The glossiness of a printed matter refers to the closeness of the surface of the printed matter to the reflection ability of incident light and the ability of complete specular reflection. The higher the gloss of a print, the more its surface reflects light like a mirror, and the more bright or shiny it can be. The glossiness of paper after printing determines the beauty of printed matter. The gloss of printed matter is mainly determined by factors such as paper, ink, printing pressure and post-press processing methods. This article analyzes the influence of paper, ink, printing pressure and other factors on the gloss of printed matter.
1. The effect of paper properties on the gloss of printed matter
The glossiness of printed matter is highly related to the type of paper. Specifically, it is related to five aspects of paper surface smoothness, gloss, ink absorption, strength, and PH value.
1) The effect of the smoothness of paper on the gloss of printed matter. Ink film gloss on paper determines
Whether the incident light can be specularly reflected, only the paper with high smoothness can produce specular reflection after the ink film is leveled; if the smoothness of the paper is poor, the surface of the paper is rough, after the ink is printed, the ink film is uneven, Only diffuse reflection can be formed for light, and the gloss of the printed matter will be very poor. After the paper is coated, the fine particles of the coating fill the depressions on the surface of the base paper. After super calendering, the smoothness of the paper is greatly improved. Paper with high smoothness can ensure the complete reproduction of dots, which is conducive to the formation of a uniform and smooth ink film, and the printing gloss will naturally increase. Therefore, in order to obtain high-gloss prints, it is necessary to choose paper with high smoothness, such as coated paper and coated paper.
2) The glossiness of the paper affects the printed matter
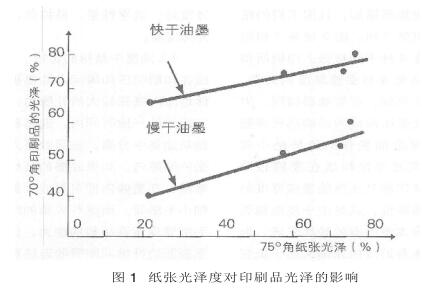
Gloss effect. There is a good correlation between the gloss of the paper itself and the gloss of the printed matter, and the gloss of the paper determines the gloss of the printed matter. The relationship curve between the glossiness of paper and the glossiness is shown in Figure 1, that is, whether it is fast-drying ink or slow-drying ink, the glossiness of printed matter increases with the glossiness of the paper itself. In actual printing, to print high-gloss prints, it is often necessary to use high-gloss paper. Paper gloss from low to high is uncoated paper, light weight coated paper, coated paper, and glossy paper. The gloss of the coated paper surface mainly depends on the glossy materials used in papermaking and the processing accuracy of the paper. The brightening materials include paraffin wax, insect wax, aluminum stearate, etc., and the finishing method is super calendering.
3)纸张的吸墨性对光泽的影响。纸张是由纤维交织而形成毛细管网络结构,具有大量孔隙,印刷时就是靠这些孔隙吸收油墨。纸张的吸墨性实际上是指纸张对油墨连结料的吸收性能。越是粗糙的纸张,其纤维间隙越大,对连结料的吸收能力越强。而连结料是油墨在纸张表面固着的成膜剂,连结料的过分吸收就会使油墨失去了流平性能,油墨颜料颗粒散落在纸张表面,无法结成光滑的墨膜层,使印刷品表面暗淡无光。只有纸张具有较弱的吸墨性,才能避免油墨连结料甚至颜料的过分渗透,使纸面得到鲜艳光亮的墨膜。但也不能吸收性太差,否则虽印刷光泽好,但易引起印刷时纸张粘脏等现象。
4)纸张表面强度对印刷品
光泽的影响。纸张表面强度不高,印刷时就会产生掉毛、掉粉现象,印迹墨膜就会高低不平,对光形成漫反射,此时印刷品的光泽度就会下降,甚至无光泽。
5)纸张表面的PH值对印刷品光泽的影响。酸性纸有延缓干燥的作用,这是因为纸中的无机酸与油墨中的干燥剂起反应,会降低干燥剂的活性,所以酸性纸印刷时要适当增加干燥剂。中性或碱性纸则有利于油墨干燥。如果纸张表面的PH数值高(偏碱性),油墨在纸面干燥就快,利于形成印刷品的高光泽。
2油墨对印刷品光泽的影响
影响印刷品光泽的油墨因素主要是墨膜的平滑度,它是由连结料的性质和数量多少决定的。油墨应含有分散均匀的细微颜料,并具有足够的粘度和较快的干燥速度,以避免连结料过多地渗入纸张孔隙。此外,油墨还应具有良好的流动性,以便使印刷后的油墨流平,形成平滑的墨膜。油墨的性质对印刷品光泽的影响主要在以下几个方面:
1)墨膜厚度对印刷品光泽的影响。在纸张尽可能吸收油墨的连结料以后,剩余的连结料仍保留在墨膜中,它可以有效地提高印刷品的光泽。墨膜越厚,剩余的连结料越多,越有利于提高印刷品的光泽。光泽随墨膜厚度的增加而增加,且因不同的纸张而有所不同。图2显示了相同油墨在4种不同纸张上印刷所得印刷品光泽与墨膜厚度的关系。
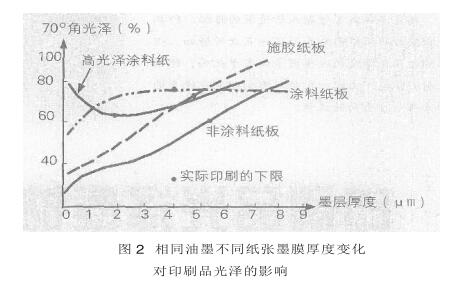
从图2可知,尽管油墨相同,但不同纸张所形成的印刷品光泽随墨膜厚度而变化的趋势是不同的。高光泽涂料纸在墨膜较薄时,其印刷品光泽随墨膜厚度的增加而降低,这是由于墨膜掩盖了纸张本身原有的较高光泽,而墨膜本身形成的光泽又由于纸张吸收而降低;随着墨膜厚度的逐渐增加,纸张对连结料的吸收基本饱和之后,其表面保留连结料增多,光泽度亦不断提高。涂料纸板印刷品的光泽度随墨膜厚度的增加很快提高,在墨膜厚度增加到3.8μm以后,光泽便不再随墨膜厚度的增加而增加。
2)油墨的流动性。油墨的流动性太大,网点增大,印迹尺寸扩大,墨层变薄,印刷光泽度差;油墨流动性太小,光泽度高,但油墨不易转移,也不利于印刷。因此,为了得到较好的光泽度,应控制油墨的流动性,不能太大也不能太小。
3)油墨的流平性。在印刷过程中,油墨的流平性好,则光泽度好;流平性差,易拉丝,则光泽度差。
4) The content of pigment in the ink. Generally, at the moment of embossing by the printing machine, the ink is pressed into the larger pores of the paper as a whole; within a period of time after embossing, the binder begins to separate from the ink and is absorbed into the gaps in the paper. If the pigment content of the ink is high, a large number of tiny capillaries can be formed in the ink film. And these a large number of tiny capillaries retain the ability to connect the material, which is much larger than the fiber gap on the surface of the paper to absorb the binder. Therefore, an ink with a high pigment content will allow the ink film to retain more of the vehicle than an ink with a low pigment content. Prints using inks with a high pigment content have a higher gloss than prints with inks with a low pigment content. Therefore, the capillary network structure formed between ink pigment particles is the main factor affecting the gloss of printed matter. In actual printing, another method is to use varnish to increase the gloss of the printed matter. This method is completely different from the method of increasing the pigment content of the ink. When these two methods of increasing the gloss of printed matter are applied, they should be selected according to the components of the ink and the thickness of the printing ink film. Due to the need for color reproduction in color printing, methods for increasing pigment content are limited. For inks formulated with small particle pigments, when the pigment content decreases, the gloss of the printed matter will decrease, and only when the ink film is quite thick can a higher gloss be produced. Therefore, in this case, the method of increasing the pigment content can be used to improve the gloss of the printed matter. However, the amount of pigment can only be increased to a certain limit, otherwise, the light scattering phenomenon on the surface of the ink film will be aggravated and the gloss of the printed matter will decrease because the pigment particles cannot be completely covered by the linking material.
5) The size of the pigment particles and their degree of dispersion. Ink film capillary action is the main reason for the gloss of printed matter. The size of the pigment particles in the dispersed state directly determines the state of the capillary of the ink film. If the ink particles urinate, more small capillaries can be formed. Increase the ink film's ability to retain the binder and improve the gloss of the printed matter. At the same time, if the pigment particles are well dispersed, it will also help to form a smooth ink film and improve the gloss of the printed matter. The restrictive factors affecting the degree of dispersion of pigment particles are the pH value of the pigment particles and the content of volatile substances in the ink. The PH value of the pigment is low, the content of volatile substances in the ink is high, and the dispersion of the pigment particles is good.
6) Transparency of ink.
透明度高的油墨形成墨膜后,入射光线一部分被墨膜表面反射,另一部分到达纸张表面,再反射出来,形成两次滤色,这个复杂的反射丰富了色泽的效果;而不透明的颜料形成的墨膜,其光泽只是由表面反射而得,光泽效果肯定不如透明油墨。
7)连结料的光泽性。
连结料的光泽性是油墨印迹能否产生光泽的主要因素,早期的油墨连结料以亚麻仁油、桐油、梓油等植物油为主,结膜后表面的光滑度不高,只能呈现脂肪性的膜面,对入射光形成漫反射,印迹的光泽度较差。而现在油墨的连结料以树脂为主要成分,印迹结膜后表面光滑度高,入射光的漫反射减少,因而印迹的光泽高出早期的油墨好几倍。
8)溶剂的渗透速度。
印刷刚刚结束时,由于油墨的干燥和固着尚未全部完成,因此,印刷面的光泽度很高,如涂布纸,它的印刷面实地部分的光泽度往往比白纸面高出15~20度,而且表面还湿润闪亮。但是随着墨迹的进一步干燥和固着,光泽度就会慢慢下降。这是因为,当油墨中的溶剂还停留在纸面上时,油墨保持一定程度的流动性而有很高的平滑性。然而随着溶剂向纸内的渗透,表面的平滑性便是由颜料的粒子来决定的,而这时的颜料粒子比溶剂的分子大得多,因此,印刷面的平滑性是随着溶剂的渗透而不得不下降的。在此过程中,溶剂渗透速度直接影响到印刷面的平滑性和光泽度。如果渗透进行得缓慢,而且树脂的氧化聚合作用也以相适应的速度进行,油墨表面就可在保持相当高的平滑性的状态下成膜变硬。这样印刷光泽度就可保持在较高的程度上。相反,如果溶剂的渗透是快速进行的,那么树脂的聚合硬化,只有在印刷面的平滑性已大大降低的情况下才能完成,这样印刷品光泽度就明显降低了。
因此,在纸张光泽度相同的情况下,油墨的渗透速度越慢,印刷光泽度就越高。即使在白纸光泽度和油墨渗透速度都相同的情况下,印刷光泽度也会因油墨在纸面的渗透状态不同而不同。一般来说,在相同的渗透速度下,致密而细微的渗透状态比稀疏而粗大的渗透状态更有利于印刷光泽度的提高。但减小油墨的渗透和结膜速度来提高印刷光泽度会引起背面粘墨故障。因此,单靠造纸技术的改进是不能够达到既提高印刷光泽度又能防止粘墨故障“一箭双雕”的目的,这个问题的解决还有待于油墨制造技术的提高。
9)油墨的干燥形式。
相同的墨量采用不同的干燥形式,其光泽度也不一样,一般氧化结膜干燥比渗透干燥的光泽度高,因为氧化结膜干燥的油墨中成膜性连结料多。
3印刷压力对印刷品光泽的影响
印刷压力是印迹良好转移的关键,压力过大,印迹扩大,光泽度变差;压力过小,印迹不清晰,造成印品无光泽。因此,胶印时在保证能将橡皮布上的油墨正确转移到纸张上的前提下,应尽量采用较小的印刷压力,主要依靠油墨的渗透和氧化结膜作用干燥,才能印出光泽度好的印刷品。
4提高光泽度的方法
在相同纸张、油墨的条件下,由于工艺操作中存在问题,往往造成印刷后成品光泽度相差较大。
1)According to不同的印刷品档次选择不同光泽度的纸张,如对于彩色宣传印刷品,为了加大反差,抓住人的视觉,仍以高光泽度的涂料纸为主。对于以文字为主的印刷出版物采用低光泽度的纸张,如非涂料纸或无光涂料纸。
2)提高润版液的PH值
因为润版液的酸性越强,对油墨连结料和颜料的分解力、腐蚀性就越大,致使印迹膜面粗糙,降低印刷品光泽。只有提高润版液的PH值,才能保证印刷品光泽。
3)加凡立水(0号油)。
这种油黏度很大,可调节油墨浓度,使稀墨变稠,增加印品光泽度。
4)加入亮光浆。
Gloss paste is processed from high-gloss raw materials, which can increase the gloss of the ink, but the amount should not be too large, otherwise it will reduce the drying speed of the ink and cause sticking and stringing.
5) Add desalination agent.
When some inks are too dark to meet the requirements of spot color printing, they need to be lightened. Adding a lightening agent can not only make the ink lighter, but also improve the gloss of the printed matter.
6) Add 01~94 resin gloss varnish (commonly known as No. 19 resin oil).
When the fluidity and transferability of the ink are not good, it can be transferred directly , which can not only improve the gloss of the ink, but also not affect the multi-color overprinting






