1. Salt spray test
According to the different components of the solution used, the salt spray test can be divided into neutral salt spray test (NSS), acetic acid salt spray test (ASS) and copper salt accelerated acetic acid salt spray test (CASS). The NSS test was applied earlier and widely, but compared with the outdoor exposure test, the reproducibility is poor and the test cycle is long. ASS test is a kind of accelerated test with good attention. The CASS test is a general method for accelerated corrosion testing of copper-nickel-chromium or nickel-chromium decorative coatings.
See the table for specifications of various salt spray test solutions.
(1) Preparation of salt spray test solution
Distilled or deionized water should be used to prepare the salt spray test solution. Sodium chloride should not contain copper and nickel in principle, and the amount of sodium iodide (Nal) should be less than 0.1%, and the total impurities calculated in terms of dry salt should not exceed 0.4%. The pH value of the NSS solution after preparation should be 6.0~7.0, otherwise the harmful impurities in the water, salt or both should be checked. Adjust the pH value with analytically pure hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide.
Add glacial acetic acid to the NSS test solution, and adjust the pH value to 3.1~3.3 with analytically pure glacial acetic acid or sodium hydroxide to prepare the ASS solution.
The pH value of the CASS test solution is the same as that of the ASS test solution, the only difference is that 0.26±0.02g/L copper chloride (CuCl2 2H2O) is added to the ASS solution to accelerate the corrosion, and the test temperature is also increased to 50±2 ℃.
To remove any material clogging the nozzle, the test solution needs to be filtered before use. The spray test solution can only be used once.
(2) Salt spray test equipment
The salt spray Test Chamber that has been certified to meet the relevant standards should be selected. The volume of the salt spray box is not less than 0.2m³. The salt spray device includes a spray gas source, a spray chamber and a brine storage tank. The structural materials in the Test Chamber should not affect the corrosion performance of the salt spray; the salt spray must not be sprayed directly on the sample; the condensed droplets on the top of the fog chamber are not allowed to drop on the sample.
The salt spray Test Chamber can only be used after the following method is used to measure and adjust the salt spray deposition rate. In the exposure area of the box, place at least two clean mist collectors. The mist collector consists of a 10 cm diameter funnel inserted into a graduated container. Its collection area is 80cm². When placed, one is close to the nozzle inlet and one is away from the nozzle inlet. Only salt spray is required to be collected, not liquid dripping from the test specimen or other parts of the chamber. Start the salt spray box for continuous spraying for 8 hours, and calculate the average number of sedimentation milliliters collected by the 80cm² fog collector per hour. According to the measurement results, adjust the spray collection speed and collection concentration in the box to keep it within the range specified in the table.
At present, continuous spraying is commonly used, and the recommended test cycle is shown in the table.
(3) Placement and requirements of samples
① The number of samples is generally specified as 3 pieces. Before the test, the sample needs to be fully cleaned. The cleaning method depends on the surface condition and the nature of the dirt. Do not use any abrasives and solvents that will attack the surface of the specimen.
② The position of the sample in the box should be such that the flat sample to be tested forms an angle of 15~30° with the vertical line, the main surface of the sample is upward, and is parallel to the main direction of the salt spray flow in the box.
③ During the test, the samples shall not touch each other or the box wall. The spacing between the specimens shall be such that the salt mist can settle freely on the major surfaces of the specimens. The saline solution on one specimen shall not drip on any other specimen.
④ Specimen holders shall be made of inert non-metallic materials such as glass, plastic or properly coated wood. If the sample needs to be hung, the material of the hanger cannot be metal, but artificial fiber, cotton fiber or other inert insulating materials are required, and the liquid droplets on the bracket must not fall on the sample.

The 1986 national standard used in this article is equivalent to the ISO1976 standard, which is the current new standard.
⑤ The cutting edge of the sample and the place where identification marks are made shall be coated with appropriate materials.
⑥After the test, take out the sample and let it dry naturally indoors for 0.5~1h, then gently wash or soak it with running cold water to remove the salts deposited on the surface of the sample, blow it dry with a hair dryer, check it, and evaluate the grade.
(4) Evaluation of results
In order to meet special requirements, many different test result evaluation criteria can be used. Examples include changes in mass; changes shown by microscopic observation; or changes in mechanical properties. Routine records for most tests should include: appearance after test; appearance of removal of surface corrosion products; distribution and number of corrosion defects, i.e. pitting, cracks, bubbling; time of onset of corrosion, etc.
For various electroplating layers and product parts that need to be used in different environments, the salt spray test cycle, evaluation method and qualification standards should meet the product technical conditions.
2. Corrosion paste test (CORR test) (ISO4541-78)
Apply the mud paste containing corrosive salts on the sample to be tested, and after the corrosion paste dries, expose the sample under high relative humidity conditions for a specified period of time. This method is suitable for rapid identification of the corrosion resistance of copper-nickel-chromium coatings and nickel-chromium coatings on iron and steel substrates and zinc alloy substrates. The corrosion images of CASS test and CORR test are closer to the actual use conditions.
(1) Composition of corrosion paste
Copper nitrate Cu(NO3)2 3H2O——0.035
Ferric chloride FeCl3 6H2O——0.165g
Ammonium chloride NH4Cl——1.0g
Washed ceramic grade kaolin - 30g
Distilled water H2O——50ml
(2) Preparation of corrosion paste
将计算量的硝酸铜、氯化铁、氯化铵溶于 )50ml蒸馏水中,然后加入高岭土,充分搅拌均匀即可。腐蚀膏应现配现用,所有化学药品需要为化学纯。
(3)试验方法
①试验前试样可用适当的溶剂如乙醇、丙酮清洗,但不能使用有腐蚀性或能生成保护膜的溶剂进行清洗。
②用干净的刷子将腐蚀膏均匀地涂敷在试样上,并使其湿膜厚度达到0.08~0.2mm。在室温和相对湿度低于50%的条件下干燥1h。
③干燥后将试样移到温度为38±2℃相对湿度为80%~90%且无凝露在试样表面上产生的湿热箱中,连续暴露16h为一个周期。除投放或取出试样需要短暂间断外,湿热箱应连续运行。
④试验周期及循环次数应在受试覆盖层或产品技术规范中规定。若试验需进行两个周期以上,则第一个周期结束后,用清水及海绵将试样上的膏剂清除干净,再用前述方法涂上新的腐蚀膏,重复循环试验。
(4)试样的检查和评定
①钢铁试样上的镀层,将试样干燥后,检查腐蚀膏中出现的腐蚀点的大小和数量。为使锈点便于观察,可除去试样上的腐蚀膏,并在中性盐雾条件下暴晒4h。或在温度为38℃、相对湿度为100%的湿热箱里暴露24h,以显示出腐蚀锈点。有时为了检查试样外观破坏情况,用清水和海绵将腐蚀膏清除,干燥后检查外观光泽和开裂变化情况。
②锌合金或铝合金制件上的镀层用清水及海绵将腐蚀膏清除,干燥后检查镀层外观光泽、开裂及基体金属腐蚀锈点等。
3、周期浸润腐蚀试验(HB5194-81)
周期浸润(简称周浸)试验是一种模拟半工业海洋性大气腐蚀的快速试验方法。本试验适用于锌、镉镀层、装饰铬镀层以及铝合金阳极氧化膜层等的耐蚀性试验。其加速件、模拟性和再现性等方面均优于中性盐雾试验。
(1)试验设备
采用FL-65类型的轮式周浸试验机。
(2)试验溶液和补给溶液
试验溶液、补给溶液及试验规范见表。
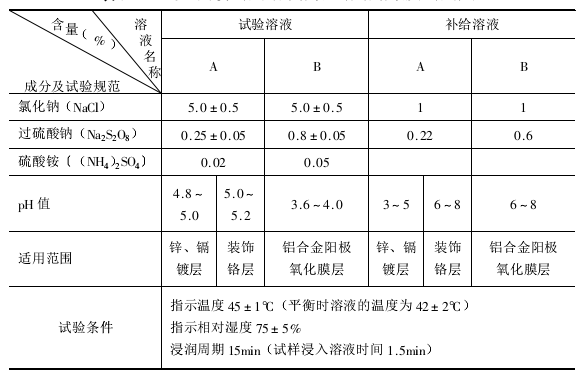
注:
1.除过硫酸钠为分析纯外,其余化学试剂均为化学纯,并用蒸馏水配制。
2.溶液的PH值用醋酸或冰醋酸调整。
3.液面高度和溶液浓度由周浸试验机补给系统自动保持与补偿
(3)试样
试样尺寸一般为60×40mm或100×50mm,每组试样一般为5个,不应少于3个。
(4)试验结果的检查与评定
According toHB5192-81镀层和化学覆盖层表观腐蚀等级评定方法,腐蚀等级的规定可According to腐蚀破坏百分率分成8个级别。腐蚀破坏百分率是According to试样表面斑点状破坏的多少和大小,对照标准图评出密度和大小,再通过计算和查表便可得出腐蚀等级。具体评定方法见HB5192-81。
(5)试验周期
试验延续时间及耐蚀性质量要求见下表。
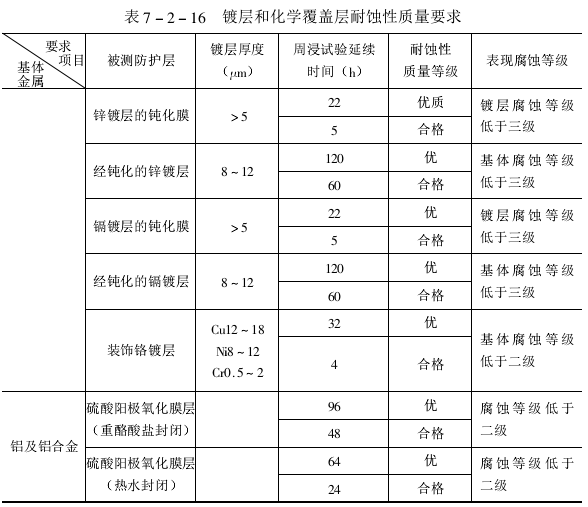
注:锌镀层、镀层钝化后应放24h(但不超过一个月),再进行周浸试验。
4、通常凝露条件下二氧化硫试验(ISO6988-85)
含有二氧化硫的潮湿空气能使许多金属很快产生腐蚀,其腐蚀形式类似于它们在工业大气环境下所出现的形式。因此,二氧化硫试验作为模拟和加速试样在工业区使用条件下的腐蚀过程。主要用于快速评定防护装饰性镀层耐蚀性和镀层质量。
(1)试验设备
试验箱应安装有温度调节、排气处理、加热装置;SO2气体瓶及气体定量稀释装置;浓度调节装置等,且密封性能要好。
(2)试样的暴露方式
①置于箱内支架上的试样,它们之间的距离不得小于20mm,试样距箱壁或箱顶不得小于100mm,试样下端与箱底水面的距离不得小于200mm,试样与支架之间的接触面积要尽可能小。
②放置试样时,要使试样或支架上的任何冷凝水不得滴落到下方的其它试样上。
③暴露试样表面严格朝南。平板试样表面应与垂直方向成15°±2°角倾斜放置。
试验周期:以 24h为1个试验周期。一个试验周期内可在试验箱内连续暴露;也可先在试验箱内暴露8h,然后将试样置于室内环境大气中(温度为23±5℃,相对湿度<75%,暴露16h。
试验总时间按产品技术条件规定进行。
5、电解腐蚀试验(EC试验)(ISO4539-80)
本试验对户外使用的钢铁件和锌合金压铸件上铜-镍-铬或镍-铬镀层的耐蚀性鉴定是个快速、准确的方法。
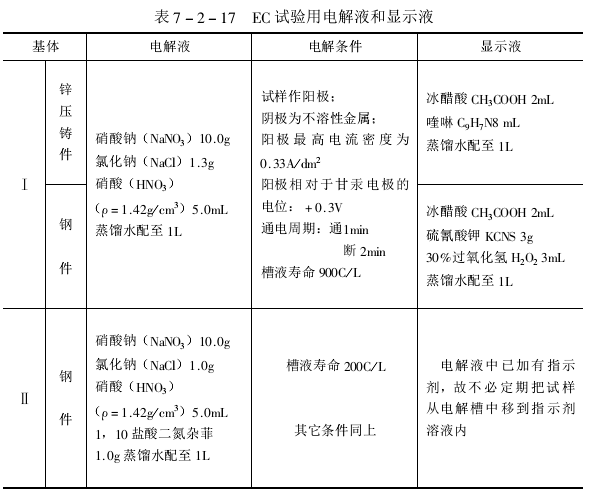
电镀试样在规定的电解液中使用一定的电位和预定时间进行阳极处理(一般通电1min),然后断电,让试样在电解液中停留约2min,再取出清洗,并将它浸入含有指示剂的溶液中,使指示剂与基体金属离子(锌或铁离子)产生显色反应,以检查试样的腐蚀点。检查后再把试样浸入电解液,按产品试验要求重复上述实验多次。电解时间由模似的使用年限决定。
EC试验所用的电解液和腐蚀点显示液见表:
6、硫化氢试验
本方法采用必要的空调和减压装置,直接向试验箱内通入含硫化氢(#$%)气体的空气,H2S含量为10×10-4%~15×10-4%。箱内温度为25±2℃,相对湿度为 75%±5%。也可以在玻璃干燥器的底部贮水,以保持干燥器内有较大的相对湿度(一般大于75%即可)。将盛有适量硫化钠的烧杯放入干燥器,再从分液漏斗向干燥器导入相应量的硫酸溶液,使其产生硫化氢气体,浓度大约为0.3~0.5%。
本方法常用来检验银镀层及带有保护层的银镀层在含H2S气体中的大气腐蚀情况。但硫化氢毒性大,且有特别臭味,故不建议作为一般的镀层质量鉴定。
7、硫代乙酰铵腐蚀试验(TAA试验)
本试验是将试样暴露在由硫代乙酰铵逸出的蒸汽之中,并由饱和醋酸钠溶液维持具有75%的相对湿度。本试验适用于评价银或铜防变色处理的效能和检查这些金属上的贵金属镀层的不连续性。
应当注意,硫代乙酰胺是一种致癌物,应避免与皮肤接触。
8、湿热试验
为了模拟电镀层在湿热条件下受腐蚀的状况,所以由人工创造洁净的高温高湿环境进行试验。但由于这种试验对电镀层的加速腐蚀作用不很显著,故湿热试验一般不单独作为电镀工艺质量的鉴定,而是作为对产品组合件、包括电镀层在内的各种金属防护层的综合性鉴定。
(1)试验设备
可采用湿热试验箱或湿热试验室。
(2)试验方法
①恒温恒湿试验:温度40±2℃,相对湿度95%以上,用于模拟产品经常处于高温高湿条件下的试验。
② Alternative temperature and humidity test: temperature rise from 30°C to 40°C, relative humidity ≥ 85%, time 1.5~2h. High temperature and high humidity 40±2℃, relative humidity 95%, time 14~14.5h. Cool down, from 40±2°C to 30°C, relative humidity 85%, time 2~3h. Low temperature and high humidity, 30±2°C, relative humidity 95%, time 5~6h.
This method simulates that products are often exposed to environmental conditions that cause condensation due to changes in temperature and humidity.
③High temperature and high humidity test: the temperature is 55±2°C, the relative humidity is higher than 95%, and it is exposed for 16 hours when there is condensation. Turn off the heat source to circulate the air. When the temperature drops to 30 °C , keep the sample for 5 hours as a cycle. Check the samples after each cycle.
This method is suitable for the hot flush test of the colorless passivation film on the zinc layer, but the effect is not significant and the cycle is long, so it is not commonly used in the corrosion resistance test of the coating.
(3) Quality evaluation of coating damp heat test
Good: the color is darkened, the coating and the underlying metal are free of corrosion;
Qualified: the corrosion area of the coating does not exceed 1/3 of the coating area, but the underlying metal has no corrosion except for edges and corners;
Unqualified: The corrosion of the plating covers 1/3 or more of the total area, or the underlying metal is corroded








