Authors: Lu Libo, Liu Yulin, Zhang Hui
(School of Textile and Materials, Xi'an Polytechnic University, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710048)
In order to improve the efficiency of measuring fiber and yarn diameters and fabric thickness, a coating Thickness Gauge was used, the test results were compared with those of conventional measurement methods, and a relationship table between the two measurement methods was established. Knowing: The test results of the two methods have a good correlation, indicating that the coating Thickness Gauge can be used to quickly measure fiber and yarn diameters and fabric thickness.
During the production, trade and testing of textile materials, it is often necessary to measure the diameter of fibers and yarns as well as the thickness of fabrics. At present, the methods for measuring fiber diameter mainly include linear density method (arrangement method and interrupt weighing method), vibratIon Meter method, laser scanner method, airflow meter method and optical microscope projection method. For different types of fibers , due to their appearance and uneven thickness, the test results obtained by different measurement methods are quite different. The cross-sectional shape of the yarn is irregular, and it is prone to deformation. The spun yarn has more hairiness, and the bulking of the deformed yarn makes the yarn boundary unclear, and the geometric shape measurement is very cumbersome. Compared with fibers and yarns, the measurement of fabric thickness is relatively simple, and it can generally be completed with a fabric Thickness Gauge.
The coating Thickness Gauge can non-destructively measure the thickness of the non- magnetic and the thickness of the non-conductive coating on the non-magnetic metal substrate. It has the advantages of small measurement error, high reliability, good stability, and easy operation. It is a testing , and is widely used in testing fields such as manufacturing, metal processing, chemical industry, and commodity inspection. In this experiment, we tried to use the instrument in the textile industry to measure yarn, fiber diameter and fabric thickness, and compared the measurement results of this method with the results of traditional measurement methods .
1. Test
1.1 Materials and Instruments
8 different types and diameters of fibers such as viscose, cotton, coco fiber, cashmere, wool and polyester; 17 different types and diameters of cotton, wool, linen, viscose, polyester, wool/polyester and polyester/cotton yarn, and fabrics of 17 different thicknesses such as cotton, polyester, spandex, and nylon. MVS300 fiber projector produced by Changzhou Second Textile Instrument Factory, YG141D digital fabric Thickness Gauge produced by Wenzhou Darong Textile Standard Instrument Factory, MiniTest740 coating Thickness Gauge produced by German ElektroPhysik company, computer, objective micrometer, loaded Slides, coverslips, etc.
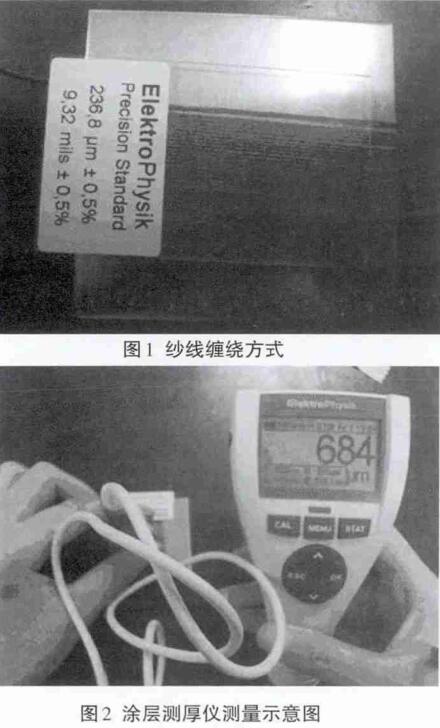
1.2 Measurement method
1.2.1 Yarn diameter test There are two methods to test the yarn:
One is the conventional method, using the MVS300 fiber projector to measure the diameter of the yarn;
The second is to use a coating Thickness Gauge. The specific method is as follows: the yarn is evenly wound on the surface of the iron substrate, that is, only one layer of yarn is spread on the surface of the substrate, and the calibration plate used for instrument calibration is placed on the surface of the yarn, as shown in Figure 1. In the test, we put the probe lightly on the surface of the standard plate. According to the principle of the coating Thickness Gauge, the reading of the instrument is the yarn
The sum of the apparent diameter of the wire and the thickness of the calibration plate. The point of the calibration plate is to average the pressure on the yarn surface. The calibration plate we use is relatively hard and light, and because it is the calibration plate used in the test, the thickness is fixed. As shown in Figure 2, lightly place the probe on the surface of the test material and get a reading of 684 μm, then remove the yarn and put it on separately
Calibration plate, you can get the reading of the calibration plate. Thus, if the calibration plate reads 239 µm, the approximate diameter of the yarn obtained by the test is 684 µm - 239 µm = 445 µm.

10 sets of data are obtained for each measurement, and the average value obtained from the measured values at different points is the yarn diameter data. The instrument can automatically obtain the variance of 10 sets of data, and the stability of the yarn data can be known. Since the reading of the obtained yarn adopts the difference method, no matter whether the calibration is accurate or not, the difference between the two values obtained under the same instrument state is always certain.
1.2.2 Measurement of fiber diameter
Taking wool fiber as an example, two methods are used to test its diameter: one is the conventional method, that is, the MVS300 fiber projector is used to measure the fiber diameter [2]; the other is the coating Thickness Gauge is used to measure the fiber diameter. The specific method is as follows: flatten the fiber soaked in liquid paraffin on the substrate, and place a suitable calibration plate on the fiber to buffer the artificial pressure and reduce the error caused by the fiber gap, so as to ensure a smooth surface under the probe . Place the probe lightly on the calibration plate and read, the reading is the sum of the fiber diameter and the thickness of the calibration plate. In the fiber test, iron and aluminum substrates were used to understand the influence of the substrate material on the test data.
1.2.3 Test of fabric thickness
Two methods are used to test the thickness of the fabric: the first one uses the YG141D digital fabric Thickness Gauge to measure the thickness of different fabrics, and selects representative fabrics with different thicknesses [3]; the second one uses a coating Thickness Gauge to measure the thickness of different fabrics [3]. Measurement. The specific method is as follows: put the cloth sample on the iron substrate, and put a suitable calibration plate on the cloth sample to buffer the artificial pressure and the error caused by the uneven surface of the cloth sample, as shown in Figure 3. Gently place the probe on the calibration plate to read, the reading is the sum of the thickness of the cloth sample and the thickness of the calibration plate.
2 Results and Analysis
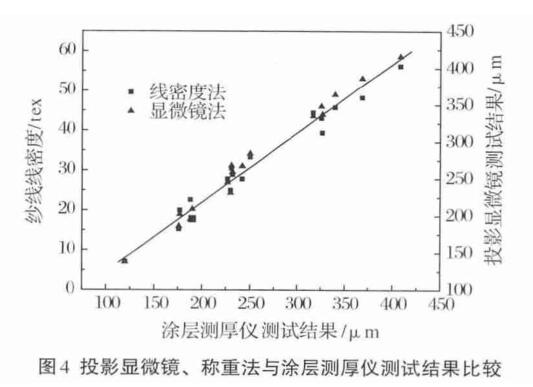
(1) Using a fiber projector to measure 17 different types and diameters of yarns such as cotton, wool, linen, viscose, polyester, wool/polyester and polyester/cotton; and then according to the national standard GB/T 4743-2009 "Textile Determination of Yarn Density of Package Yarn Skein", the tex number of the yarn was measured by the weighing method, and the diameter of the yarn was measured by a coating Thickness Gauge at the same time , the results are shown in Figure 4. It can be seen from Figure 4 that there is a good correlation between the test results of the coating Thickness Gauge and the projection microscope method and the weighing method. After statistical regression, the test results of the projection microscope and the coating Thickness Gauge meet a linear relationship, the regression equation is Y 1 =21.62+0.99X 0 , the correlation coefficient R 1 =0.993; the weighing method and the coating The results also satisfy a linear relationship, the regression equation is Y 2 =-10.90+0.16X 0 , and the correlation coefficient R 2 =0.985. Among them: Y 1 and Y 2 are the yarn diameter and tex number measured by projection microscope and weighing method respectively; X 0 is the yarn diameter measured by coating Thickness Gauge.
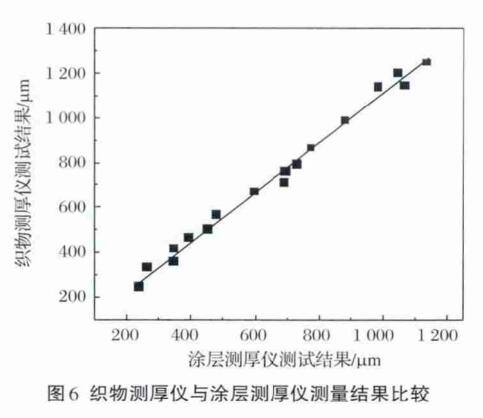
(3) According to the national standard GB/T 3820-1997 "Determination of the thickness of textiles and textile products", using the YG141D digital fabric thickness meter to measure 5 kinds of thin, 5 kinds of medium thick and 7 kinds of thick cotton, polyester, The thickness of fabrics such as spandex and nylon was measured by using a coating Thickness Gauge to measure the thickness of 17 kinds of fabrics, and the results are shown in Figure 6. It can be seen from Figure 6 that there is also a good correlation between the fabric Thickness Gauge and the coating Thickness Gauge, the linear regression equation is Y 5 =6.11+1.10X 2 , and the correlation coefficient R 5 =0.996. Among them: Y 5 is the fabric thickness measured by the fabric Thickness Gauge; X 2 is the fabric thickness measured by the coating Thickness Gauge.
In this test, we try to use the MiniTest740 coating Thickness Gauge to measure the diameter of fibers and yarns and the thickness of fabrics, and compare the measurement results of this method with those measured by traditional methods. After statistical regression analysis, it can be seen that there is a good correlation between the test results of the coating Thickness Gauge and the projection microscope method and the weighing method; substrates with different have no effect on the test results; the coating Thickness Gauge and the fabric There is also good correlation between Thickness Gauge The successful use of this method can greatly increase the speed of fiber, yarn diameter and fabric thickness measurement.
In order to use the instrument more widely and make the measurement results more accurate, we can transform , such as changing the probe parameters, expanding its range, and developing a special coating Thickness Gauge for textiles. Further exploration is required.
