Baking oven is one of the equipment required in powder coating. According to the curing characteristics of powder coatings, it is divided into two types: heat curing and UV light curing, and the drying equipment used is also divided into two types. For heat-cured powder coatings, after spraying, they cannot form a coating film as the solvent volatilizes like solvent-based coatings, but only form a loose coating. Only after baking can melt leveling or cross-linking solidify into membrane. For thermoplastic powder coatings, it only needs to be melted and leveled to form a film. For thermosetting powder coatings, it must be cross-linked and cured to form a film while melting and leveling. Therefore, the powder coating after spraying can only be baked at a certain temperature for a certain period of time to ensure the formation of a good coating film. Most of them need to be cured at a temperature of about 180 ℃ for 20 minutes (including the melting and leveling process). The time requirement for curing is very strict, and it is necessary to start timing after the temperature of the coating film of the workpiece reaches the specified temperature. If the time is too short, the curing of the coating film will not be complete, and the properties of the coating film, especially the mechanical properties, will deteriorate. In order to ensure the drying time and temperature, the length of the drying channel in the drying equipment of the production line needs to be tens of meters long.
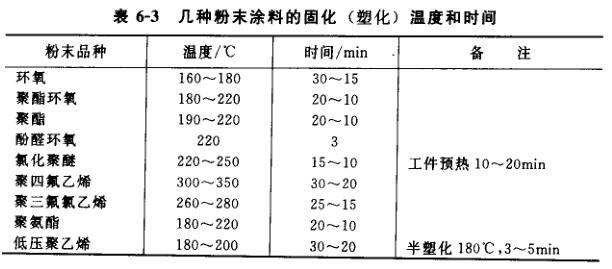
See Table 6-3 for the curing temperature and time of commonly used powder coatings. In addition to strictly ensuring the baking temperature and time during baking, sufficient gaps and distances between workpieces should be kept in the oven-type drying tunnel to ensure smooth convection of hot air, while avoiding mutual contact and damage to the coating film.
1. Thermal curing oven
(1) configuration
At present, there are three main configurations of thermal curing baking furnaces used in powder coatings: bridge type, tunnel type and Cabinet-type. The first two are suitable for automatic spraying production lines, and the box-type oven is suitable for intermittent production. The structural diagrams of the three baking ovens are shown in Figure 6-33.
1. Bridge type oven
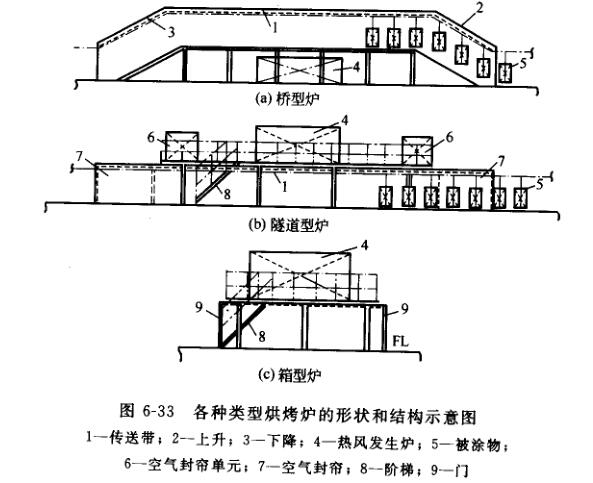
After being designed as a bridge structure, because the hot air is lighter than the cold air, it is not easy to form convection between the hot air in the furnace and the cold air outside the furnace. When the coated object enters the baking furnace, the heat loss in the furnace is small, and the temperature of the furnace Good insulation effect. The disadvantage of this kind of baking oven is that the space occupied by the furnace body is large, and when the shape of the object to be coated is complex, the distance between the hangers is not suitable. When the hangers go up or down, the objects to be coated are prone to collision and adhesion And affect the quality of coating products.
2. Tunnel oven
This type of oven takes up less space than a bridge oven, and the product quality is not affected by the complex shape of the workpiece and the distance between the hangers. However, it has the disadvantage that the hot air in the oven and the cold air outside the oven are prone to convection, and the heat loss in the oven is large. Therefore, air curtains are installed at the entrance and exit of the coated object in this type of oven to prevent convection. occurs, reducing heat loss.
3. Box type oven
Its structure is relatively simple, and because of its good airtightness, it is equipped with a blast system to stir the air in the furnace to make the air convective, so it has the advantage of relatively uniform temperature distribution in the furnace, but it is not suitable for continuous automatic production, so it is only suitable for For small amounts of drying.


