This paper introduces the detection methods of various ship coatings, and focuses on the detection methods of hull antirust paint, antifouling paint, ship ballast tank paint and crude oil tanker cargo oil tank paint. The development direction of the detection method of marine coatings is prospected.
0 Preface
Ships travel at sea and are affected by various corrosive environments. Above the waterline, the deck and superstructure are affected by the high salinity, high humidity, and high radiation of the ocean atmosphere; below the waterline, the hull is not only corroded by seawater, but also by various marine organisms (such as barnacles, oysters, seaweed, etc.) ) attachment, which not only greatly increases the navigation resistance and reduces the navigation speed, but also causes more fuel consumption, and even causes shipwreck accidents; liquid tanks loaded with various corrosive media, such as seawater ballast tanks, crude oil tanker cargo oil tanks, Chemical tanks, due to long-term exposure to seawater, crude oil, and strong corrosive chemicals, have always been concerned by shipbuilding and shipping departments for their corrosion and protection. For hydraulic natural gas ships, the fireproof performance of fireproof materials is the first consideration, but the importance of preventing extreme low temperature (down to -198°C) shocks caused by hydraulic natural gas leakage is also important. At present, coating is one of the most important measures for ships to carry out anti-corrosion, anti-fouling and special protection. With the continuous development of science and technology, the performance of marine coatings has also been greatly improved. For example, high weather resistance topcoat and high solid general-purpose epoxy antirust paint have been widely used in ship hulls, hulls and other parts [1]. In addition, with the continuous improvement of environmental regulations, marine coatings are also paying more and more attention to environmental protection. In 2015, the State Administration of Taxation issued regulations on the collection of paint consumption tax. The National Paint Standardization Technical Committee is also preparing the national standard "Limits of Harmful Substances in Ship Paints" to reduce the content of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and reduce the use of toxic and harmful antifouling agents. The use has become an important trend in the development of marine coatings [2].
The development of marine coatings is inseparable from the support of testing technology, and professional testing technology plays an important role in improving the research and development efficiency and quality of marine coatings products. Various international regulations and conventions have proposed methods to simulate and accelerate the performance of marine coatings in the laboratory. As stipulated in the IMOMSC.215 (82) and IMOMSC.288 (87) resolutions of the International Maritime Organization, the protective coatings on the ballast tanks of all types of ships and the double-sided skins of bulk carriers must pass the simulated ballast tank test and the cargo oil tank of crude oil tankers. The coating needs to pass the simulated crude oil tank airtight cabinet and immersion test; "2001 International Convention on the Control of Harmful Anti-fouling Systems on Ships" (ASF Convention) requires antifouling paints to provide organotin-free reports; "2009 Hong Kong International Safety and Environmental Safety The Convention on Hazardous Ship Recycling (Hong Kong Convention) includes asbestos and heavy metal content in the testing requirements [3] and so on. In addition, marine coatings are currently developing towards long-term effects, and the anti-corrosion period often reaches more than ten years or even longer. Therefore, how to quickly evaluate the service performance of marine coatings and obtain data support for coating design is very important. At present, the performance tests of marine coatings are natural environment exposure test and indoor accelerated simulation test. The natural environment exposure test data is reliable, but the test period is too long; and the indoor accelerated simulation test can greatly shorten the test period by setting appropriate test conditions and determining the acceleration factor, and can well reflect the actual performance of the coating [4] . According to the characteristics of marine coatings, the following introduces the current detection methods of various types of marine coatings, focusing on the cathodic disbonding resistance of hull antirust paints, performance tests of antifouling paints, performance standards for protective coatings for ballast tanks and cargo oil tanks (PSPC) and other detection methods.
1 my country's current standards and specifications for marine coatings
According to the different parts of the ship, the national standards classify the ship coatings, explain the use and use, and formulate the corresponding product standards. At present, the relevant standards and specifications of ship coatings in my country are shown in Table 1.
2 Testing methods for ship coatings
2.1 Detection method of hull antifouling and antirust paint system
Hull anti-fouling and anti-rust paint system refers to the hull anti-fouling and anti-rust paint system on the outer surface of the hull below the design waterline. The product standard is GB/T6822-2014 "Hull anti-fouling and anti-rust paint system". Compared with the 2007 version, the 2014 version cancels the service life and category of the antirust paint system classification, and adds the connection paint classification. For hull antirust paint, in addition to conventional indicators such as flash point, viscosity, volume fraction, and volatile organic compound content, the functional indicators such as anti-foaming, immersion resistance, and cathodic disbondment resistance of the paint film are mainly investigated. Among them , Cathodic disbondment resistance is one of the key indicators of hull antirust paint. During the service of the ship, due to the damage of the coating, the substrate is exposed to corrosive media such as seawater. Cathodic protection technology can effectively protect the metal substrate and delay corrosion, but the coating will lose its adhesion and peel off the substrate due to cathodic action, thus losing the protective metal. Ability. Therefore, the importance of improving the cathodic disbondment resistance of the coating goes without saying. The test method for cathodic disbondment resistance is GB/T7790-2008 "Determination of cathodic disbondment resistance of paints and varnishes exposed to sea water" (ISO15711-2003), using the applied current method or sacrificial anode method, the sample and the saturated The potential between calomel reference electrodes is -1050mV, and the cathodic disbonding resistance test lasts for 6 months. It is required that the average distance between the peeled coating and the outer edge of the artificial leakage coating hole after the test is not more than 8mm.
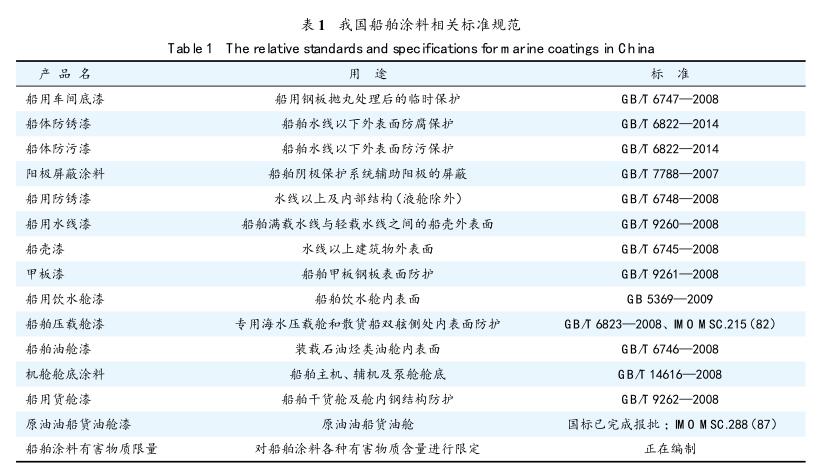
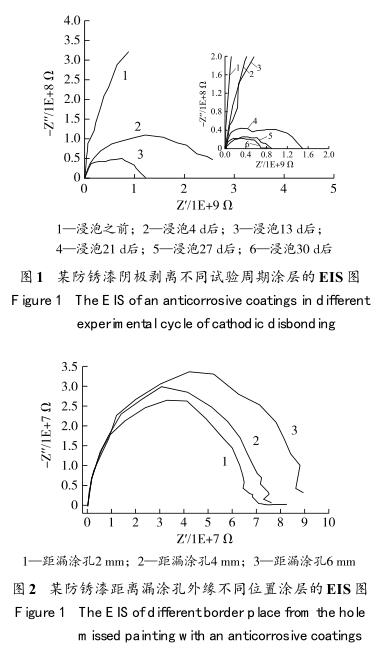
The test results can only be obtained by peeling off the coating after the test, but the sample cannot be restored after the test, and the phenomenon of coating swelling or peeling off from the substrate is not obvious during the test, and it is difficult to find out in which cycle the coating is aging or occurs. amount of change. The test conditions for cathodic disbondment resistance are harsh, the test period is long, the pass rate is not high, and often requires multiple tests to pass. For this reason, the development of in-situ nondestructive testing methods for cathodic disbondment of coatings has become a research hotspot in the current industry. Among them, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) does not cause irreversible effects on the properties of the sample system due to the small perturbation signal applied, and can measure coating capacitance, coating resistance, and coating/metal interface duality in situ. Electrochemical parameters related to coating system performance and coating failure process, such as electrical layer capacitance and reaction resistance, have become one of the most important methods for studying organic coatings in metal systems, and can be used to predict the development degree of cathodic disbonding of antirust paints. Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the electrochemical impedance spectra of the coating at different test periods for cathodic peeling of an antirust paint measured by electrochemical impedance method (EIS method) and at different positions from the outer edge of the artificial leakage hole.
从保护海洋环境和防止海洋污损生物两个功能来看,表明防污漆本身特殊性和评定的难度。目前对防污漆的评定主要分为防污性能及毒性检测,主要检测项目有浅海浸泡、动态模拟、藤壶剪切力试验、防污剂渗出率、防污涂层磨蚀率、降阻性能等。
浅海浸泡是防污漆体系最基本的性能检测方法,也是评定防污漆体系防污能力的最可靠检测方法,但试验周期较长,最少需要一个完整海生物生长旺季。检测方法为GB/T5370—2007《防污漆样板浅海浸泡试验方法》,建议样板尺寸为350mm×250mm×3mm,海水浸泡深度为0.2~2m,According to防污漆使用期效设定浸泡周期。短期效(3a以下)防污要求至少浸泡1个海生物生长旺季;中期效(3~5a)防污要求至少浸泡2个海生物生长旺季;长期效(5a以上)防污要求至少浸泡3个海生物生长旺季。试验后对防污漆的防污性能及漆膜物理状态进行综合评定打分,要求综合分数≥85分。另外,动态模拟通过模拟船舶航行与停泊的实际工作状态,可以在较短时间内对防污漆的防污性能进行评估。检测方法为GB/T7789—2007《船舶防污漆防污性能动态试验方法》,样板运转线速度为20节,连续运行200h后移入实海浮筏浸泡1个月为一个周期。短期效防污漆的试验周期为3个,中期效为5个,长期效为8个,要求最后一个周期应在海生物生长旺季浸泡。对Ⅲ型污损释放型防污漆,动态模拟以浅海浸泡开始,According to产品技术特点,浸泡周期从10d到2个月,浸泡后主要考察硬壳海生物(如藤壶、硬壳苔藓虫等)的附着情况。ASTMD5618—94(2011)《测量藤壶剪切强度的标准试验方法》通过测量将藤壶从涂层附着面剥离所需的剪切力以及藤壶附着面积,从而计算藤壶剪切强度,是考察防污漆,特别是污损释放型防污涂层防硬壳海生物污损性能的一项重要方法。
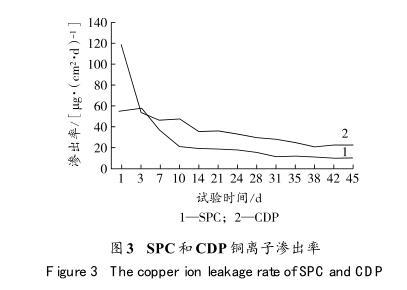
防污漆要起到防止海生物污损的效果,需要防污剂稳定渗出。防污剂的渗出率太大,则防污涂层使用寿命降低,也增大了环境风险;渗出率太小,则起不到防污作用。防污剂渗出率的检测方法主要According toISO15181—6—2012,包括防污剂萃取方法,以及铜离子、代森锌(Zineb)、吡啶三苯基硼(PTPB)、甲苯氟磺胺和苯氟磺胺及灭钉螺剂(Tralopyril)等防污剂渗出率的检测方法。自抛光防污漆(SPC)和溶解型防污漆(CDP)铜离子渗出率比较见图3。由图3可见:SPC和CDP初期铜离子渗透率均较大,30d后趋于稳定。另外,无论是初期还是后期铜离子渗出率,CDP都比SPC大得多。According to环境保护部HJ/T2515—2012《环境标识产品技术要求船舶防污漆》,要求在稳定状态铜离子渗出率≤25μg/(cm2d)。
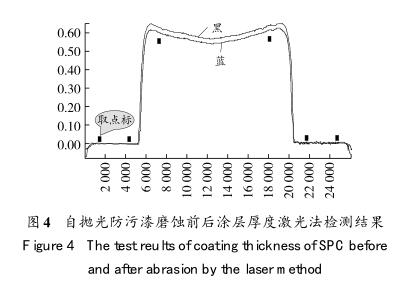
自抛光防污漆的防污机理是利用可水解的丙烯酸成膜物发生水解反应,释放出防污剂,同时防污涂层表面在一定流速海水的冲蚀作用下不断被消耗磨蚀,防污涂层持续保持新鲜的表面来达到防污的作用,因此考察防污涂层的磨蚀率对自抛光防污漆来说具有重要意义,也是自抛光防污漆的一项特性指标。磨蚀率检测方法主要有转鼓法及圆盘法,转鼓法测定在固定转速下的磨蚀率,而圆盘法由于不同位置涂层的线速度不同,可以测定在不同速度下的磨蚀率。对防污涂层厚度的磨蚀率表征一般通过激光平整度检测仪或显微镜进行测定,其中激光法操作简便,可以快速并无损测定涂层磨蚀前后的厚度;光学法需要包埋环氧树脂进行涂层磨蚀前后的参照,并通过光学或数码显微镜进行磨蚀厚度测量。自抛光防污漆磨蚀前后涂层厚度激光法检测结果见图4,黑色和蓝色分别表示磨蚀前后防污涂层的厚度。由图4可见:自抛光防污漆磨蚀效果良好,呈均匀磨蚀状态。目前我国船舶防污漆磨蚀速率测定的检测方法已经完成标准报批,预计将很快发布实施。
随着船舶节能减排及能效设计指数(EEDI)不断推进,人们意识到,表面状况良好的防污涂层也能有效地降低船舶航行阻力,即防污涂层的降阻性能。防污涂层的降阻性能可实海检测,也可以在实验室内进行模拟试验,但在实验室内可以稳定控制海水温度、盐度等,更便于不同防污漆进行对比。防污漆降阻性能检测方法According toGB/T7791—2014《防污漆降阻性能试验方法》,其原理是通过测定涂装有防污涂层的圆筒试样在海水湍流状态下的某一速度旋转时的扭矩,得出某一速度下防污涂层与海水界面的阻力,同时结合航行模拟试验,对比海水冲刷前后涂层在相同速度下阻力的变化,从而测定防污漆的降阻性能和降阻率。
2.3压载舱涂层的检测方法
船舶压载舱用于为船舶提供稳性及调整船舶吃水量,以满足船舶良好的操纵性能要求。船舶压载舱随航行的需要和海况的不同可能遭遇到的腐蚀环境主要有海水大气区、海水飞溅区、海水全浸区和舱底泥沙区。在整个航行过程中,船舶压载舱始终处于空舱/海水压载这样的干湿交替状态,而且难以维修,因此其腐蚀环境非常严酷,甚至引起海难事故,因此,压载舱涂层的防腐性能显得尤为重要。2006年国际海事组织(IMO)海上安全委员会(MSC)第82次会议通过了海上人命安全公约(SOLAS)修正案,其中作为公约的附件之一,专用船舶压载舱保护涂层性能标准(简称PSPC)也成为了强制性标准。PSPC是船舶压载舱涂层最关键的一项检测项目,主要包括模拟波浪舱、冷凝舱、高温、涂料类型鉴定等试验。
通过对PSPC试验结果进行分析发现,涂层附着力及电流需求均可满足规范要求,环氧涂层与车间底漆界面的划痕剥离和阴极剥离是影响PSPC试验的重要因素,而且由于阴极产物的影响,阴极剥离往往要比划痕剥离严重得多,阴极剥离性能是涂层体系能否通过PSPC试验的关键。另外,在实际涂装作业中,压载舱焊缝处涂层往往达上千微米。这些涂层在受到热胀冷缩及海水压载/空载循环暴露冲击等影响时,很容易出现开裂等现象,从而严重影响涂层的防腐性能。近年来,也有不少涂料公司在进行压载舱超厚膜涂层的抗开裂试验方法研究,但目前船舶行业、国家标准及国际海事组织均未有统一的试验方法。
2.4原油油船货油舱涂层的检测方法
随着各国对石油需求的日益增长及造船技术的不断发展,目前油船最大的吨位已超过50万t。由于原油成分的多样性和含有多种酸性腐蚀介质,以及造船工艺的复杂性和油船航行中的各种海况,装载原油的货油舱往往腐蚀严重,使得油船的寿命大大缩短,甚至威胁到原油运输的安全。自1990年代以来,国际海事组织(IMO)针对不断出现的海损和污染事件,推出了一系列改善油船结构、提高安全性的强制要求,如单壳改双壳。2010年国际海事组织通过了MSC.288(87)决议案,《油船货油舱保护涂料性能标准》(PSPC-COT)在2012年5月正式生效。这是国际海事组织在2001年通过《船底有害防污体系》公约和2006年通过《船舶专用海水压载舱保护涂料性能标准》后的第3个与船舶涂料直接有关的强制性标准。PSPC-COT是原油油船货油舱涂层最关键的一项检测项目,主要包括气密柜试验和浸没试验。
According to对多套PSPC-COT试验统计,气密柜试验相对容易通过,浸没试验腐蚀则严重得多,这也是货油舱涂层能否通过PSPC-COT的关键。浸没试验模拟原油由DMA级船用馏分型燃料油、环烷酸、苯、甲苯、通入硫化氢气体的海水等组成,试验温度高达60℃,且试验周期长达6个月,腐蚀环境十分严酷。在这种环境下,涂层受热膨胀、孔隙率增大,使得硫化氢或苯系物等小分子物质更容易渗入涂层中,从而引起起泡。由于PSPC-COT试验条件苛刻且试验周期长,船舶涂料生产厂家往往需要多次改进产品、不断试验才能通过,已经给涂料生产厂家带来极大影响。
2.5车间底漆的检测方法
车间底漆是船用钢板、型钢和成型件经抛丸(或喷砂)处理后涂装、暂时保护钢材的防锈底漆。由于船厂作业的特殊性,车间底漆需适应自动化流水线作业,应能在5min内干燥,且具有良好的焊接与切割性。目前国家标准GB/T6747—2008《船用车间底漆》对车间底漆的检测项目主要有干燥时间、附着力、耐海洋性气候、焊接与切割等。由于大多数车间底漆属于湿固化底漆,固化程度直接影响到漆膜的理化性能,如在相对湿度较低的环境下施工,车间底
漆将很难完全固化。因此,对车间底漆很有必要增加耐溶剂擦拭性测试,以检测车间底漆的固化程度。另外,随着压载舱及油船货油舱PSPC规范的相继实施,要求车间底漆为不含缓蚀剂的硅酸锌基含锌涂料,且与压载舱或货油舱主涂层具有良好的相容性,这可能也是未来车间底漆检测的重点。
2.6船壳漆、水线漆及甲板漆的检测方法
船壳漆是涂覆在船舶满载水线以上的建筑物外部用的涂料,亦可是桅杆和起重机械用涂料;甲板漆主要是船舶甲板及其它海洋设施的表面用漆;水线漆是船舶满载水线和轻载水线之间船壳外表面用漆(不具有防污作用)。国家标准GB/T6745—2008《船壳漆》对船壳漆的检测项目主要有附着力、冲击、盐雾、紫外/氙灯老化、海洋气候曝晒等;GB/T9260—2008《船用水线漆》对水线漆的要求与船壳漆类似,但增加了耐划水性2周期;GB/T9261—2008《甲板漆》According to甲板的环境特点增加了防滑性、耐磨性等指标。从使用环境可以看出,船壳漆、水线漆及甲板漆均暴露于海洋性气候中,受到盐雾、雨露、光照等交替变化的腐蚀,与采油平台或其它海上结构物的面漆相似。目前国家标准对这3种面漆分别进行盐雾、光老化或附着力等“静态”检测。NORSOKM-501:2012《表面处理和防护涂层》及ISO20340—2009《色漆和清漆海上平台及相关结构用防护涂料体系的性能要求》则将盐雾、光老化及温度冲击结合起来,进行循环老化,试验条件更苛刻,也更加符合实际环境。因此,未来船壳漆、水线漆及甲板漆的耐性检测可能会模拟更加符合海洋气候环境的多项目组合检测。
2.7船用防锈漆、船用货舱漆及机舱舱底涂料的检测方法
船用防锈漆主要用于船体设计水线以上及内部结构(液舱除外)用防锈漆;货舱漆主要用于干货舱或其他舱内防护漆;机舱舱底涂料主要用于主机、辅机及泵舱舱底。这三种涂料主要考察耐盐雾、耐磨、耐机油等指标,检测项目相对简单。对于货舱漆而言,由于载运物质差别很大,如煤炭、矿砂、谷物等。不同物资对漆膜造成的磨损是不同的,因此,未来针对运输货物的不同、设计更合理的模拟磨损试验可更有效地反映货舱漆的耐磨性能。
2.8其他船舶涂层体系的检测方法
目前我国关于船舶涂料的检测已经比较全面,覆盖船舶各个部位,但某些舱室(如空舱、化学品舱)防护涂层、甲板热反射涂层、舱室防火涂层、液化天然气船(LNG)耐低温泄漏涂层等检测标准均尚未制定。这需要检测机构、船舶业主、涂料厂家等各方共同参与制定,也是未来船舶涂料检测的一大重点。
3船舶涂料有害物质检测
随着人们对健康、环保的日益重视,船舶涂料也向低毒、无毒方向发展。2001年国际海事组织通过的《2001年国际控制船舶有害防污底系统公约》(ASF公约),规定所有船舶不得施涂含有机锡化合物作为杀生物剂的防污底系统或任何其他AFS公约禁止施涂或使用的防污底系统;2009年通过的《2009年香港国际安全与环境无害化拆船公约》(简称香港公约),禁止使用石棉,对铅、铬、镉、汞等重金属有害物质的限量也作了严格的规定,对多氯联苯(PCB)、臭氧消耗物质等及某些短链氯化石蜡的含量都进行了限定。2015年,国家税务总局涂料消费税政策及全国涂料标准化技术委员会正在编制的《船舶涂料中有害物质限量》国家标准,也对船舶涂料检测提出了新的要求。特别是石棉,由于其是一级致癌物,一旦被吸入人体就会附着并沉积在体内,会对人的生命健康造成巨大危害。国际海事组织及中国船级社多次紧急规定,所有船舶材料石棉检出阈值应为0,即不得检出。目前《船舶涂料中石棉含量测定》国家标准已经完成报批,预计将很快实施。标准提出以X射线衍射仪(XRD)及偏光显微镜(PLM)对温石棉、青石棉等6种石棉进行定性定量检测。大多数热稳定性良好的小分子(一般相对分子质量<1000)有机物检测主要依靠气相色谱质谱联用仪(GCMS);对热稳定性差或大分子有机物(如代森锌等有机防污剂)一般采用有效液相色谱仪(HPLC)进行检测;金属元素含量一般采用电感耦合等离子体光谱仪(ICP-OES)或原子吸收光谱仪(AAS)等分析设备进行检测。
4结语
The detection of ship coatings is to ensure that ships sail more safely at sea and better protect the marine environment and human health. Due to the complexity of the marine environment, it is particularly required that the future ship coating detection method is an accelerated simulation method, which can better simulate the various conditions of the actual navigation of the ship, which also puts forward higher requirements for the detection of ship paint. In addition, although my country's inspection of ship coatings has covered all parts of the ship relatively comprehensively, some cabins (such as empty cabins, chemical tanks) protective coatings, deck heat reflective coatings, cabin fireproof coatings, liquefied natural gas ships (LNG) ) Standards such as low-temperature leak-resistant coatings have not yet been formulated, which also requires all parties to develop corresponding detection methods.




