During the experiment, the mercury thermometer is often only inserted into the object to be measured for a certain depth, and a certain section is exposed. Strictly speaking, the temperature measured only when the thermometer is fully immersed in the object to be measured is accurate, because the thermal expansion coefficient of the upper table note is different from that of the glass capillary, so the measured temperature is lower than the real temperature. The error can be corrected with the following difference according to the scale range of the thermometer: when the difference between the corrected value of the exposed mercury injection is below 100°C, it is 1°C; The higher the temperature, the larger the correction value for this error. To get more accurate temperature, you can correct it according to the following formula:

In general, standard thermometers are commonly used to calibrate ordinary thermometers, and the method is simple: align the balls of the two thermometers, put them together in a hot bath, raise the temperature slowly, and record the two temperature counts at intervals at the same time. Then slowly lower the temperature, and record the values of the two thermometers at the same interval as before. Draw heating and cooling curves. Once the two curves are completely coincident, the curve can be used to read the temperature accurately.
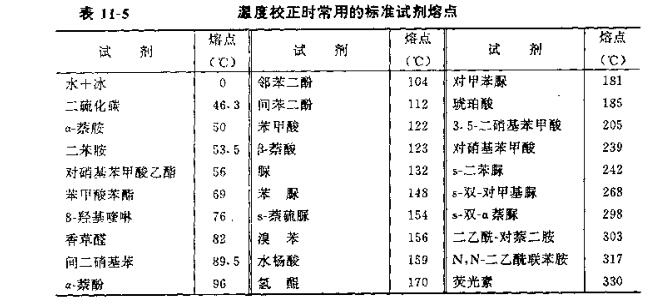
Table 114 lists the commonly used liquid thermometer temperature range.
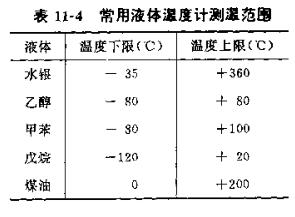
Table 11-5 lists several standard substances (high purity or reference reagents) with different melting points, and the thermometer can be calibrated by determining the melting points of these substances.