The role of paint
1. Improve the surface quality of castings
Sand molds and sand cores are microporous-porous systems. After the coating is applied, it not only fills the surface voids of sand molds and sand cores, but also establishes an effective fire-resistant barrier between molds and metal nights, which can prevent castings from mechanically sticking sand, Chemical sticky sand and surface roughness.
Surface roughness of non-painted castings is grade 11-12 (Rа25-50μm)
The surface roughness of coating castings is grade 8-9 (Rа3.2-6.3μm)
2. Reduce the tendency of many defects that are easy to occur without coating when sand casting
After using the coating, it can reduce the burr of the casting caused by the surface cracking of the sand mold or sand core
Reduce sand washing, sand loss, and sand holes that are easily produced due to insufficient surface strength of the sand mold (core)
Reduce the carbon increase, sulfur increase, phosphorus increase and subcutaneous pores caused by nitrogen in castings due to the use of resin sand
3. Improve the local surface properties and surface intrinsic quality of castings
Coating coatings containing bismuth and tellurium on the surface of sand molds and sand cores can eliminate local shrinkage and porosity of iron castings
Adding ferrosilicon powder can prevent local white spots on the surface of iron castings
Add a certain amount of alloy carbide powder (WC, TiC, Cr3C2, SiC, B4C) or some related iron alloy (Cr-Fe, W-Fe, Mo-Fe, Mn-Fe) powder, and make the surface of the cast iron part through infiltration or diffusion. It has some special properties, improves the properties of wear resistance, corrosion resistance and heat resistance, and has a certain surface alloying effect.
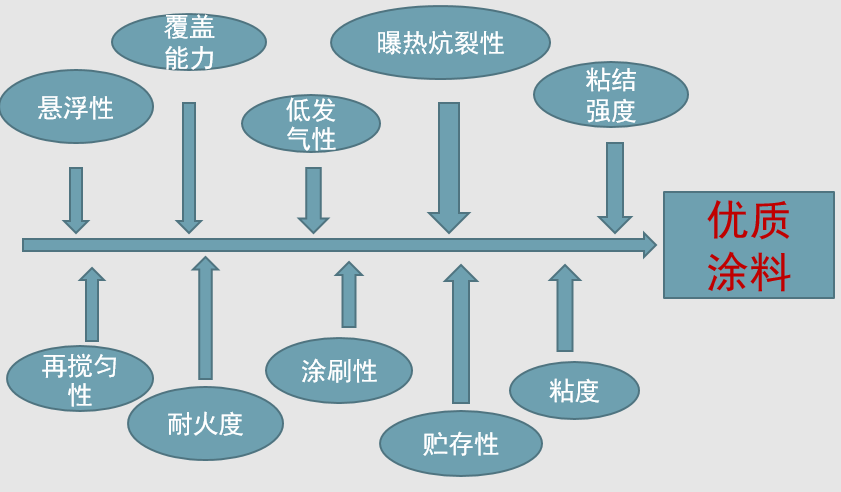
Properties of a Good Coating
1. Suspension
Water-based - Suspension ≥ 93% after standing for 24 hours
Alcohol base—suspension ≥ 90% after standing for 24 hours
2. Viscosity
Viscosity is the size of the viscosity of the paint itself, which refers to the nature of the deformation and flow of the paint when it is stressed
Viscosity is directly related to the coating and covering ability of the coating, which affects the brushing and leveling of the coating
Factors affecting viscosity are powder coating powder density, carrier liquid properties
3. Heat exposure crack resistance
Heat exposure crack resistance refers to the ability of metal to withstand high temperature stimulation without cracking and peeling after hardening or drying
Heat exposure crack resistance is generally divided into four grades according to the status of no cracks, micro cracks, medium cracks and severe cracks (including spalling): denoted as Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅱ, Ⅳ
Rating of heat exposure crack resistance:
Class I: The surface is smooth without cracks, or with very few fine cracks. There is no peeling phenomenon between the coating and the substrate sample
Class II: There are dendritic and net-like fine cracks on the surface, the crack width is less than 0.5mm, and there is no peeling phenomenon between the coating and the substrate sample
Grade III: There are dendritic or network cracks on the surface, the crack width is less than 1mm, the cracks are deep, and there are no penetrating cracks along the horizontal (horizontal circumferential direction) or vertical direction. There is no obvious peeling phenomenon between the coating and the substrate sample
Grade IV: There are dendritic or network cracks on the surface, the crack width is greater than 1mm, and there are penetrating cracks in the horizontal or vertical direction. There is peeling between the coating and the substrate sample
Coating application method
1. Brush method
A method of manually brushing the paint onto the mold (core), which requires the paint to have good brushability and leveling
Advantages: simple, flexible and commonly used coating method, commonly used in single piece small batch production
Disadvantages: the production efficiency is very low, and the coating quality is not easy to be stable
2. Spraying method
Under certain pressure conditions, the coating method is to spray the paint on the surface of the mold (core) in the form of mist or powder
Advantages: The spraying method has high production efficiency and can be used for large-area types (cores), especially for mass production occasions. The coating is smooth and clean with uniform thickness
Disadvantages: Since spraying is carried out under pressure conditions, the working environment is dusty, and protective equipment is required
3. Flow coating method
A method of manual low-pressure pouring with a flow coating device, generally suitable for large castings
Advantages: high production efficiency of flow coating, smooth and smooth coating, less paint waste, less environmental pollution, easy operation, suitable for both water-based and alcohol-based paints
Disadvantages: The thickness of the coating is not easy to control, and the requirements for the performance of the coating are relatively high
4. Dip coating method
The coating method is to dip the sand core into the coating tank mechanically or manually and then take it out, so that the sand core can be coated.
Advantages: high production efficiency, easy to obtain smooth and uniform coating, easy to realize mechanized operation, not only suitable for large-scale assembly line production, but also suitable for single-piece small-batch and manual operations
Disadvantages: The dip coating method requires the coating to have good consistency and yield value, and has high requirements for the carrier liquid, and no stratification can occur
The choice of coating method depends on the production method, the rhythm of on-site production, the size, structure and batch size of the sand mold (core), etc.
