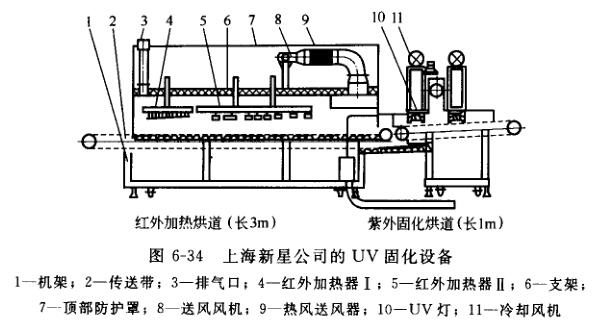
The UV curing furnace structure is shown in Figure 6-34. It is a combination of a melt leveling infrared section and a UV curing section. In order to form the two parts into a whole, when the two sections of the drying tunnel have independent conveyor belts, the two sections of the drying tunnel are connected by the heat preservation section. Smooth transition to the UV curing section on the conveyor belt to complete the UV curing process.
1. The heating method of the infrared section
The working purpose of the infrared section is to melt and level the powder coating, and the heating method is a combination of infrared radiation and convective hot air. The first step uses infrared strong radiation heating to make the powder melt quickly; the second step uses infrared convective hot air to further melt and level the powder; the third step uses convective hot air to fully level the powder on the surface of the workpiece. The infrared heating device is shown in Figure 6-35.
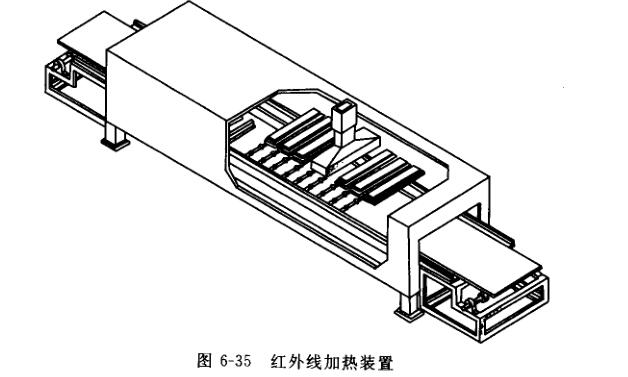
Infrared heating elements usually use mid-band infrared lamps. This is because for many materials, the infrared absorption range is 2~3.5µm, and the maximum emission wavelength of the medium-wave infrared lamp is 2.4~2.7µm, so it is most effective to use it as a radiation heating element. In order to achieve a better leveling effect, the medium-wave infrared lamp tubes are densely distributed at the entrance of the drying section, the middle section is scattered, and the convective hot air is sent to the end of the drying tunnel. The horizontal arrangement in the vertical direction of the length is conducive to the uniform heating of the coating film.
2. UV curing section
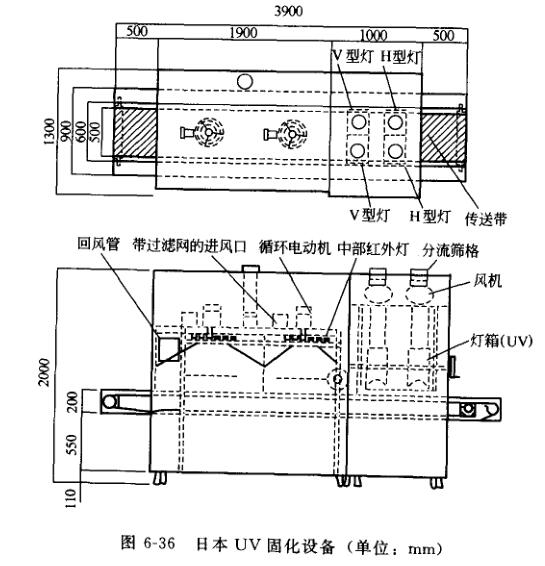
Arrange UV lamps that emit ultraviolet rays in the UV curing section. The lamp width is 250mm, the power reaches 240W/cm, and the light intensity can be adjusted within the range of 0~100%. The structure of a Japanese UV curing equipment is shown in Figure 6-36.