What is paint?
Coating refers to coating on the surface of an object to form a dense, continuous and uniform film under certain conditions for protection, decoration or other special functions (insulation, rust prevention, mildew resistance, heat resistance, flame retardant, antistatic, wear-resistant, etc.) of a class of liquid or solid materials.
What is painting?
The paint is applied to the surface of the object with certain equipment and methods, and then dried and cured by natural or artificial methods to form a uniform thin film coating. This process is called coating.

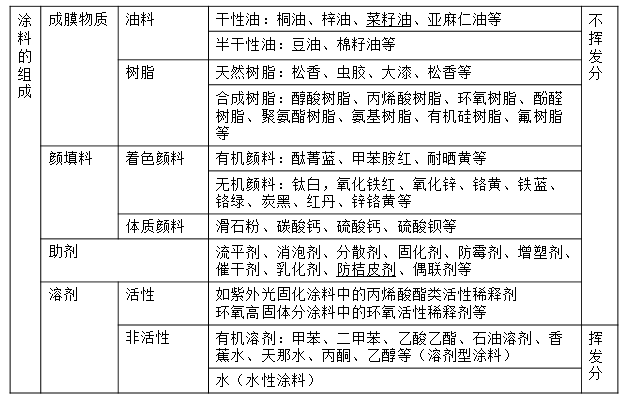
Classification of paint
(1) According to the form of coatings, it can be divided into water-based coatings, solvent-based coatings, powder coatings, high-solid content coatings, etc.;
(2) According to the construction method, it can be divided into brush coating, spray coating, roller coating, dip coating, electrophoretic coating, etc.;
(3) According to the construction process, it can be divided into primer, intermediate paint (surfacer), top coat, finish paint, etc.;
(4) According to the function, it can be divided into decorative coatings, anti-corrosion coatings, conductive coatings, anti-rust coatings, high-temperature-resistant coatings, temperature-indicating coatings, heat-insulating coatings, flame-retardant coatings, invisible coatings, antibacterial coatings, etc.;
(5) According to the application, it can be divided into architectural coatings, can coatings, automobile coatings, aircraft coatings, home appliance coatings, wood coatings, bridge coatings, plastic coatings, paper coatings, etc.
(6) my country's chemical industry department has classified coatings into 17 categories based on their main film-forming substances.
The role of paint
(1) Protective effect
(2) Decorative effect
(3) Special role
In addition to the functions of protection and decoration, the coating can also endow special functions such as insulation, antifouling, antibacterial, mildew resistance, damping, flame retardancy, temperature display, electrical conductivity, magnetic conduction, radiation protection, antistatic, and stealth.
Coating film formation method
(1) Physical film formation method
①Solvent volatilization and film formation
Such as nitrocellulose paint, asphalt paint and rubber paint, etc.
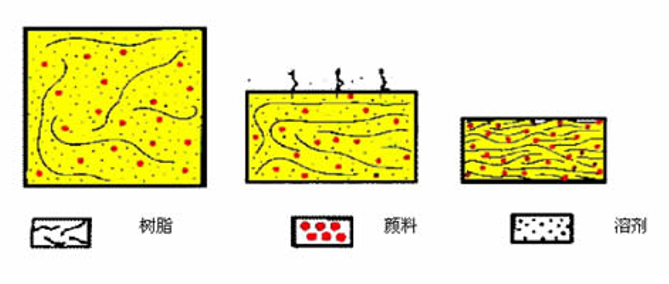
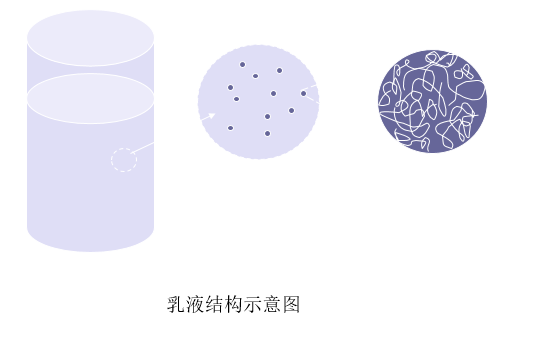
② Polymer coagulation and film formation
Such as architectural latex coatings, non-water-dispersible coatings and organic sols.
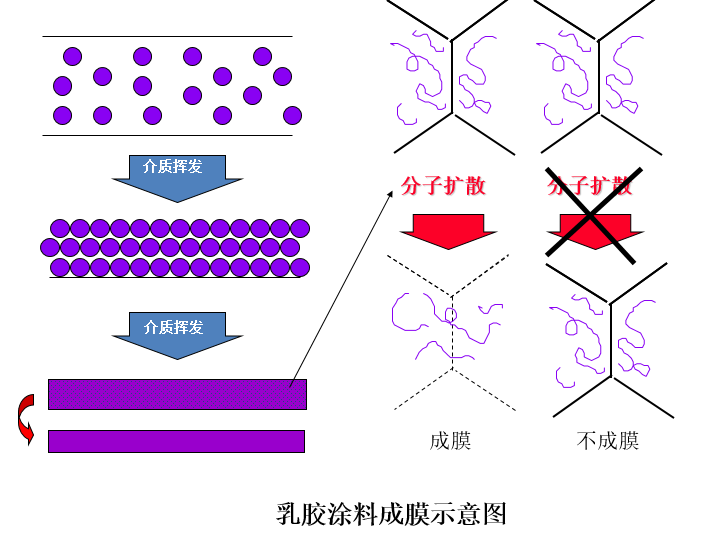
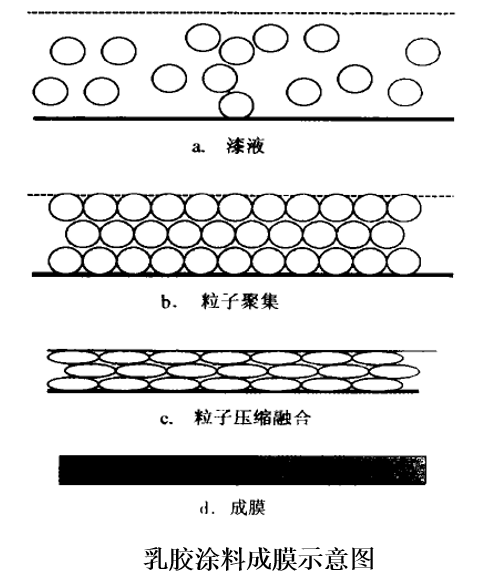
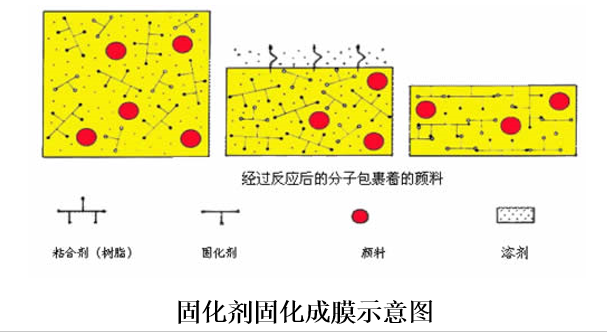
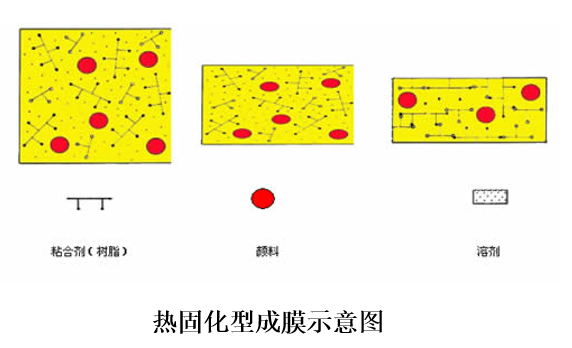
② Cross-linked curing type
According to the different ways of cross-linking initiation, the cross-linking curing type film can be divided into: curing agent curing type, heat curing type, ultraviolet light curing type, etc.
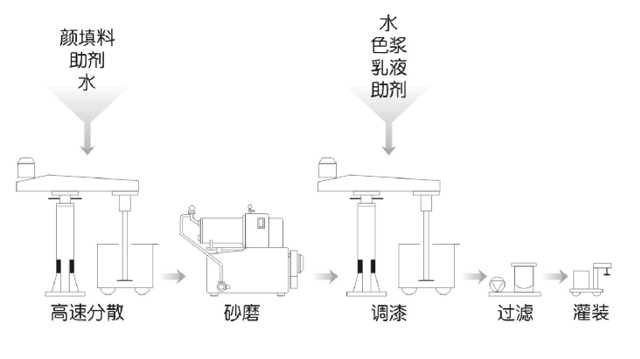
The characteristics of commonly used coatings
(1) Acrylic latex paint
(2) Solvent-based acrylic paint
(3) Polyurethane coating
(4) Nitro paint
(5) Epoxy coating
(6) Amino paint
(7) Alkyd paint
(8) Unsaturated polyester coating
(9) Vinyl paint
(10) Phenolic paint
Development Direction of Coatings and Functional Coatings
1 water-based paint
(1) Common water-based paints
(2) Water-based coatings with special functions
①Water-based anti-corrosion coating
② Water-based glitter paint
③ Water-based fluororesin coating
④ Functional water-based architectural coatings
⑤ Automotive water-based paint
⑥ Electrophoretic coating
⑦ High decorative water-based paint
Characteristics of light-curing coatings
a Save energy, the energy consumption is about 1/5-1/10 of heat curing paint.
b There is no solvent emission, which is safe and does not pollute the environment.
c Fast curing speed (0.1-10s), high production efficiency, suitable for assembly line production.
d can be coated on heat-sensitive substrates.
e The coating has excellent properties, such as good friction resistance, solvent resistance and adhesion resistance.

Coating Technology
Pre-painting treatment
Degreasing:
Degreasing (degreasing) mainly uses the dissolution, saponification, emulsification, wetting, penetration and mechanical effects of various chemical substances to remove oil on the surface of objects.
Rust removal on steel surfaces
Commonly used derusting methods include manual, small machinery (pneumatic, electric), spray (shot) shot (sand), high-pressure water (abrasive), pickling, electrochemical and flame derusting methods.
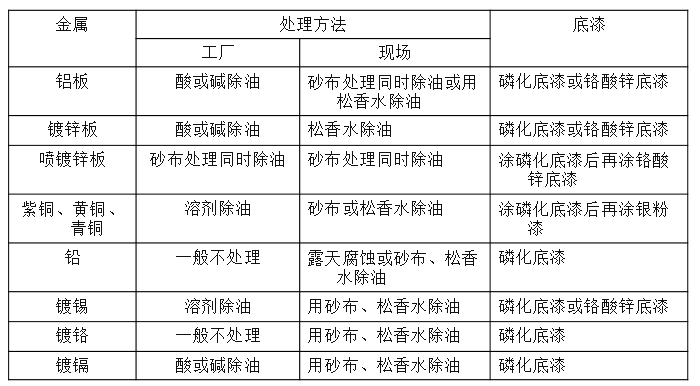
Surface treatment of plastic materials
Such as chemical treatment, surfactant treatment, flame treatment, grinding treatment, etc.
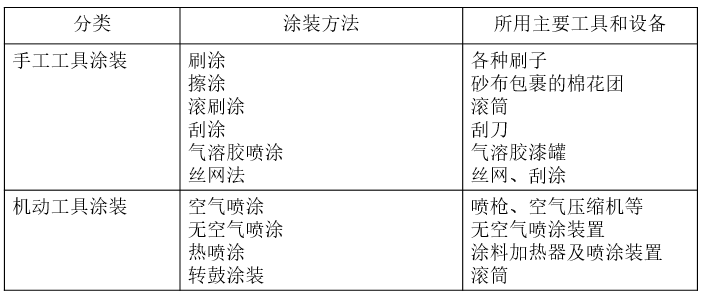
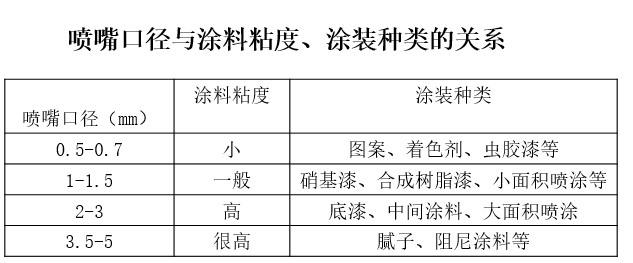
powder coating method
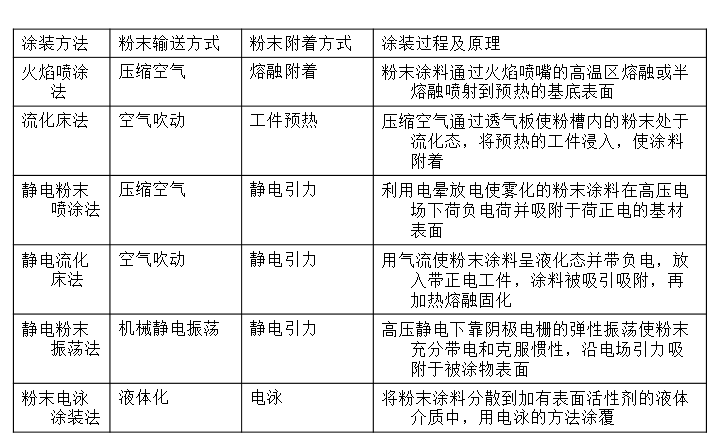
Electrostatic spraying method

