 The single-pan balance has the characteristics of easy operation, high weighing rate and stable performance.
The single-pan balance has the characteristics of easy operation, high weighing rate and stable performance.
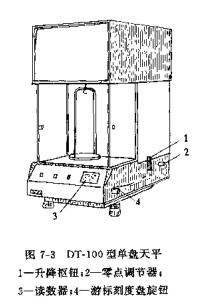
The beam of the single-pan balance is divided into two structures: unequal arms and equal tubes, and the common one is the single-pan balance with unequal arms. Its structure is more complex than the double-disk balance, but it has fewer failures. Taking DT-100 single-disc balance as an example to briefly introduce its working principle and operation method. Its appearance is shown in Figure 7-3.
(l) Weighing principle of single-pan balance
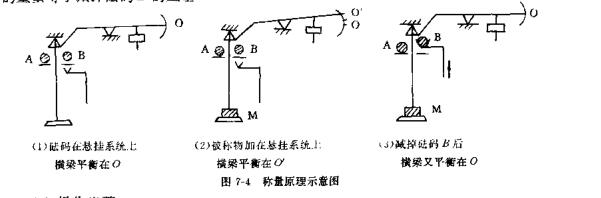
The weighing of the single-pan balance is based on the substitution method principle. The accumulator beam of the single-pan balance has only one fulcrum knife and one load-bearing knife, and the inner connection code and the object to be weighed are in the same suspension system. After opening the balance, the accumulating beam is stably balanced at a certain position. When the object to be weighed is placed on the weighing pan, the suspension system sinks due to the increase in weight, and the beam changes the original balance position. In order to maintain the original balance position of the beam, It is necessary to subtract a certain amount of built-in French codes in the suspension system until the beam returns to the original equilibrium position. The mass of the object to be weighed on the weighing pan replaces the quality of the included connection code that is subtracted from the suspension system, then the reduced quality of the included connection code is equal to the mass of the object to be weighed, as shown in Figure 7_4. The weight of the object M to be weighed is equal to minus the weight of the code 9.
(2) Operation steps
Turn on the power, turn the mechanical subtraction code to the zero position, so that the reading window shows a value of 00.0 (see Figure 7-5), and align the zero position of the micro-reading device with the reading mark. After turning on the balance, if the zero point of the micro-marker is not in the middle of the reading double line, turn the zero-adjustment collar; if the requirement is still not met, then close the balance, open the top difference of the balance, adjust the balance energy, and adjust the zero-point position of the micro-marker.
When the double line of reading is between the two divisions of the differential sign, the micro-reading knob can be turned so that a certain engraved line of the differential sign is between the double lines of reading and the reading of the micro-reading mechanism can be read.
After weighing the results, clean the balance, close the side door, restore all the reduction collars to zero, cut off the power supply, and put on the dust cover.
