The measurement principle of the potentiometer is very similar to that of the balance, and it uses the "zero" value method for measurement, as shown in Figure 9-33. R in the figure is a precision resistor with high linearity, its resistance value does not change with temperature, and the current I flowing through it is constant, so the potential difference generated on R is uniformly distributed, standard, and quite Magnetic code on the balance. G is the galvanometer, which is equivalent to the zero pointing device of the balance. Ex is the unknown voltage to be measured (such as the thermoelectric potential Et to be measured). When measuring, adjust the position of point d. When the pointer of the galvanometer points to zero , indicating that the unknown voltage is equal to the known potential difference vb. By hand, these two voltages are in opposite directions and synchronized with each other, so the galvanometer points to zero. When balanced, their relationship is:
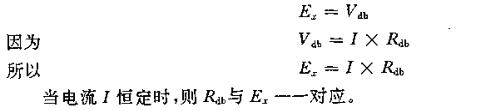
From the above simple analysis, it can be seen that the significant advantage of applying the zero-value measurement method is: since there is no current flowing in the galvanometer when the measurement reading is performed, the size of the external connection resistance has no effect on the reading, and This enables accurate measurement of weak potentials without consuming the energy of the measured object. The accuracy of the measurement results mainly depends on the accuracy and stability of the manual operating current I and the internal sliding wire resistance r of the meter. In order to keep the working current of the manual potentiometer constant, a standard battery En, a standard resistance RN and a potentiometer Rn for adjusting the working current are added to the internal circuit of the meter, as shown in Figure 9-34. When measuring, follow the following two steps:
① Calibrate the working current: close the switch K to the "l" position, adjust the potentiometer R1, and make the galvanometer indicate zero, that is, make the working current s make the voltage drop of the working current I on the standard resistance RN equal to that of the standard battery The standard potential En is equal, that is:

