1. Evaluation of electroplated samples after corrosion resistance test of cathodic coating --- evaluation of appearance level and protection level (GB6461-86)
This rating method is based on the 10×15cm standard electroplating sample exposed to the outdoor natural atmosphere test, and is also used to evaluate the corrosion state of the sample after the accelerated corrosion test. Such as neutral salt spray test, acetic acid salt spray test, copper salt accelerated acetic acid salt spray test, corrosion paste test.
This method is only suitable for decorative and protective coatings that are cathodic to the substrate, such as nickel-chromium or copper-nickel-chromium plating on steel and zinc die castings. This method is generally not used for anodic coatings such as zinc and cadmium coatings on steel.
(1) Rating principles
①Since this method is applicable to the decorative and protective coatings that are cathodes to the substrate, the rating of the coating’s ability to protect the substrate from corrosion is called the “protection” grade. The grades evaluated for the comprehensive appearance defects (including defects caused by exposure) of the samples after the test are called "appearance" grades. For purely protective (not decorative) cathodic coatings, the appearance grade may be omitted.
② For the test results of the sample, use slashes (/) to record the two levels respectively, and record the protection level first.
③ In addition to recording the grade of the sample, the type and severity of the defects affecting the rating are also to be indicated.
(2) Evaluation of protection level
According to the area covered by the corrosion defect, the protection level is calculated according to
R=3(2-lgA)
Among them, R represents the protection level, and A is the percentage of defects in the total area.
The relationship between the defect area percentage and the protection level is as follows:
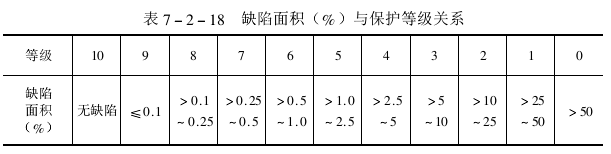
The area of corrosion defects can be identified by means of sample photos and dot diagrams as comparison standards (see ISO4540-86, GB6461-86 for details).
The types of common corrosion defects vary with the type of atmospheric exposure. Typical decorative coatings tend to be prone to corrosion pitting damage in marine atmosphere exposure, while pinhole corrosion is more likely in industrial atmospheres. At the same time, the coating is more severely corroded than the base metal in the industrial atmosphere. (Therefore, comparison photos or charts of the same standard are not available for all area types.) Photo ratings are more appropriate for tests exposed to marine atmospheres, while dot plots are more appropriate for industrial atmospheric tests.
The evaluation process should not only evaluate one by one against the standard system, but also conduct comparative evaluation on the whole group of samples, so as to re-examine each sample and make sure that the grades evaluated can truly reflect the advantages and disadvantages among them.
(3) Evaluation of Appearance Grade
①Assessing the appearance level is related to many factors, so the appearance level is not evaluated with the same precision as the protection level. It is not only based on the area of the defect, but also on the severity of the defect loss.
②Appearance grade is based on protection grade, but cannot be higher than protection grade. Because the corrosion of the base metal also damages the appearance.
If corrosion of the base metal is the only defect and there are no other defects affecting the coating, the appearance class is the same as the protection class. If there are surface defects that do not belong to the protection class, the appearance class is 1 or more grades lower than the protection class.
③ During evaluation, according to the test requirements, the damage to the appearance of the covering layer should be divided into:
a. Very slight; b. Slight; c. Moderate; d. Serious.
According to the above classification, the evaluation shall be carried out according to the following principles.
① For minor appearance defects, the appearance grade shall be lowered by one or two grades compared with the protection grade, for very minor defects by one grade, and for slight ones by two grades.
② If the appearance defect is moderate, the appearance grade shall be lowered by three or four grades than the protection grade.
③ If the appearance defect is serious, its appearance level shall be lowered by five levels or more than the protection level.
2. Evaluation of accelerated corrosion test results of cathodic coating——Evaluation of corrosion resistance grade (GB9797-88)
This method is only applicable to cathodic coatings such as nickel-chromium or copper-nickel-chromium coatings on steel or zinc die-castings after atmospheric exposure tests, salt spray tests, acetic acid salt spray tests, copper salt accelerated acetic acid salt spray, etc. Test, industrial atmospheric test, and decorative chromium coating after corrosion paste test, the various corrosion results produced, make a corrosion resistance rating. This method only considers the corrosion of the base metal. It uses 25mm² as the calculation unit of area, and the small parts whose main area is less than 100mm² do not use this rating method.
(1) Calculation of corrosion rate
Use a piece of transparent plexiglass or plastic film with squares (5mm×5mm) to cover the main surface of the sample coating, then the main surface of the coating is divided into several squares, calculate the total number of squares N, and Among these squares are squares η containing one or more corrosion sites.
Corrosion rate γ (%) = η/N × 100
(2) Corrosivity Rating
According to the relationship between the corrosion rate and the rating (see the figure below), the corrosion resistance rating result is determined.
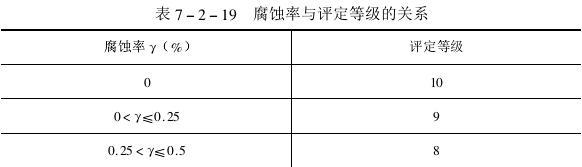
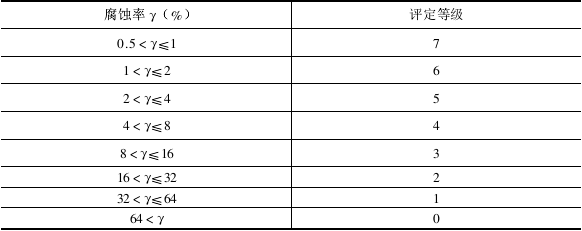
The larger the percentage value of the corrosion rate represented by the numbers in the table, the lower the rating, indicating the worse the corrosion resistance. opposite
In other words, the smaller the percentage of corrosion rate, the higher the rating, indicating the better the corrosion resistance.
(3) Rating description
①Main surface: refers to the part of the coating surface that plays an important role in the appearance or performance of the coating.
②腐蚀点:它是一种表面腐蚀缺陷,该处镀层被穿透,出现基体金属的腐蚀产物或镀层起皮。若镀层变色或其他外观损伤,但不穿透至基体,则在作耐蚀性评级时,不作为腐蚀点计算。腐蚀点的大小,是指被穿透的镀层面积大小,而不是伴随产生的锈迹面积大小。
③取样时应注意试样面积:用作评定镀层质量的试样主要表面,面积应大于5000mm²若单个试样主要表面面积小于5000mm²,则应取含有足够数量的试样,使得试样总表面积不小于5000mm²。
3、阳极性镀层———经腐蚀试验后的电镀试样评级(GB12335-90)
GB1235-90规定了阳极性覆盖层试样经腐蚀试验后试样腐蚀状态的评定方法。
本评定方法适用于对基体金属呈阳极性的保护覆盖层例如钢上经或未经钝化处理的锌镀层或铜上经或未经钝化的锡镀层等的试样,经户外大气暴露试验后的评级,也用于同类试样经加速腐蚀试验后的评级。
(1)外观评级
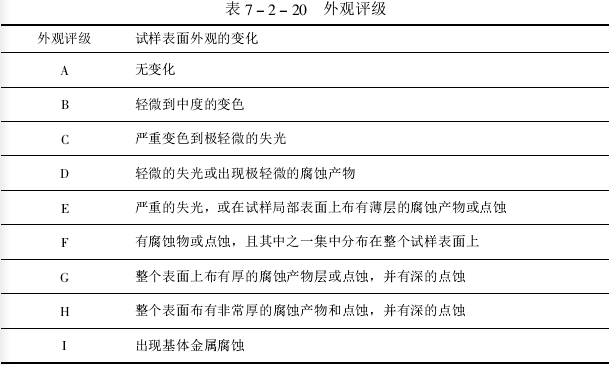
According to试样表面的外观变化(包括变色、失光、覆盖层腐蚀和基体金属腐蚀)对试样表面的腐蚀缺陷程度进行外观评级(以英文字母 1 2 3 表法)。
外观评级与试样表面的外观变化关系见下图。
(2)腐蚀评级
According to腐蚀缺陷占总面积的百分数,按下列公式计算而得:
R=3(2-lgA)
其中R表示腐蚀评级;A表示腐蚀缺陷占总面积的百分数。
According to公示求出R值并修正为较接近的整数。
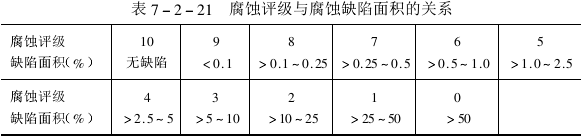
腐蚀缺陷面积的判定可借助于 GB12335-90附录中“腐蚀缺陷圆点图”作为比较标准。如果试样缺陷比X级稍好,但又不如X+1级,则评为X 级,如果试样比X级稍差,但又好于X-1级,则评为X-1级。
(3)腐蚀等级
试验结果的评定应综合表7-2-20和表7-2-21所表示的腐蚀缺陷程度和被腐蚀面积提出腐蚀等级报告。其表示方法是先定外观评级字母,接着写腐蚀评级数字。当基体金属出现腐蚀时,再加斜线,斜线下方定1。例如腐蚀等级为C1,则表示外观评级为C级,腐蚀评级为1;又如,腐蚀等级为F4/1,则表示外观评级为F级,腐蚀评级为4级,I表示有基体腐蚀。
4、金属镀层和化学处理层的耐蚀性标准
(1) The corrosion resistance of zinc electroplating layer and cadmium electroplating of steel parts (see GB9800 for details) neutral salt spray test method, the time for white corrosion products to appear on all levels of chromate conversion coatings should not be less than the time shown in the table Values listed on 7-2-22
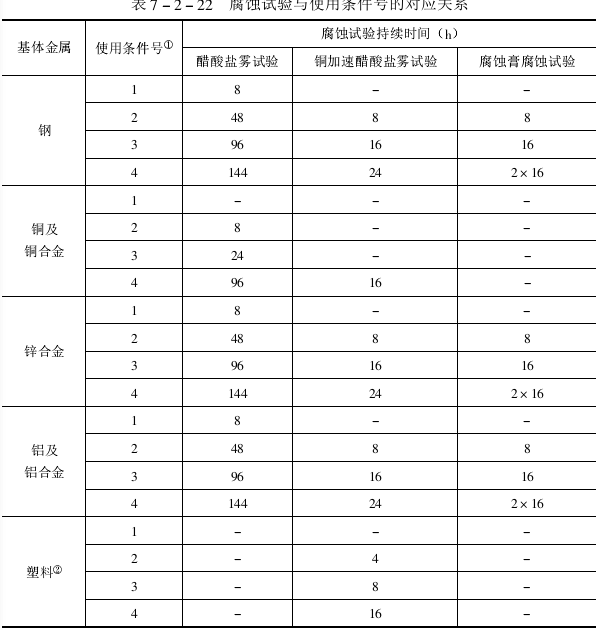
① For the corresponding relationship between the service condition number of the coating and the coating classification number, see GB9797-88 for details, and the horizontal line in the table indicates that there is no test requirement.
② After the plastic parts are subjected to the copper-accelerated acetic acid salt spray test, there should be no defects such as copper layer corrosion, plastic substrate exposure, and plating layer blistering.
2. Corrosion resistance of nickel/chromium and copper/nickel/chromium plating on various substrates (see GB9797-88, GB12600-90 for details)
The nickel/chromium and copper/nickel/chromium plating layers on iron and steel parts, copper and copper alloys, zinc alloys, aluminum and aluminum alloy plating parts, and plastic parts shall be tested according to one of the corrosion tests listed in Table 7-2-22. Corrosion test, the duration of the test should correspond to the service condition number, and the type of corrosion test should be specified by the user.



