A centrifuge is an instrument widely used in medical laboratories to complete sample separation and analysis techniques. Due to the different technical positioning or different experimental purposes of each laboratory, there are also large differences in the technical function configuration requirements of the centrifuge. In practice, there are many examples of unreasonable function configuration configuration and unsuitable resource waste. Therefore, it is of great significance to explore the relationship between its application requirements and functional configuration in equipment configuration management.
1 Centrifugal technology and general laboratory centrifuges
Centrifugation is under the action of centrifugal force, using the sedimentation coefficient, buoyancy, and density difference of the centrifuged sample material to separate, concentrate, extract and prepare, analyze and determine the molecular weight and purity of biological macromolecules.
1.1 Centrifugal technology
The design principle of the centrifuge is to use the centrifugal field force generated when the rotor is driven to rotate to accelerate the sedimentation velocity of the sample particles, and to separate the substances with different sedimentation coefficients or buoyant density differences in the sample. In addition to the rotational speed (Revolvedperminute, r/min or rpm) and the radius of the centrifugal (rotor head), the factors that determine the size of the centrifugal force are also related to the influence of the force (gravity, buoyancy, friction) on the particle during the rotational motion, such as Figure l shown. The direction of the centrifugal force is perpendicular to the gravity, so it is often expressed by relative centrifugal force (Relative centrifugal force, rcf), that is, the centrifugal force acting on the rotating particles relative to the gravity, and the gravitational acceleration g (980cm/s2) is used as the value, also known as "g-Force ”, the expression is: RCF=ω2r/980. The key to using centrifugation technology is how to determine the settings of centrifugal force, rotational speed and centrifugation time according to the properties of sample particles and media and the technical parameters of the rotor. The rate of sedimentation or separation of particles (collectively termed cells, organelles, and macromolecules) depends on centrifugal force, the size, shape, and density of the particles, and the density and viscosity of the settling medium. According to the working mode of the centrifuge, the technology realized can be divided into centrifugal filtration, centrifugal sedimentation (or clarification) and centrifugal separation [1].
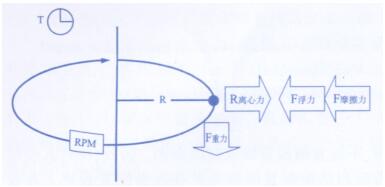
Figure 1 Generation of centrifugal force
1.2 General laboratory centrifuge
In recent years, a class of models known as Universal Laboratory Centrifuges (Universal laboratory centrifuge) has entered the medical laboratory. The so-called "universal" is that it takes into account the performance of low-speed machine and high-speed machine, trace volume and large capacity, and is small in size, light in weight, low in power consumption, and easy to operate; the maximum speed of common models is ≥15000r/min, and the maximum rcf can generally be It can reach more than 20000×g, some models reach ≥60000×g, and the maximum centrifuge capacity is ≥3000ml. The performance complies with the needs of conventional separation and preparation technologies in molecular biology, cell biology and other related fields.
通用实验室离心机在结构上与高速机基本相同,但为实现其通用性能可谓浓缩了近代离心机制造方面的高新技术:⑴驱动系统采用无碳刷变频电机取代了直流串激电机,在不同转速都能输出最大扭矩,为开发一机多功能型的通用离心机提供了重要前提;低噪声,免除了碳刷摩擦产生的高频噪声,不需要安装在专门房间;且因无碳粉污染,还可在特定样品分离要求的无菌、无尘实验室内使用;起动速度快;整机体积、重量和功耗减小,故大多制作成台式机型。⑵离心转头,不同技术性能的转头代表着离心功能,通用离心机所配置的转头充分体现了当代离心技术的特征;主要可概括为采取计算机三维计算优化设计,具有体轻、转速高等优点;碳纤维制造高速转头,容量大、重量轻、耐腐蚀性能强;开发出大离心力转头,缩短了某些难以分离生物样品的分离时间,减少了浓度扩散作用,提高了分离纯度和分辨率;角转头采取小倾角设计,兼有垂直转头沉降距离小、纵剖面面积大、分离时间短的优点,尤其适于质粒DNA、RNA分离;多样式,每管位容量覆盖0.2 ̄750ml,除角转头外,还有水平(含微量高速水平转头)、鼓式、区带、微板、涂片等转头。⑶控制和显示,采用微处理机控制,自动转头识别;可设置rpm和rcf,并实时显示实际值,减少了计算麻烦;多档设置的升速/降速控制;瞬时离心控制;自检和故障提示。⑷安全性,如电子盖锁、超温、过速、失平衡保护等,一旦发生误操作或故障将发出提示声音报警。⑸控温系统,低温控制机型多为一级压缩机无氟制冷,控温范围一般在﹣9℃(或﹣20℃)~+40℃,精度≤1℃;具有预冷程序、待机状态可恒冷维持功能,以适应实验室机动性、连续性工作需要。
2装备应考虑的主要问题及功能配置
General-purpose laboratory centrifuges may go deep into every technology- related laboratory, and it is a potential development market, which should attract great attention from equipment management. On the premise of clarifying the technical orientation of the laboratory, the primary and secondary technical requirements, and the corresponding centrifugation methods, the rotor type, maximum rcf, rpm, sample volume, etc. are the basic parameters for selecting centrifugation technology. On this basis, the selection of centrifuges should be considered. Type, main function and configuration of both functions.
2.1 Functional requirements of conventional centrifugal technology in medical laboratories
2.1.1 RNA preparation by centrifugation
After the cultured cells were centrifuged at a low speed (horizontal rotor, 300×g) to complete cell separation and lysis, the RNA precipitation extract was added, at 4°C, 10,000-12,000×g (angle rotor, trace 1.5/2.0ml Eppendorf tube, or ≥15ml, 50ml tube) step-by-step extraction; tissue samples need to be pretreated with homogenate[2].
2.1.2 DNA preparation by centrifugation
Rotate the head horizontally, about 2000×g (1.5/2.0ml Eppendorf tube, 15ml, 50ml conical bottom tube or larger volume); and then 12000~27000×g. Preparation of plasmid DNA: Angle rotor, 250ml or 500ml/bottle, 5000-6000×g; 15-50rnl/tube, 12000-27000×g; 4°C or specific temperature.
2.1.3 Separation of vector-expressed proteins
Angle rotor, 250-500ml/bottle, 4000×g; 15-50ml conical bottom tube, 3000×g; angle rotor, 50ml tube/bottle, 27000×g; 4℃.
2.1.4 Cell purification and subcellular organelle isolation
Differential centrifugation is used to separate cell organelles and cells with disparity in size [3]. Step by step from low speed to high speed centrifugation, the sedimentation order of cell organelles is nucleus, mitochondria, lysosome, peroxisome, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosome, and the temperature of all processes is controlled at 4°C. Cell collection: horizontal rotor, 850-1850×g, preferably conical bottom tube; separation of nucleus and cytoplasm, 3300×g; nuclear extraction, 25000×g. Further purification and separation will be combined with ultracentrifugation. The density gradient velocity sedimentation method separates cells or organelles with similar densities but unequal sizes. Use a suitable density gradient medium, and turn the head horizontally at 100-900×g. Separation of organelles by isopycnic gradient method, 10000-30000×g.
2.1.5 Cytological smear centrifugation
In addition to special cell smear centrifuges, cytology smear centrifugal rotors can be configured on individual laboratory centrifuges to achieve centrifugation of ≥4 pieces at a time. According to cytological characteristics, rcf was controlled at 50-1000×g. When purchasing, pay attention to whether the sample throughput of the centrifuge container meets the purpose of the experiment.
2.1.6 Centrifugal ultrafiltration, concentration, extraction
Cooperate with commercially available centrifugal filter concentration tubes (1.5-80ml, Coming, Millipore, Spectrum, etc.) or sample extraction containers, using angled or horizontal rotors, the angled rotor can make the ultrafiltration membrane and centrifugal force not at right angles Avoid concentration polarization; ranging from 1000 to 12000×g, please refer to the instructions of the purchased container.
2.1.7 Microplate centrifugation
Centrifugation of enzyme plate, TC plate, PCR plate and sample extraction and purification plate . In a general centrifuge, it can be realized by configuring a microplate hanger on a large-capacity horizontal rotor (rcf will generally be lower than the rated value of the rotor) or using a special centrifugal rotor for microplates, about 1000×g. Each hanger can hold 1-4 standard 96-well plates or more, and there are also centrifugal adapters that can double as slides
2.2 Model selection and function configuration evaluation
General-purpose laboratory centrifuges still have large differences in performance and price . In order to save resources, it is suggested that in the practice of equipment, the function configuration and application requirements should be related and appropriate.
2.2.1 Two-way functional decomposition evaluation of functional configuration and actual demand
实验室离心制备小样本RNA常用的功能参数是:容量1.5/2.0m1/管,最大rcf≥10000×g。表1列出4种可供选择的通用离心机功能配置方案(A,B,C,D),投入成本依次递增有较大差别,配置功能与需求功能达到适时一致,将是资源配置的很好的结果。如果装备对象仅以小样本制备为主选择方案A即可满足,兼顾细胞学工作还可选择B,当然如2项技术的使用率均较高也可采用分别单一功能配置。
2.2.2注意各实验室间的资源共享
方案C或D的选择,需要对实验室的性质以及对各项扩展功能的权重做出进一步的评估。另外,一个卫生单位内如有多个实验室不同程度地涉及到某(些)种功能,但利用率均不高,要注意资源共享,研究功能配置的数量、搭配及管理等问题。对特殊离心功能配置如大容量离心转头、鼓式转头等,可考虑装备在能公共利用的地点专管共用或实行借用。
表1医学实验室样品制备离心机的选择及功能配置

2.3其它配置评估因素
在完成功能需求配置评估的基础上,还要According to实验需求及实验室的具体情况在器材的选择上考虑以下因素:
2.3.1转速与离心力
要对离心机的综合性能做出全面评估,在进行产品比较时不能单纯评估转速,还要注意相应的最大rcf值。
2.3.2生物安全
离心机是可引发气溶胶污染的器材之一[4],如在BSL2级别以上实验室使用应注意:(1)离心室的密封性能;(2)选择带密封盖、可进行121℃高温灭菌的生物安全密封式转头.配套的离心管f瓶)也应具备密封措施;(3)如果要将离心机放人生物安全柜或超净工作台中使用,要充分考虑离心机的体积、重量、稳定性以及安全柜的承受能力等指标。
2.3.3温度控制
高速离心特别是大容量高速离心转头的温度控制,要注意在最大转速时可控制的温度值是否满足实验要求。
2.3.4 Minimum starting speed/speed reduction and speed adjustment increment
This parameter requires strict centrifugation experiments, and attention should be paid to the selection.





