Porosity is one of the important indicators to test the quality of coating. For anti-carburizing, nitrogen, and cyanide coatings, the determination of this index is even more important.
The methods for measuring the porosity of coatings include corrosion method, electrographic method, gas infiltration method, and photographic method.
The gas permeation method is determined according to the penetration of gas through the electroplating layer. This measurement requires a special vacuum device. Moreover, only the thin coating (within 5 μm) peeled off from the base metal can be measured, and the measurement results are quite different from the actual situation.
The photographic method is to use light to pass through the stripped coating, and develop and fix it on the photographic negative plate, so as to obtain a photo with black spots, so that the pores of the coating can be seen at a glance. Its disadvantage is the same as that of the gas infiltration method, and the small and tortuous pores are not easy to find.
Corrosion method and electrographic method are commonly used methods in CHINA at present. Among them, the corrosion method is simple, effective and widely used.
1. Corrosion method
After neutral salt spray, acetic acid salt spray, copper accelerated acetic acid salt spray test and corrosion paste test, the pores of the coating can be predicted according to the corrosion spots on the surface of the coating. However, the commonly used corrosion methods are wet filter paper sticking method, pouring method, followed by gas corrosion method.
1. Wet filter paper sticking method
(1) See the table for the test solution composition and measurement conditions.
(2) Measurement precautions
① In order to show the pores to the steel, copper or brass substrate, the test paper that can show the pores should be placed on a clean glass plate, and a few drops of * potassium ferrocyanide solution should be dropped on the test paper to remove the paper and Yellow spots from nickel plating, leaving only blue spots from steel substrates or reddish-brown spots from copper or brass substrates.
② In order to show the pores of the nickel coating, put the test paper that can show the pores flat on a clean glass plate, and evenly add a few drops of ammonia solution of dimethylglyoxalxime on the test paper (the solution preparation method is Dissolve '+ dimethylglyoxalxime in 500ml of 25% ammonia). At this time, the yellow spots on the filter paper showing to the bottom layer of nickel changed to an easily identifiable rose color. After washing with clean water and drying, the colored spots on the steel and copper layers disappear.
③ In order to measure the porosity of the multi-layer coating whose outer layer is chrome, it should be carried out more than 30 minutes after chrome plating. For copper-plated steel parts, multi-layer chrome-plated layers on copper and copper alloys, when measuring pores, the spots that show the pores of the bottom layer of copper and copper alloys cannot all be printed on the filter paper. Therefore, reddish-brown spots appearing on the specimen should be counted.
(3) Calculation of porosity
The porosity of the coating can be calculated by the following formula
Porosity=n/S
Among them, n represents the number of pore spots; S is the measured coating area (cm²)

The arithmetic mean of three tests was taken as the measurement result.
2. Impregnation method (dipping method, pouring method)
See Table 7-2-24 for the solution and measurement steps used to measure the porosity of the coating by dipping method.
3. Gas test (ASTM B583-80)
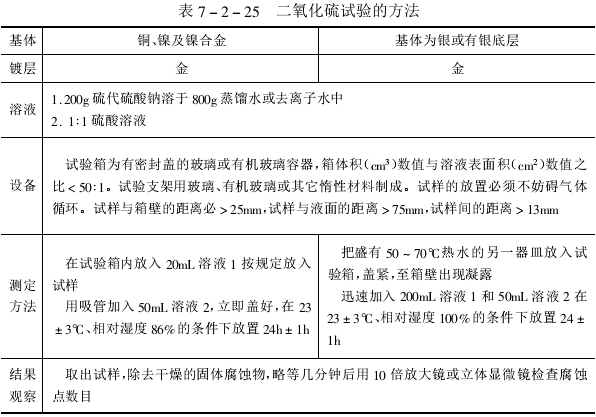
(1) Sulfur dioxide test
The method of sulfur dioxide test is shown in Table 7-2-25.
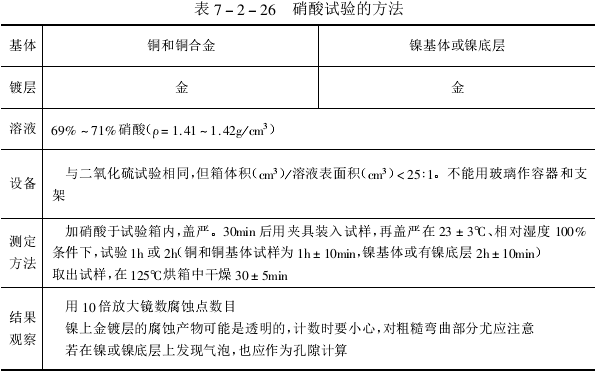
(2) Nitric acid test
The method of nitric acid test is shown in Table 7-2-26.


Note: 1. The test should be carried out in a fume hood.
2. When used in high-strength alloy substrates (especially when the copper content is greater than 10%), there will be cracks caused by stress corrosion, which will significantly increase the number of defects and result in inaccurate results.
Second, the electrographic method
1. Test principle
During the test, the base metal of the coating is energized to dissolve the anode. The dissolved metal ions pass through the pores in the coating and electrophoretically migrate to the test paper. Staining spots are formed due to the reaction of metal ions and certain chemical reagents on the test paper. Therefore, the number of coating pores can be judged according to the number of staining spots on the test paper, and the test principle diagram (see Figure 7-2-12). This method can be applied as long as the appropriate anodic dissolution conditions and chemical reagents with specific reactions are selected.
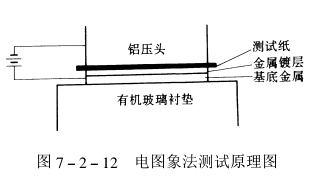
The electrographic method is easy to operate; the display is rapid; the obtained data is accurate, so it is a better test method. It can provide permanent information on the shape, size and location of the coating's pore structure.
The electrographic method is suitable for porosity testing on flat surfaces and low-curvature surfaces where suitable fixtures can be used.
2. Instrument
The domestic DXY-1 coating porosity Tester has been widely used in the electronics, machinery, chemical industry, light industry and instrument industries to test the porosity of various metal coatings.
3. Test procedure
Clean the coating surface of the sample to be tested with ethanol or distilled water, then place the sample on the plexiglass pad under the pressure block of the test instrument, and cover the surface of the tested part with two layers of test paper wetted with distilled water (use barium-based paper or more than 200g Coated paper), use dry blotting paper or filter paper to absorb excess water and maintain a certain humidity, you can start the test. The specific test procedure, the preparation and selection of the color developer shall be carried out according to the instruction manual of the instrument.
