There are many contents and various treatment methods before painting. When selecting the pretreatment process, it should be selected reasonably according to the actual situation.
(1) Select according to the form and degree of dirt
For cold-rolled steel sheets, the surface has more oil and less rust, so the focus of pretreatment is degreasing, and degreasing can be carried out twice without rust removal; if the oil is mainly saponifiable oil, you can choose a degreasing solution based on strong alkali for saponification Hydrolysis cleaning; if the oil stain is mainly mineral oil, a degreasing solution based on surfactant should be selected for treatment.
(2) Select according to the working environment of the workpiece
If the workpiece is used in a harsh environment, cleaning, phosphating, passivation and other processes can be used to improve the corrosion resistance of the coating; for workpieces used indoors, the requirements for pretreatment can be appropriately reduced.
(3) Select according to the characteristics of the coating
The composition of coatings is different, the binding force with the substrate is different, and the requirements for pretreatment are also different. Perchlorethylene coatings, silicone coatings, etc. have poor adhesion on steel and other substrates, and strict pretreatment is required, especially for effective degreasing. Otherwise, the coating is easy to peel off. For example, epoxy resin primer, polyurethane primer, etc. have strong binding force to steel and other substrates, so the requirements for pre-treatment are low. Rust paint can be painted on a certain amount of rusted substrates.
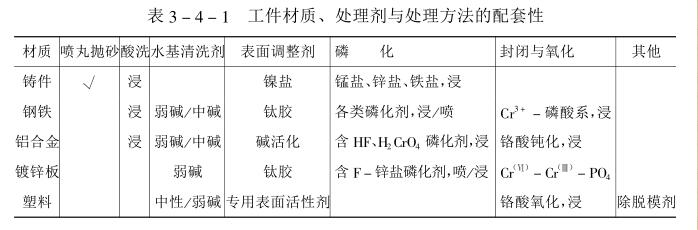
(4) Select according to the material of the workpiece
At present, engineering materials mainly include steel, non-ferrous metals, engineering plastics, etc. The materials are different, and the content and requirements of pretreatment are also different. For example, strong alkaline degreasing liquid can be used for degreasing steel materials, and weak alkaline degreasing liquid should be used for non-ferrous metals. The release agent on the plastic surface is often scrubbed with organic solvents, and for example, the surface of steel is often phosphating, the surface of aluminum alloy is often oxidized, and the surface of plastic is often treated with ultraviolet roughening or solvent etching. See Table 3_4-1 for matching of treatment methods.