(1) For iron and steel workpieces, the nickel plating layer is a cathodic plating layer, and a single layer of nickel cannot play an electrochemical protective role. Therefore, when plating nickel on steel parts, the pores of the coating should be reduced as much as possible to ensure that the coating has a certain thickness. In order to improve the protective performance of the coating , the above-mentioned multi-layer combination of double-layer and triple-layer nickel plating is often added with microporous chromium or microcracked chromium.
(2) Due to the good polishing properties of nickel, with the continuous innovation of nickel plating brighteners, full bright coatings can be directly plated in the electrolyte. If a layer of chrome is plated on its surface, the protective and decorative ability will be stronger. Therefore, nickel plating has been widely used in automobiles, bicycles, clocks, medical equipment, instruments, sewing machines, stationery and daily hardware, etc. , as a protective decorative coating.
(3) The basic principles of all nickel plating processes are the same. Nickel plating is the process of depositing a nickel coating on a base material. The nickel anode is dissolved and converted into nickel ions, and a metallic nickel coating is formed on the cathode. At the same time, due to the precipitation of , the current efficiency is reduced by 3%-7% compared with the normal process range. If the pH is too low, the hydrogen ions will detach and the hydrogen deposition rate will decrease. At the same time, under normal conditions, there will be no OH - discharge at the anode, and the anode current efficiency reaches 100%. If the pH is too high, the OH - will first release the charge and produce oxygen before the nickel dissolves . Therefore, the nickel anode will passivate and stop dissolving, and the concentration of nickel ions in the plating solution will gradually decrease, which will seriously affect production. It can be seen that improving the state of and electroplating conditions are important issues for nickel plating.
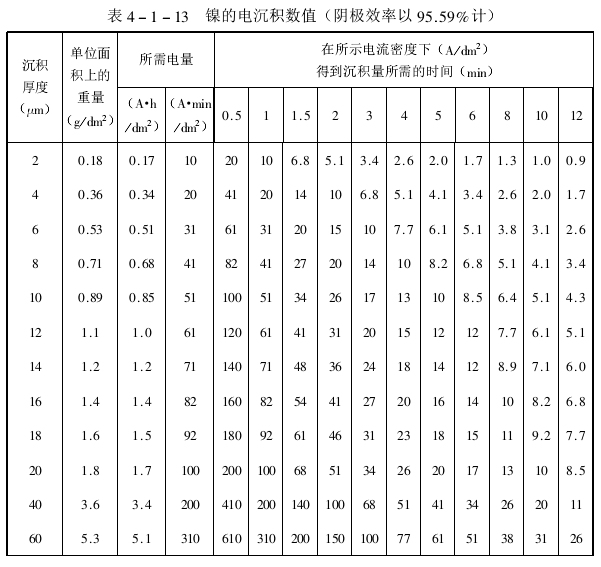
(4) Improve coating thickness and current distribution. In fact, the cathodic deposition efficiency of nickel is less than 100% due to the above-mentioned partial current consumption for hydrogen evolution. Table 4-1-13 lists the nickel electrodeposition values, which can be used to refer to some relevant nickel deposition data when the cathode efficiency is 95.59%, for practical reference. In actual production, the substrate of the plated parts cannot be absolutely flat, and there are always unevenness. The thickness of the natural nickel layer cannot be equal, and each plating solution has a certain conductivity. Generally, the protrusions on the surface of the plated parts are closer to the anode, from The current from the anode to the upper convex is larger than that to the lower concave, so the nickel deposited on the concave is thinner than the convex. Because metal deposition is closely related to the surface, geometry, position, cathode polarization, cathode efficiency and the electrochemical characteristics of the plating solution to the current distribution, etc., if the deposition resistance caused by cathode large, it is beneficial to the uniformity of the coating . Polarization reduces the current at the convex part of the surface of the plated part and increases the current at the concave part. When using a low average current density, the uniformity of the nickel bath can be increased. Typical nickel bath uniformity depends on the current density used.
Many metals require complexes in the bath to achieve electroplating. However, nickel plating does not require any complexes and additives , and nickel can be plated from simple nickel salts.
