According to the drying method in the curing process of the coating film, it can be divided into three categories: natural drying, drying and radiation curing.
(1) Natural drying
Under natural conditions, use air convection to evaporate the solvent, oxidatively polymerize, or react with the curing agent to form a film. It is suitable for self-drying coatings such as volatile coatings, air-drying coatings, and curing agent-curing coatings. Their drying quality is affected by environmental conditions. great influence.
When the ambient humidity is high, solvent volatilization is inhibited, and drying is slow, causing defects such as whitening of the coating film; when the temperature is high, solvent volatilization is fast, curing reaction is fast, and drying is fast, which is beneficial to reducing dust on the surface of the coating film, but may make the leveling property worse . When the ambient temperature is too high , an appropriate amount of moisture-proofing agent should be added to the paint.
Therefore, in the natural drying area, it is better to set up an air conditioning system and an air filtration system to ensure the quality of the coating.
(2) drying
Drying is divided into low temperature drying, medium temperature drying and high temperature drying. Curing temperature lower than 100°C is called low-temperature drying, which is mainly used for forced drying of self-drying coatings or drying of coating films on the surface of materials with poor heat resistance. The drying temperature is usually 60-80°C to make self-drying The curing time of the paint is greatly shortened to meet the industrial production line.
Medium temperature drying temperature is 100~150℃, mainly used for condensation polymerization reaction curing film-forming coatings. When the temperature is too high, the coating film will turn yellow and the brittleness will increase. The best curing temperature of this type of coating is generally between 120 and 140 °C.
Curing temperature above 150°C is high temperature curing, such as powder coatings, electrophoretic coatings, etc.
According to the heating and curing method, drying can be divided into three methods: hot air convection, thermal far-infrared radiation, and hot air convection plus radiation.
Hot air convection curing uses a fan to introduce the combustion gas or heated high-temperature air generated by the heat source into the drying chamber, and circulates in the drying chamber, so that the coated object is heated by convection. The convection drying chamber is divided into a direct combustion heating type and an indirect heating type using a heat exchanger.
The hot air convection heating is uniform and the temperature control precision is high. It is suitable for high-quality coatings and is not affected by the shape and structure complexity of the workpiece. The heating temperature is limited, so this method is widely used. However, the heating speed of this method is relatively slow, the thermal efficiency is low, the equipment is huge, the floor area is large, and the dustproof requirements are high. The temperature of the coating gradually increases from the outside to the inside, and the surface is cured first. When the internal solvent volatilizes, it is easy to cause pinholes in the coating. , Bubbles and wrinkling and other ills.
The heat sources used include steam, electricity, diesel, coal gas, liquefied petroleum gas and natural gas. The heat source should be selected according to the curing temperature, the quality requirements of the coating, the curing temperature, local resources and comprehensive economic effects. The usage range of commonly used heat sources is shown in Table 6-1.
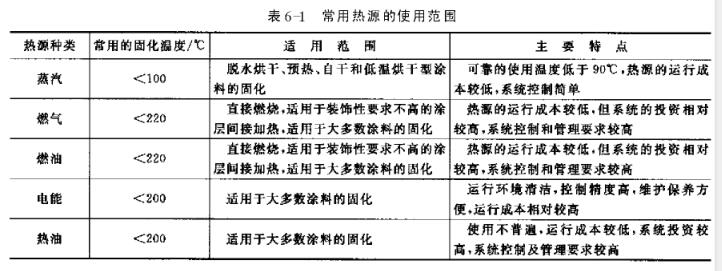
Electric heating devices include far-infrared Electric Heating Plates, far-infrared electric heating belts and far-infrared heating lamps, etc., which are easy to install, easy to debug, and easy to maintain and manage. Fuel is cheap, but the atomization effect of fuel directly affects the quality of heating. A few days ago, the quality of domestic fuel atomizers was not satisfactory, resulting in insufficient oil combustion. Gas is simpler than fuel oil, especially in northern my country, where natural gas resources are abundant, so it is a more satisfactory heating method.
Thermal radiation heating usually uses infrared and far-infrared rays to radiate to objects, directly absorb and convert them into heat energy, so that the substrate and coating can be heated at the same time, the heating speed is fast, the thermal efficiency is high, and the solvent vapor is naturally discharged without a large amount of circulating air. The quantity is reduced, the coating quality is high, the drying chamber is short, and the floor space is small. However, the temperature is not easy to be uniform, and it is only suitable for workpieces with simple shapes.
The wavelength range of infrared rays is 0.75~1000µm, of which the wavelength is 0.75~2.5µm is near infrared, the radiator temperature is about 2000~2200℃, and the radiation energy is very high; the wavelength is 2.5~4µm is mid-infrared rays, and the radiator temperature is 800 ~900°C; the wavelength greater than 4µm is far infrared, the temperature of the radiator is 400~600°C, and the radiation energy is low. Although the energy of far-infrared rays is low, the molecular vibration wavelengths of organic matter, water molecules, and metal oxides are all above 4 μm, that is, in the far-infrared wavelength region, these substances have strong absorption peaks. Under far-infrared radiation, molecules The vibration is intensified, the energy is effectively absorbed, and the coating film is cured quickly.
In order to improve the heat radiation and absorption efficiency and ensure the coating quality, when using far-infrared radiation for heating, it is necessary to pay attention to the matching of the absorption capacity of the coating and the radiation wavelength. Near-infrared rays only produce electronic vibrations, and a thin layer of 1µm on the metal surface will absorb it, while a thin layer of 0.1µm coating film will absorb all far-infrared rays. Therefore, far-infrared radiation curing can make the metal surface and the entire coating absorb radiation and convert it into heat energy at the same time, so that the coating film can be effectively cured and the metal will not be heated as a whole.
However, the energy of far-infrared rays is low. In many cases, the Pu curve of far-infrared radiated light and the Pu curve of paint absorption light do not achieve a good match. Experiments have proved that the matching effect of radiated light 1,P and absorbed light 1,P is not only related to the wavelength, but also related to the energy of radiated light. In the short-wavelength range, the domestic high-temperature radiation element, as the temperature continues to increase, the matching effect is also continuously improved, reaching the highest thermal efficiency. At this time, the radiation is full-band, which belongs to high-density and powerful infrared radiation, and this radiation heating is called high infrared radiation heating.
The heat source of the high infrared radiation element is tungsten wire, and the temperature is as high as 20~2400℃, which radiates short-wave high-energy infrared rays; the heat source is a single quartz tube, with an external temperature of about 800℃, which radiates medium-wave infrared rays; the backside directional reflective screen, the temperature can reach 500~600℃, radiate low-energy far-infrared rays. The proportion of infrared components in each band is not equal, so that it has a good energy matching for the absorption of the heated object, and it is accompanied by a fast thermal response characteristic.
High-infrared quartz tube specifications are divided into ∅12mm and ∅20mm, the length is 1.0m, 1.2m and 1.5m, the power is 3~5kw, and the service life is more than 5000h. The surface power of the high-infrared heating element is 15-25kW/crn2, and the start-up time is only 3-5s (the surface power of the far-infrared element is 3-5kW/cm2, and the start-up time is 5-10min), and the thermal inertia is small. Therefore, the characteristic of high infrared heating is instant rapid heating to drying temperature.
For the transparent quartz tube heating element, the infrared rays produced by the tungsten wire 2 at 0°C almost all pass through the quartz glass and radiate directly to the outside. The energy near-infrared rays will penetrate the coating film and directly heat up the substrate. Heating from the inside to the outside makes the solvent in the coating film evaporate and escape faster. The heating time (about ten minutes) is greatly shortened. Therefore, high red line heating is a new type of heating method, which has a wide application prospect.
Hot air convection and radiation heating have their own characteristics. In order to give full play to their respective advantages, they can be combined in the design of the drying room, that is, radiation plus convection. Generally, radiation is first followed by convection, and the advantage of fast heating of radiation is used to heat up the workpiece and volatilize the solvent, and then use hot air convection to keep warm to ensure the drying quality.
No matter what kind of heating method is used, during the entire curing process of the coating in the drying chamber, the temperature of the workpiece coating changes with time, which can be divided into three sections, namely, the heating section, the heat preservation section and the cooling section. The relationship between curing temperature and time is called the
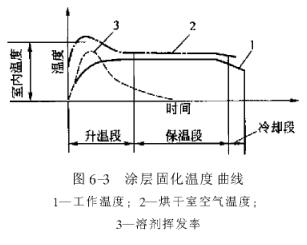 Curing curve, as shown in Figure 63.
Curing curve, as shown in Figure 63.
The coating rises from room temperature to the required drying temperature as the heating period, and the time required is the heating time. During this period, a large amount of heat is required to heat the workpiece, and most of the solvents evaporate rapidly during this period, so it is necessary to strengthen ventilation during this period to remove solvent vapor and add fresh air. The heating time is selected according to the boiling point of the paint solvent. The boiling point is high, and the heating time should be short (that is, the heating speed is fast) to accelerate the volatilization of the solvent. However, if the heating rate is too fast, the solvent will evaporate unevenly, and the coating may have defects such as orange peel. If it volatilizes slowly, the coating quality will be good, but the production efficiency will be low and the operating cost will increase; the solvent has a low boiling point, and the heating time should be long, so as to prevent the defects of the coating caused by the solvent boiling. Generally, 90% of the solvent in the coating escapes within 5-10 minutes, so the heating time is generally within 5-10 minutes.
After the coating reaches the required drying temperature, the extended time is called the holding period, and the required time is the holding time (ie, drying time). During this period, the coating is mainly used to form a film by chemical action, but a small amount of solvent is also evaporated, so not only heat is needed, but also fresh air is needed, but the amount required is less than that in the heating section. The length of the heat preservation time is selected according to factors such as the coating material, coating quality requirements and drying method. The specific data can refer to the information provided by the supplier, or can be determined through experiments.
The coating temperature begins to drop from the drying temperature. This period is called the cooling time, which generally refers to the exit area of the drying chamber. The temperature of the drying chamber is generally several tens of degrees Celsius lower than the drying temperature. For the situation where the workpiece is sprayed immediately after drying (generally, the temperature of the workpiece is not higher than 40°C), a forced cooling section is required after the drying chamber.
(3) Radiation curing
Radiation curing is a new curing method that utilizes electrons and ultraviolet radiation to cure coatings and UV coatings. It has the advantages of short curing time (several seconds, tens of seconds to several minutes), normal temperature curing, and relatively low device price. However, there are blind spots in the irradiation, and it is only suitable for workpieces with simple shapes, and the height of the irradiation distance is strictly controlled.
