What is the range of visible light that the human eye sees?
The visible light range seen by the human eye is electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths between 380 nanometers and 780 nanometers, also known as the visible spectrum. This range includes colors from purple to red, and all colors and intermediate hue in between.
Visible spectrum is a continuous spectrum that can be measured and analyzed by spectrometers or spectrometers. In practical applications, visible spectrum is very important, and it is widely used in color measurement, optical instrument calibration, lighting design and other fields. At the same time, visible spectrum is also an important way for human beings to perceive the world, which enables us to see the colorful and beautiful world.
According to the different wavelengths of light, the order of chromatography is red, orange, yellow, green, blue, blue, purple
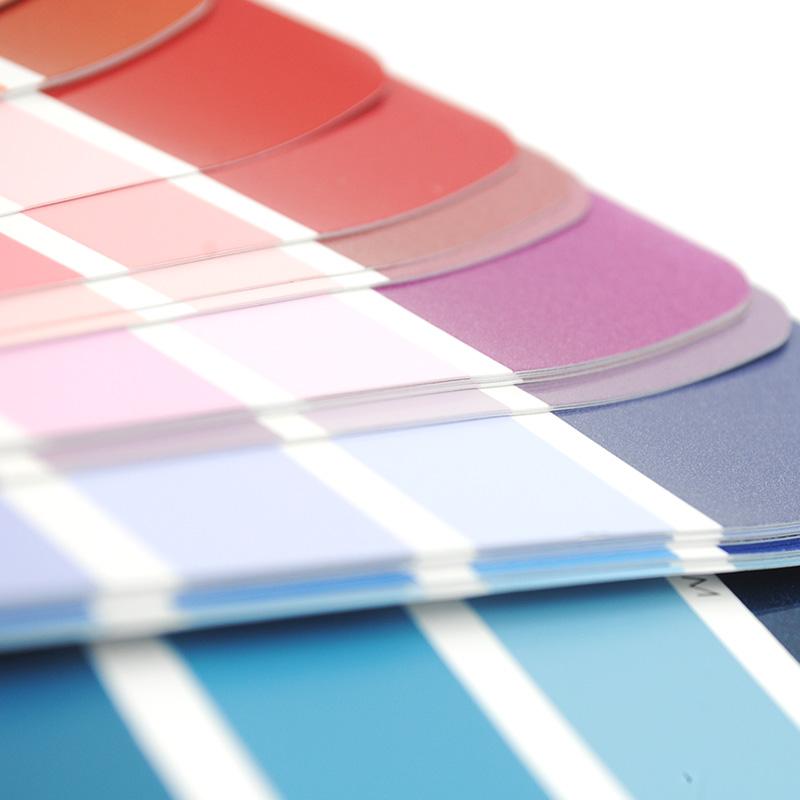

What are the three elements of color?
The three elements of color refer to hue, saturation and brightness, which are the three basic properties that represent and describe color, also known as the basic characteristics of color.
Hue: Hue refers to the position of a color in color space and is used to represent one of the basic properties of color. In a hue diagram, hue begins with red and gradually changes clockwise. Red, orange, yellow, green, cyan, blue, and purple are the seven basic hue, with countless intermediate hue between them.
Saturation: Saturation refers to the purity or intensity of the color, which is related to the degree of mixing of grey release. Solid colors have the highest saturation and gray has the lowest saturation. The higher the saturation of the color, the more vivid the color, the more it can attract people's visual attention.
Brightness: Brightness refers to the brightness of a color, which is related to the amount of white contained in the color. White has the highest brightness and black has the lowest brightness. The higher the brightness, the brighter the color, and the more it can attract people's visual attention.
These three basic attributes together determine the complete characteristics of a color, and different combinations of color attributes can produce an infinite variety of colors. In practical applications, understanding the three elements of color is very useful for designers, manufacturers and consumers, helping them better understand and use color.
Commonly used color coordinates
Commonly used color coordinates are Yxy, L * a * b, L * c * h, etc. At present, many imported domestic Colorimeters use L * a * b color coordinates.
Yxy: The Yxy model is a color model based on how the human eye perceives color. It consists of three parameters: Y represents brightness, x and y represent chromaticity. Y represents the brightness of a color, and x and y describe the hue and saturation of a color. The Yxy model can be used to describe and measure color, especially in computer graphics and the printing industry.
Lab: Lab is a color space that is more widely used than Yxy, and it can represent all visible colors, including small differences that the human eye cannot distinguish. L represents brightness, and a and b represent the difference in color in both red-green and yellow-blue directions. The Lab color space is a color model based on experimental results, often used to describe differences in color and measure the quality of color.
Lch: Lch is a variant of the Lab color space, which consists of three parameters: L for brightness, c for chromaticity, and h for hue angle. The c and h in the Lch model represent the saturation and hue angle of the color, respectively. The Lch model can be used to describe the brightness, saturation, and hue of colors, and is often used for color standardization and comparison.
These color models can be converted to each other. For example, the color value of Lch can be calculated through the Lab color space, the color value of Lab can be calculated through the Yxy color space, and so on. The application and selection of these color spaces need to be determined according to specific application scenarios and needs.
Because light sources make colors look different, in order to measure color, the CIE specifies several different types of typical light sources.
D65 light source: normal sunlight with a color temperature of 6504K, measure the sample illuminated by sunlight.
C light source: normal sunlight with a color temperature of 6774K, measuring specimens illuminated by sunlight in the visible wavelength range.
A light source: incandescent light with a color temperature of 2856K, used to measure samples illuminated by incandescent light
F2 light source: cold white light
F7 light source: daylight
F11 light source: three narrow-band cold white light