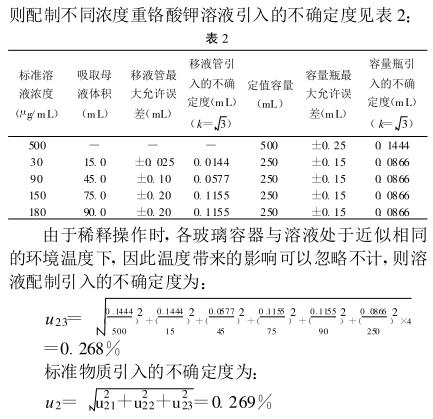
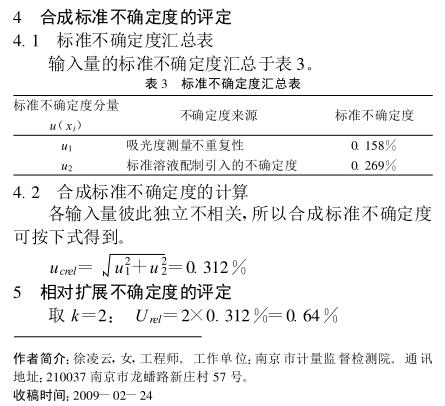
1 Overview
1.1 Measurement basis: JJG179-1990 "Verification Regulations for Filter Photoelectric Colorimeter".
1.2 Environmental conditions: temperature (5 ~ 30) ℃, relative humidity ≤ 85%.
1.3 Measurement standard: national standard substance potassium dichromate GBW(E)060018b, mass fraction 99.998%, relative expanded uncertainty 0.02%, k=2.
1.4 Measured object: filter photoelectric Colorimeter.
1.5 Measurement process: Use 0.05mol/L sulfuric acid solution as a reference to measure the absorbance of standard solutions of various concentrations. Each solution was measured twice, and the average value was taken.
1.6 Use of evaluation results: Generally, the evaluation results of this uncertainty can be directly used when the measurement results meet the above conditions.
2 Mathematical Model
A=-logτ=abc
In the formula: A—absorbance of the substance; τ—transmittance of the substance; c—concentration of the solution (μg/ml); a—absorption coefficient; b—optical path length.
When the absorption coefficient a and the optical path length b are constant, the absorbance of the substance
A is proportional to the concentration c of the solution.
3 Evaluation of standard uncertainty of input quantity
3.1 Evaluation of type A standard uncertainty
The source of the uncertainty of the input amount A is mainly the non-repeatability of the absorbance measurement of the filter photoelectric Colorimeter, which can be obtained by continuous measurement and evaluated by the Class A method.
For a filter photoelectric Colorimeter, 0.05mol/L sulfuric acid solution is used as a reference, and the potassium dichromate standard solution is continuously measured 10 times, and the absorbance measurement series are 0.4644, 0.4647, 0.4648, 0.4646, 0.4639, 0.4648, 0.4635 , 0.4631, 0.4633, 0.4627.

Four concentrations of standard solutions need to be measured in the verification , each of which is continuously measured 10 times under repeatability conditions , and a total of 4 sets of measurement columns are obtained . The standard deviation of a single experiment is calculated by the above method, as shown in Table 1 .