There are many types of Air Compressors, which can be divided into two categories according to their working principles: positive displacement compressors and speed compressors. In the volumetric compactor, the increase of gas pressure is formed by reducing the volume of gas in the sub-compressor, which increases the density of air molecules per unit volume. In the speed compressor, the pressure of the air is converted from the speed of the air flow, that is, the air gets a high flow speed first, and then a part of the speed can be further converted into the pressure energy of the gas in the fixed element.
According to the structure type of the compressor, it can be classified as follows:
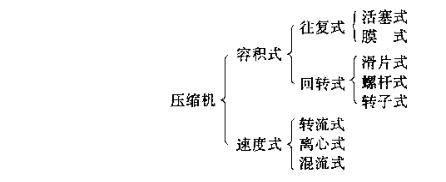
The compressor used to compress air is widely used for small and medium flow, piston Air Compressor, and for large flow, centrifugal Air Compressor is mostly used.
Classification of small and medium piston Air Compressors:
Small and medium-sized plug-clearing Air Compressors are often classified according to the following principles according to their structural forms, and named according to one or more of the classification methods.
1. According to the mutual aesthetic system of the distribution of the air-axis axis, the commonly used ones are L-type, V-type, W-type, bedroom type, vertical type, symmetrical balance type, etc. This section only introduces widely used L, V and other types of compressors with better inertia force and flat street performance.
2. There are two types of cooling methods: water-cooled (water-cooled) and air-cooled (air-cooled) based on the compressor cylinder sleeve and stage gas cooling. Where the compressor is required to run continuously and the ambient temperature of each installation is high, the water-cooled type should be used, otherwise the air-cooled type can be considered.
3. According to the compression times experienced by the compressed gas to the final discharge pressure, it is divided into single-stage, two-stage or multi-stage. Generally, low-pressure air compactors (discharge pressure 0.7~0.8MPa) are mostly two-stage, and those with small displacement (<3m 3 /min) and low discharge pressure (<0.8MPa) adopt single-stage compression.
4. According to the type of prime mover driving the compressor, it is divided into two types: electric (electric motor drive) and diesel drive (diesel engine drive). Diesel-powered can be used in areas lacking power supply.
5. The number of inhalation or exhaust completed by the piston reciprocating once in the cylinder is divided into single-acting (the piston reciprocates once to complete one inhalation and exhaust) and double-acting, also known as single-acting and double-acting.
6. According to the lubrication method of the transmission parts of the compressor, it is divided into splash type and pressure type, and the cylinder part is divided into oil lubrication and oil-free hole lubrication. Generally, the pressure type lubrication method is used for the large displacement and continuous operation, and the oil-free lubrication type is suitable for the production that requires the compressed air to be oil-free.
7. According to whether the compressor can move during use, it can be divided into mobile type and fixed type.
8. In the product series, it is often divided into small and medium-sized and large (divided by displacement) and low pressure (exhaust pressure 0.7~0.8MPa gauge pressure) and medium and high pressure ( Exhaust pressure is greater than 1Mla gauge pressure), etc. The expression method of the product model has not been unified, and it is generally expressed by the combination of main indicators such as cylinder layout, displacement and final exhaust pressure. For example, V-0.6/7 type indicates that the cylinder arrangement is V type. The displacement of the compressor is 0.6m 3 /min, and the final exhaust pressure is 0.7MPa (gauge pressure).







