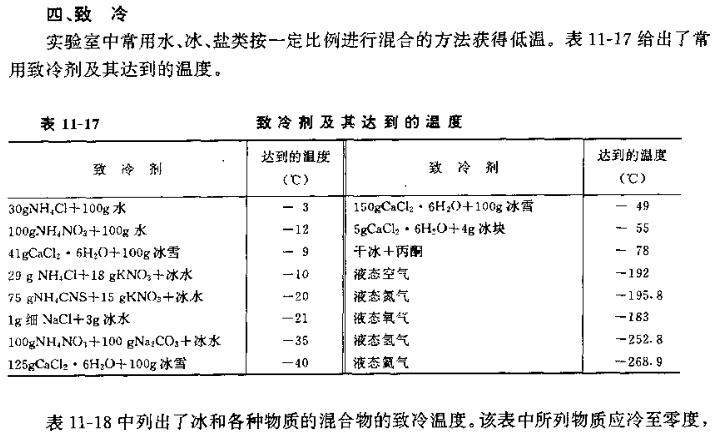
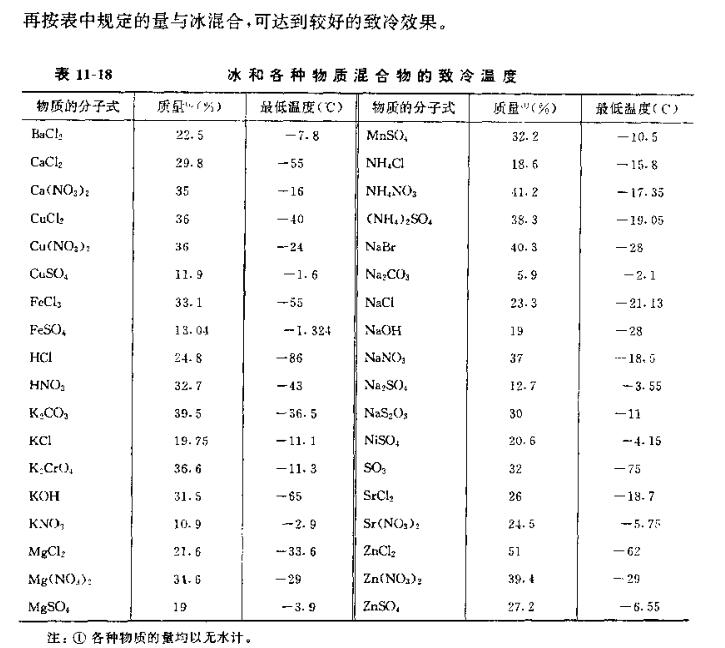
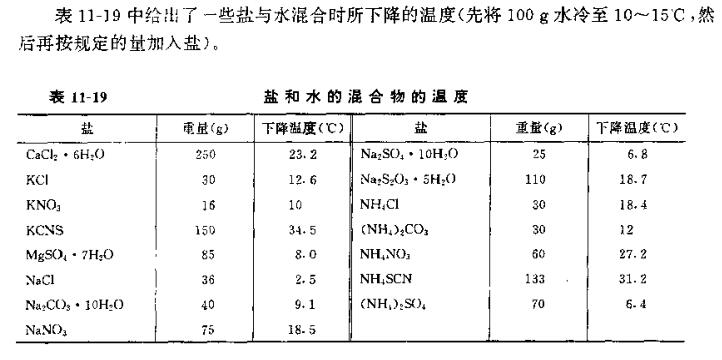
According to the requirements of various chemical reactions in the laboratory, different heating methods and different temperature ranges are often required, and sometimes different degrees of cooling are required.
1. Ignition temperature of commonly used heat sources
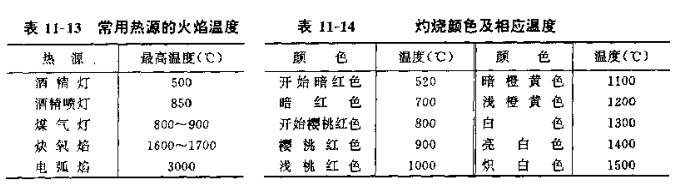
The flame temperature of commonly used heat sources is shown in Table 11-13, and the temperature is estimated according to the burning color (see Table 11-14).
2. The maximum heating temperature of laboratory electric furnace and oven
Muffle furnace: platinum wire heating 1050 ℃; nickel chromium wire heating 800~900 ℃;
Tube furnace: platinum wire heating 1300℃_; nickel-chromium wire heating 900~950℃;
Crucible furnace: platinum wire heating 1100 ℃; nickel-chromium wire heating 850~900 ℃;
Silicon carbide rod high temperature furnace: 1350℃;
Granular carbon (resistance) furnace: 1800°C;
High frequency induction furnace: 2300℃;
Electric heating wire oven: 100~300℃
Far-infrared oven: 200°C.
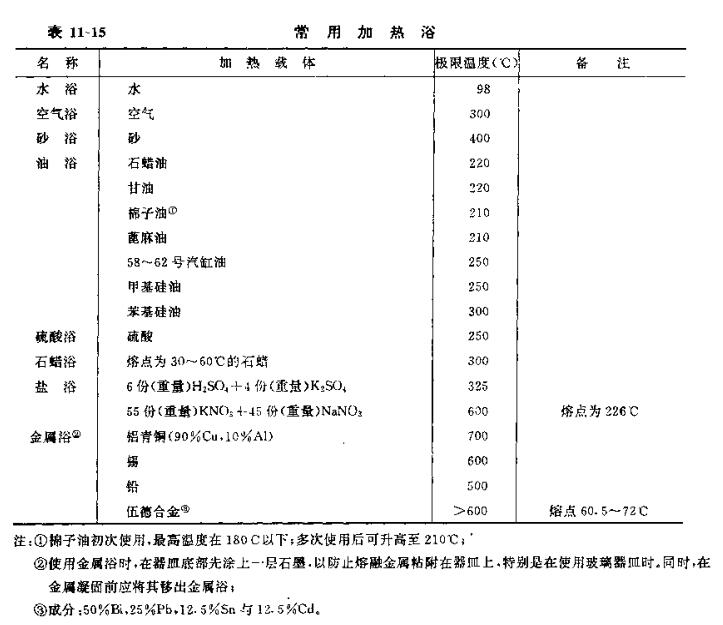
Three, commonly used heating bath
Table 1l-15 lists various heating materials and their limit temperatures, and Table 11-16 gives the properties of the liquid medium used in the heating bath.