There are many factors affecting soil corrosion, among which the main ones are soil porosity, electrical conductivity, dissolved salts, water content, acid mechanical properties and bacteria. The following briefly introduces several factors that have a greater impact on soil corrosion.
(1) Resistivity (conductivity)
The resistivity of soil is directly affected by the size and distribution of soil particles, and at the same time affected by the water content and dissolved salts of the soil. The soil with coarse particles (such as sandy soil) has large porosity. The water penetration ability is strong, and it is not easy to protect water in the soil, while the soil with small particles (such as clay) has poor permeability. The water content in the soil is large, and soluble salts can be dissolved into it and become an electrolyte solution, so the resistance As far as it is small, in most cases, the corrosiveness of the soil can be measured by the resistivity of the soil. Table 4_3_6 shows the relationship between the resistivity and corrosion of the soil.
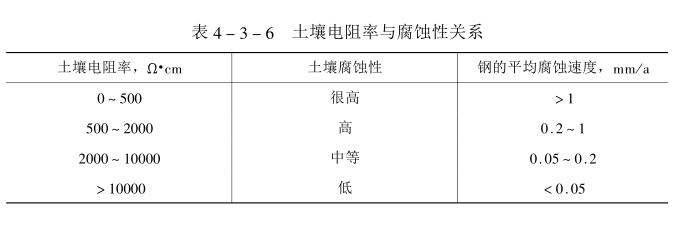
Generally speaking, the resistivity of soil is more than thousands of a cm, and the corrosion to steel is relatively slight. In the low injection land and saline-alkali land with seawater penetration, the resistivity is very low, 100~300 a cm, and its corrosion resistance is quite strong,
(2) Oxygen content
The oxygen content in the soil also has a great influence on the corrosion process, because usually the corrosion of metals in the soil is mainly controlled by the oxygen depolarization of the cathode, and the main effect on soil corrosion is the gap between soil particles. Oxygen, in dry sandy soil, because oxygen is easy to permeate, so the oxygen content is more; in wet and dense clay, because oxygen is very difficult to pass through, the oxygen content is less. If metal pipes are buried in the deep soil, a corrosion battery with uneven inflation may be formed. The pipes in contact with the soil with more oxygen content become the cathode area of the macro cell, while the pipes in contact with the soil with less oxygen content become the anode area of the battery and are corroded.
(3) Acidity (pH value)
The pH value of the extraction solution of most soils is 6-7.5, which is neutral, but the pH value of saline-alkali soil is 7.5-9.5, and the pH value of acidic soil is 3-6.
It is generally believed that the soil with a low pH value is more corrosive, because under acidic conditions (pH<4), the corrosion of steel may proceed according to the hydrogen depolarization process, that is, H2 is generated at the cathode.
(4) Bacteria
Sulfate is contained in the soil, such as under anaerobic conditions, anaerobic bacteria, sulfate-reducing bacteria, will multiply, and its activities will promote corrosion of nearby steel components.
Sulfate-reducing bacteria need hydrogen or some reducing substances in the process of life to reduce sulfate to sulfide, and the bacteria themselves use the energy of this reaction to reproduce.
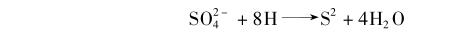 ,
,
On the surface of iron and steel components buried in the soil, if hydrogen gas is generated during the cathodic process of corrosion, the activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria will be promoted, and the result of the activity will consume the hydrogen on the steel surface and accelerate the reproduction of the bacteria themselves. In this way, the corrosion of steel is also accelerated.
The S 2 -high son produced after sulfate reduction can combine with Fe 2+ high son to form black FeS. Therefore, when sulfate-reducing bacteria are active, the corrosion products produced on the steel surface are not rust-colored, but black.
