0 Preface
With the rapid development of my country's modernization, my country's aluminum industry, especially the production of aluminum alloy profiles for construction, has developed rapidly. my country has become the world's largest producer and consumer of aluminum extrusions. Due to the good performance of environmental protection, aesthetics, durability and recyclability of aluminum alloy profiles, good aluminum alloy building profiles have become the preferred choice for very good projects [1]. The main basis for evaluating the quality of aluminum profiles is GB5237 [2]. According to the surface treatment, aluminum profiles are divided into anodic oxidation, electrophoretic coating, powder coating, fluorocarbon spraying, etc. GB5237 also specifies the inspection standards for these types of aluminum profiles according to the surface treatment. The updates of GB5237 over the years are: GB5237-1985, GB5237-1993, GB5237-200, GB5237-2004, GB5237-2008, and the new GB5237.6-2012. It can be seen that the standards for aluminum alloy building profiles have been revised and improved many times to adapt to the technological development of various surface treatment methods that are emerging. The new GB5237-2008 has been implemented for five years. In the past few years of testing, the author has doubts about some details of the new standard on coating performance testing, and hereby raises it, hoping to be corrected by professionals.
1 Electrophoretic paint test in GB5237.3
GB5237.3 stipulates the test method and judgment standard of electrophoretic paint. In the course of the experiment, the author's general experience is that in the test of the project, the electrophoretic paint often fails in the project of alkali resistance. Literature [3] discussed the reasons for the unqualified alkali resistance and the improvement measures. The test showed that the reason for the unqualified alkali resistance of the electrophoretic painted profiles was due to the uneven temperature in the drying furnace (the temperature difference can reach 72°C). The temperature of some parts is too low. The item of the license is to make double samples. In this case, you need to pay attention when sampling, try to sample evenly, and it is better to make more samples when doing the test, so as to ensure the accuracy of the results.
The pencil hardness test of electrophoretic paint is unscientific to the author. Pencil hardness is measured using a pencil Hardness Tester. The original intention of using a pencil Hardness Tester is to unify the size of the force, which is a standard specification. However, the pencil Hardness Tester is now an iron block. When measuring, the force and the moving speed of the pencil cannot be measured. Definitely, so the effect of this pencil Hardness Tester is very small, and I hope these factors can be considered in the new revision of the standard.
Another test of electrophoretic paint that is prone to failure is detergent resistance. Generally, if the sample is not good in alkali resistance, it is often unqualified in detergent resistance. This may be related to the quality of the paint film.
2 Powder spraying test
In GB5237.4-2008, there are often unqualified or, often confusing, impact resistance tests. The impact resistance test was changed from version 08 to recoil, and the back of the coating was impacted during the test. The author feels that this test is somewhat similar to cupping. If it is to characterize the change of the coating under the action of a sudden external force, it is more realistic to hit the front side. In addition, the requirement for the impact depth is 2.5+0.3mm, which is a relatively high requirement for the Tester. Without the use of calipers, it is difficult to observe with the naked eye whether the impact depth is within the required range. Moreover, the plate thickness of each manufacturer is different, and the height of the hammer lift is also different, so it is difficult to punch out the required depth at one time. In addition, some samples are small in size, so it is impossible to punch out three qualified pits on one board. In addition, the impact test also sometimes fails. Most of the reasons should be that the curing is not done well, resulting in severe cracking of the coating during impact.
In GB5237.4-2008, there is another question that is often confused about hydrochloric acid resistance. Generally, the samples coated with white powder have no obvious change after the hydrochloric acid resistance test. However, there are some green or brown samples that will be slightly discolored after the hydrochloric acid resistance test, and the standard judgment is that "the surface of the coating after the visual inspection test should not have bubbles or other obvious changes", I do not know when a little discoloration How should it be assessed?
In GB5237.4-2008, the solvent resistance test becomes a separate method in Appendix B. The method for solvent resistance is to check the coating surface after wiping it 30 times with xylene. In the experiment, the author encountered that after the solvent resistance test, a change similar to a fuzzy layer occurred on the surface of the coating, the gloss decreased, and it was greater than 5 gloss units, and there was no scratch on the fingernail. How to judge at this time test results?
3 About the ambient temperature and humidity in the standard
In GB5237.3~GB5237.5, in the test of coating performance, the requirements for temperature and humidity are shown in Table 1 below.
Table 1 Requirements for coating performance test on temperature and humidity
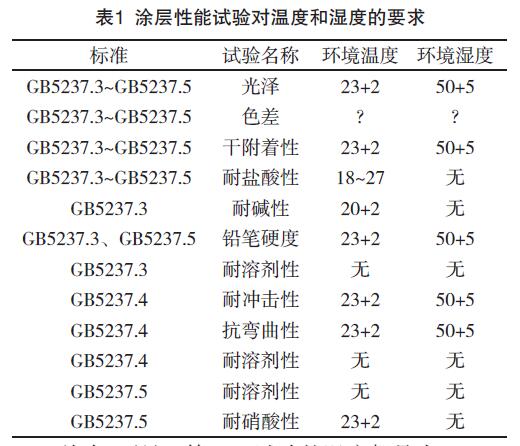
It can be seen from Table 1 that first, the temperature of the test is 23+2, and the humidity is 50+5. The special thing is the adjustment of alkali resistance, and the temperature is relatively low. In general, it is necessary to ensure that the test meets the temperature and humidity. Conditions, only the two temperatures of 21 and 22 are fully covered, otherwise two laboratories with different temperatures must be prepared for the test. I wonder if it is possible to test under the same temperature conditions? Second, in several standards such as gloss and color difference, the temperature and humidity are only stipulated for state adjustment, and there is no specific regulation for the test environment. The author conducted the test under the condition of state adjustment. I wonder if he understands the standard correctly? Third, the nitric acid resistance test, because of the volatility of nitric acid, needs to be carried out in a fume hood, and the fume hood is generally installed in the chemical laboratory. The chemical laboratory is not air-conditioned, and the temperature at this time is completely uncontrollable.
4 Suggestions and comments
As mentioned above, in the actual operation of the coating performance part of GB5237, some test methods are not particularly suitable for laboratory operations. It is expected that these tests can be considered to be improved when the standard is revised again, so that it can be quickly and accurately tested in accordance with the standard .





