a valuable instrument, so be careful not to place it casually. Generally, it should be placed in the thermometer box, or installed on the instrument shelf.
(2) When adjusting, be careful not to make the quenching ring hot
(3) When placing the adjusted Beckmann thermometer, be careful not to reconnect the mercury in the capillary with the mercury in the storage tank.
 (1) Structural features
(1) Structural features 2. Scale reading adjustment method
2. Scale reading adjustment method


