With the development of modern technology, infrared thermometers are widely used in power line inspection, maintenance and substation operation, to detect abnormal temperatures of power equipment, power distribution equipment, cables, electrical connectors, etc. under operating and electrified conditions, and found that Defects in electrical equipment. Whether the infrared thermometer in use is in good working condition directly affects the safe and stable operation of the power grid. In order to improve the quality of work and ensure safety, self-calibration of infrared thermometers must be carried out to ensure that the infrared thermometers in operation are in good working condition.
1. The principle of black body radiation and infrared temperature measurement
All objects with a temperature higher than absolute zero are constantly emitting infrared radiation energy to the surrounding space. The size of the infrared radiation energy of an object and its distribution according to the wavelength have a very close relationship with its surface temperature. Therefore, through the measurement of the infrared energy radiated by the object itself, the optical system of the thermometer is converted into an electric sensor on the Detector. Signal and through the display part of the infrared thermometer to display the surface temperature of the measured object, it can accurately measure its surface temperature, which is the objective basis for infrared radiation temperature measurement.
Features of infrared thermometer: non-contact measurement, wide temperature measurement range, fast response speed, high sensitivity, but due to the influence of the emissivity of the measured object, it is almost impossible to measure the real temperature of the measured object, the measurement is the surface temperature.
The standardized verification method of infrared thermometer is to use black body furnace verification. A black body refers to an object whose absorptivity for incident radiation of all wavelengths is equal to 1 under any circumstances. A black body is a satisfactory object model, so a radiation coefficient that varies with material properties and surface states is introduced, that is, the emissivity , which is defined as the ratio of the radiation performance of an actual object to that of a blackbody at the same temperature. The law of radiation and absorption of infrared radiation of an object satisfies Kirchhoff's law. When a beam of radiation is projected onto the surface of any object, according to the principle of energy conservation, the sum of the object's absorptivity, reflectivity, and transmittance to the incident radiation It must be equal to 1. Generally, the emissivity is not easy to measure. Usually, the emissivity can be determined by measuring the absorptivity. Therefore, the blackbody radiation source is used as a radiation standard to verify the radiation intensity of various infrared radiation sources.
The infrared thermometer is composed of optical system, photoelectric Detector, signal amplifier, signal processing, display output and other parts. The radiation from the measured object and the reflection source is demodulated by the modulator and then input to the infrared Detector. The difference between the two signals is amplified by the anti-amplifier and controls the temperature of the feedback source, so that the spectral radiance of the feedback source is the same as that of the object. The display indicates the brightness temperature of the measured object. The temperature measured by the infrared thermometer is the radiation temperature of the object rather than the actual temperature of the object. Since the absolute black body does not exist, the total amount of thermal radiation of the actual object at the same temperature is always smaller than the total amount of absolute black body radiation, so the infrared measurement The temperature measured by the thermometer should definitely be lower than the real temperature of the object. When measuring temperature, the emissivity of the infrared thermometer should be set as much as possible (for infrared thermometers with adjustable emissivity) to the same emissivity value as the measured material, and the measured value should be as close as possible to the measured value. The actual temperature of the object is the same.
Infrared thermometers are now widely used and have become an important tool for detecting defects in electrical equipment. Due to long-term use in the production line, on-site testing of electrical equipment outlet connectors, T-shaped clamps, wall bushing connectors, busbar nodes, knife gates, cable connectors in substations; wire connection pipes, wire clamps or wire connections for transmission lines waiting. Due to the harsh on-site use environment and improper daily maintenance, the infrared thermometer in operation may not be able to measure accurately or even equipment failure, resulting in inaccurate measurement and affecting the safe and stable operation of the power grid. This paper studies the self-calibration method of the infrared thermometer in operation according to the principle of infrared temperature measurement. It is simple and easy. The user can make self-calibration equipment according to this method. Whether the infrared thermometer is in good working condition can be tested to reduce potential safety hazards.
2. Introduction to the self-calibration method of the infrared thermometer
The important factors for the infrared thermometer to ensure the temperature measurement accuracy are the emissivity, the distance to the spot, the position of the spot, and the field of view. Through communication and consultation with infrared temperature measurement professionals and technical personnel of equipment manufacturers, after repeated practice in various methods, a set of calibration equipment was made by referring to the principle of blackbody furnace, and the self-calibration ratio of the method was verified by comparison. Yes it is feasible. During the self-calibration, the comparison of the basic error, the influence of the measurement distance change, and the determination of the emissivity range are completed. Before the test, the infrared thermometer is adjusted to a good state and then used for on-site testing.
The self-calibration method of the infrared thermometer is introduced as follows:
2.1 Self-made simple blackbody Water Tank
Referring to the principle of the blackbody furnace and practical work experience, the comparison standard used in the self-calibration is a self-made simple blackbody Water Tank, and the specification of the Water Tank is 450 mmx300 mm, made of iron sheet, with an electric heater inside. Use a 1.5-grade pressure thermometer with good stability (can be replaced by a certified glass liquid thermometer) as a standard device to test the temperature in the Water Tank, considering that the surface temperature of most organic materials, paints or oxidized surfaces is measured When the black tape or black paint reaches the same temperature as the base material, measure the temperature of the tape or paint surface, which is the working experience of the real temperature. At the same time, considering the spot positioning test, stick an 80 mmx80 mm black tape on the liquid surface at the same depth as the pressure thermometer probe. After the water in the Water Tank boils for 5 minutes, when the temperature field in the Water Tank is uniform, use an infrared Tester to aim at the black tape center point for comparison.
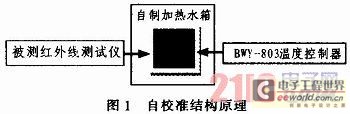
2.2 Traceability of value transmission
In order to ensure the effectiveness of the self-calibration work carried out, the comparison standard used is BWY-803 temperature controller, which can be traced to the second-class mercury thermometer standard device of the enterprise.
2.3 Technical requirements
The basic error of the infrared thermometer and the influence of the measurement distance change shall not exceed the provisions in Table 1.
2.4 Calibration items
According to the field use and practical experience, the calibration items mainly complete the visual inspection, the determination of the basic error, the determination of the influence of the change of the measurement distance and the determination of the emissivity range.
2.5 Calibration method
2.5.1 Appearance inspection
1) All parts are assembled in good condition without defects;
2) Characters, signs and scales should be completed and clear;
3) Appearance and parts should be well treated without rust and mildew ;
4) If there is a "BAT" prompt, replace the battery in time;
5) The objective lens and eyepiece are not damaged, and the aiming should be clear. If the environment is dusty, clean the surface of the lens, blow off the surface dust with clean air, or use a soft brush Brush off the dust.
2.5.2 Determination of basic error
Pay attention to the environmental conditions, there should be no intermediate media such as water vapor, dust, smoke, carbon dioxide, etc., otherwise it will block the optical system of the instrument and affect the self-calibration results. Place the infrared thermometer under test at room temperature (20+2)°C to preheat for 20 minutes before performing self-calibration. This method calibrates the basic error of the 100°C point, the influence of measurement distance changes and the range determination of emissivity, and conducts qualitative test analysis on the equipment. Heat the Water Tank until the water boils for 5 minutes, then test after the temperature field is constant, adjust the emissivity of the infrared thermometer to 0.94, and the distance is 2 m, aim at the center point of the black tape on the Water Tank for measurement, and calculate the error according to the measurement results:
γ=[(EBC-EB)/EB]×100%
In the formula: γ is the basic error; EBC is the indicated value of the measured infrared thermometer (°C); EB is the corrected standard thermometer indicated value (°C )
;
Change the measurement distance to 4 m, 6 m, 8 m, 10 m, and 12 m one by one, record the measurement results in turn, and compare them with the values measured by the basic error. The error change caused by the change of the measurement distance does not exceed the value in Table 1 Regulation.
2.5.4 Determination of the range of emissivity
Emissivity is an important indicator that affects the measurement results, and the importance of choosing a suitable emissivity goes without saying. Since long-term on-site testing may lead to changes in the emissivity measurement range of the infrared thermometer, the range of emissivity determined before use directly affects the measurement results. Adjust the measurement distance to 2 m, keep the indicated value (°C) of the infrared thermometer consistent with the indicated value (°C) of the standard thermometer, and repeatedly adjust the emissivity of the infrared thermometer to be tested. The change range of emissivity is the normal range of its operation.
2.6 Calibration conditions
1) When measuring the infrared thermometer, the temperature is required to be (20±2)°C, and the humidity is ≤85%;
2) The environment is clean, without vibration, without water vapor, dust, smoke, carbon dioxide and other intermediate media.
3) Self-calibration is performed after the water in the Water Tank boils for 5 minutes and the temperature field stabilizes.
4) When self-calibrating, it should be facing the center of the black tape of the self-made heating Water Tank, and the measurement orientation and distance should be kept consistent during repeated measurements.
2.7 Calibration interval
The calibration interval of the infrared thermometer is to calibrate at any time before field use.
2.8 Processing of test results
1) The measurement error of the infrared thermometer is rounded off at an interval of 0.1. For the number 1 on the right of the reserved digit, if it is greater than 0.5, add 1 to the reserved digit; if it is less than 0.5, The reserved bits remain unchanged; if equal to 0.5, the reserved bits remain unchanged when they are even numbers (0, 2, 4, 6, 8), and add 1 to the reserved bits when they are odd numbers (1, 3, 5, 7, 9). And determine whether it is qualified or not based on the result after the contract is revised.
2) Calibration records will be issued after the verification to facilitate data sorting and filing. The records include the calibration address, the serial number of the tested infrared thermometer, load, calibration distance, calibration result, ambient temperature, humidity, calibration date, time, calibration personnel, etc.
3) Conclusion
In the process of carrying out the research on the working principle of infrared thermometers and the comparison of self-calibration errors, I have mastered a lot of infrared knowledge, understood the process and methods of power infrared diagnosis, and studied the emissivity of infrared thermometers. The influence of parameters such as distance coefficient and distance coefficient on the test results enables technicians to master the correct use and maintenance methods of infrared thermometers. Through the self-calibration error comparison research of infrared thermometers, the company's internal self-calibration specifications have been formulated and approved for implementation. This calibration method has been promoted and applied within the company, and the measurement supervision and management of infrared thermometers has been improved. This method can effectively find the fault of the infrared thermometer, ensure that the infrared thermometer in operation is in a good working condition, ensure the accuracy and reliability of the value transmission, improve the safety factor, and ensure the work quality.

