Although X-ray fluorescence method, β-ray backscattering method, magnetic measurement method and eddy current measurement method are all non-destructive testing methods, magnetic measurement method and eddy current measurement method are suitable for coating production sites.
Measuring Principle of Magnetic Attraction and Thickness Gauge
Magnetic attraction measurement is a kind of magnetic measurement method, which is made by using the principle that the magnitude of the attraction between two magnetic materials is proportional to the distance. Using this principle to make a Thickness Gauge, as long as the difference in magnetic permeability between the coating and the substrate is large enough, it can be measured. As shown in Figure 1, the attraction force between the permanent magnet (probe) and the magnetic steel is proportional to the distance between the two, and this distance is the thickness of the coating. The thinner the coating, the greater the magnetic attraction and the greater the displacement of the permanent magnet; the thicker the coating, the smaller the magnetic attraction and the smaller the displacement of the permanent magnet. Since most industrial products use magnetically permeable steel, magnetic Thickness Gauges are widely used. The basic structure of the magnetic Thickness Gauge is composed of a permanent magnet, a spring, a scale and a self-stop mechanism. After the magnet is attracted to the measured object, the measuring spring is gradually elongated thereafter, and the pulling force is gradually increased. When the pulling force is just greater than the suction force, the thickness of the coating can be obtained by recording the pulling force at the moment when the magnet is detached. The new type of magnetic Thickness Gauge can automatically complete this recording process. Different models have different ranges and applicable occasions, and this kind of instrument is easy to operate, durable, does not need power supply, does not need to be calibrated before measurement, and the price is low, so It is very suitable for on-site quality control in the workshop.
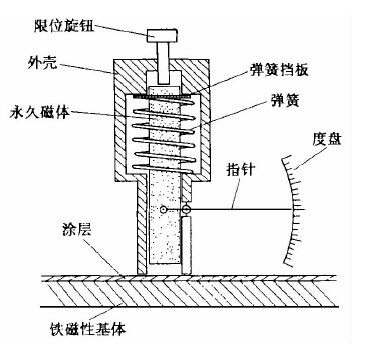
Figure 1 Detection principle of magnetic Thickness Gauge
Magnetic Induction Measuring Principle and Magnetic Thickness Gauge
Magnetic induction measurement is also a kind of magnetic measurement. Its principle is that the reluctance of non-magnetic materials has a certain proportional relationship with its thickness. The thickness of the coating is measured according to the magnetic flux flowing from the probe through the non-ferromagnetic coating into the ferromagnetic substrate. It can also be measured by Measure the corresponding magnetoresistance to represent its coating thickness. As shown in Figure 2, when the probe is in contact with the coating, the probe and the magnetic metal substrate form a closed magnetic circuit. Due to the existence of the non-magnetic coating, the reluctance of the magnetic circuit changes. By measuring the change, it can be Exports the thickness of the coating. The thicker the coating, the greater the reluctance and the smaller the flux. Thickness gauges that use the principle of magnetic induction generally require the magnetic permeability of the substrate to be above 500. If the material of the coating is also magnetic, a sufficiently large difference in permeability from the base material is required (e.g. nickel coating on a steel surface). When the probe with the coil wound on the soft core is placed on the coating to be tested, the instrument will automatically output the test current or test signal. Early products used a pointer gauge to measure the magnitude of the induced electromotive force, and the instrument amplified the signal to indicate the coating thickness. In recent years, circuit design has introduced new technologies such as frequency stabilization, phase-locking, and temperature compensation, using reluctance to modulate measurement signals, and using integrated circuits and introducing microcomputers to improve measurement accuracy and reproducibility by nearly an order of magnitude. The modern magnetic induction Thickness Gauge has a resolution of 0.1 μm, an allowable error of 1%, and a range of 10 mm. The magnetic Thickness Gauge can be used to accurately measure the paint layer, plastic, rubber coating, porcelain and enamel protective layer on the steel surface, and can also measure various non-ferrous metal coatings including nickel and chromium, as well as various metal coatings in the petrochemical industry. Anti-corrosion coating.
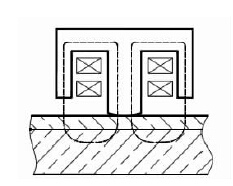
Figure 2 Magnetic induction measurement principle
Eddy current measurement principle and eddy current Thickness Gauge
Using high-frequency alternating current to generate an electromagnetic field in the coil, when the probe is in contact with the coating, an eddy current is generated on the metal substrate, and a feedback effect is generated on the coil in the probe, and the coating is derived by measuring the magnitude of the feedback effect The thickness, its working principle is shown in Figure 3. The closer the probe is to the conductive substrate, the greater the eddy current and the greater the reflection impedance. This amount of feedback characterizes the distance between the probe and the conductive substrate, that is, the thickness of the non-conductive coating on the conductive substrate. The Thickness Gauge made according to the principle of eddy current measurement is called eddy current Thickness Gauge. Since the eddy current Thickness Gauge probe is specially used to measure the coating thickness on non-ferromagnetic metal substrates, it is called a non-magnetic probe.
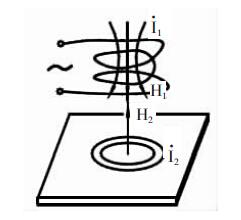
Figure 3 Basic working principle of eddy current method
Compared with the principle of magnetic induction, the principle of eddy current measurement is different in the probe, the frequency of the signal, the size of the signal, and the scale relationship. However, like the magnetic induction Thickness Gauge, the eddy current Thickness Gauge has a resolution of 0.1 μm, an allowable error of 1%, and a range of 10 mm. The Thickness Gauge using the eddy current principle can in principle measure the non-conductive coating on all electrical conductors, such as paint, plastic coating and coating on the surface of aerospace vehicles, automobiles, household appliances, aluminum alloy doors and windows and other aluminum products. Anodized film. For coating materials with certain conductivity, it can also be measured through calibration, such as chrome plating on copper, but the ratio of the two conductivity is required to be at least 3 to 5 times different. Although the steel substrate can also conduct electricity, it is more appropriate to use the magnetic principle to measure the coating on the surface of the steel substrate.
The eddy current coating Thickness Gauge has been used to measure the thickness of non-conductive coatings on non-magnetic metal substrates for decades. With the development of various new engineering materials, the application of microelectronics technology and the advancement of standardization, eddy current coating measurement Thickness gauges have continuously made breakthroughs and innovations in circuit design, multi-standard and universal measuring heads, new sensor applications, value display and data printing, measurement and control function expansion and intelligence, etc., and eddy current thickness measurement technology has developed rapidly. .
For more details, please refer to the full text of "Selection and Application of Paint Film Thickness Measuring Instruments on the Painting Production Site" (Zhang Rui, Zhang Yuefu)









