introduction
The main function of organic coatings is to protect the substrate from corrosion. Sunlight, heat and temperature, water and humidity are important environmental factors that cause the aging of various polymer coatings. The results of the natural exposure test are true and reliable, but the test time is longer, at least three to five years; the artificial accelerated test in the laboratory, because of its short test period, can make up for the shortcomings of the natural exposure test method to obtain slower results. be widely used. At present, the artificial accelerated test has been widely used in the weather resistance evaluation of materials. On the basis of not changing the aging mechanism of materials, it is an urgent research problem to establish the acceleration factor relationship between the artificial accelerated test and the natural exposure test.
In this paper, several commonly used coatings are selected for laboratory xenon arc lamp aging test, and compared with the results of outdoor air exposure test at Guangzhou Test Station to study their acceleration.
1 Test samples and test methods
1.1 Test sample
In this study, three commonly used protective coating samples with different primers and topcoats were selected to carry out the comparison test of natural exposure in Guangzhou test station and laboratory xenon arc light aging. The coating types are shown in Table 1.
1.2 Test method
a. Guangzhou station natural exposure test method
The natural exposure test in this research adopts GB/T 9276-1996 "Coating Natural Weather Exposure Test Method", outdoor natural exposure at a 45° angle to the south, and the test period is divided into 6 months, 12 months, 18 months, 24 months, 30 months and 36 months, the appearance, gloss, color difference inspection and rating are carried out periodically.
b. Laboratory xenon arc light aging test method
The laboratory xenon arc lamp aging test refers to GB/T 16422.2-1999 "Plastic laboratory light source exposure test method part 2: xenon arc lamp", and the test period is 60 days. Appearance, gloss, color difference detection and rating after the test every 5 days.
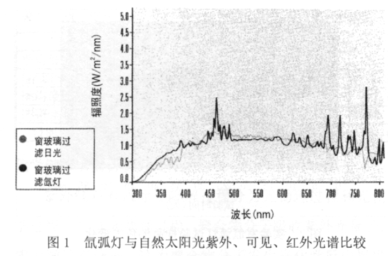
There are many kinds of artificial light sources. Since the spectrum of the xenon arc lamp is the closest to that of natural sunlight (see Figure 1), in order to better find out its acceleration effect with the natural exposure test, this paper chooses the laboratory xenon arc lamp aging test. Compared with the outdoor natural exposure test method. The test conditions are as follows:
Reference standard: GB/T 16422.2;
Irradiance: 1120±112W/m2 [(0.55±0.05)W/m2 @ 340nm ];
Temperature: 49°C;
Relative humidity: 50%;
Each cycle: 24h;
Lighting time: 20h;
Non-illumination time: 4h;
Non-light time: no water spray;
Continuous test time: 60d;
Test cycle: 5d.
2 Test results
2.1 Visual inspection
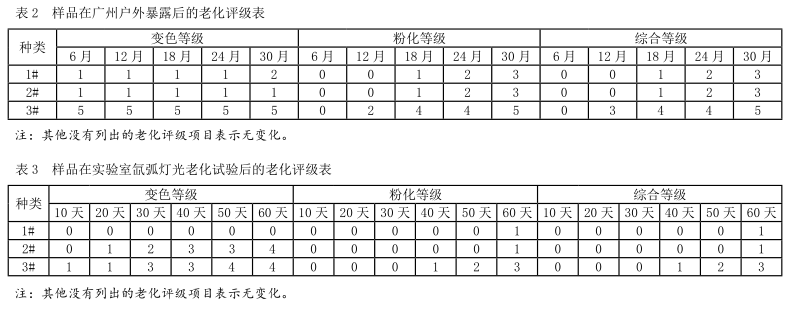
According to GB/T 1766-2008 "Rating method for aging of paint and varnish coatings", the comprehensive aging performance rating of protective paint film is shown in Table 2 and Table 3.
It can be seen from Table 2 that during the 3-year test, the 1# and 2# samples were lower than the 3# sample in terms of discoloration and pulverization performance, showing better weather resistance.
It can be seen from Table 3 that the discoloration level of the 2# sample is equivalent to that of the 3# sample, but its pulverization level is lower than that of the 3# sample, and the comprehensive level is still the same as that of the 1# sample, which is lower than that of the 3# sample. During the aging test, it showed good weather resistance.
2.2 Color difference change
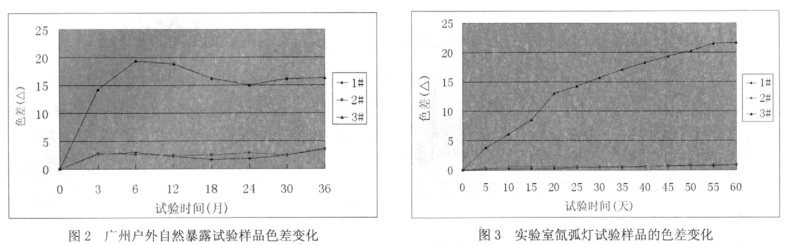
ADCI-60-C automatic color difference meter was used to test the color difference of Guangzhou outdoor natural exposure and laboratory xenon arc lamp test samples, and the changes are shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
2.3 Calculation of acceleration factor
John A Sim ms put forward the concept of AF, that is, "using a certain test method to test for h 1 hour has the same effect as using another test method to test for h 2 hours", then the acceleration factor is the acceleration factor AF = h 1 / h 2 ; or Under the same test time, divide the performance parameter results p 1 and p 2 obtained by the two test methods respectively to obtain the acceleration factor, that is, AF = p 1 / p 2 . The larger the acceleration factor, the higher the acceleration.
In this test, after the same test sample has been subjected to the Guangzhou outdoor natural exposure test and the laboratory xenon arc light aging test, the aging performance ratings of different test cycles are obtained (see Table 2 and Table 3).
After the test and laboratory xenon arc light aging test, the aging performance ratings of different test cycles are obtained (see Table 2 and Table 3). From this, the acceleration factor of the laboratory xenon arc light aging test can be calculated:
AF=T1/T2
In the formula:
AF - acceleration factor;
T 1 - natural exposure aging days when reaching the same aging performance rating;
T 2 ——the aging days of laboratory xenon arc light test when reaching the same aging performance rating.
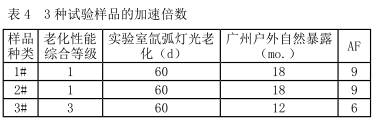
In this project, through the comprehensive grades in Table 2 and Table 3, it can be seen that 1# and 2# samples passed the laboratory xenon arc light aging test for 60 days (comprehensive grade 1) which is equivalent to 18 months of natural exposure (comprehensive grade 1 3# sample passed the laboratory xenon arc light aging test for 60 days (comprehensive level 3) which is equivalent to 12 months of natural exposure (comprehensive level 3), and the acceleration factor AF can be obtained as shown in Table 4.
表 4 可知,实验室氙弧灯光老化试验对于本文中的三种常用防护涂层具有较高的加速性,1#、2# 样品的加速倍数高于 3# 样品的加速倍数。
3 讨论
老化降解主要是光引发的氧化和水解,其影响因素主要是阳光(特别是紫外线)、温度、氧气、水和污染物等。
在研究对有机涂层的户外老化影响因素中,太阳中紫外线被认为是引发降解最主要因素。一般认为有机涂层的光降解机理是自由基反应机理,自由基反应过程如下所示 :
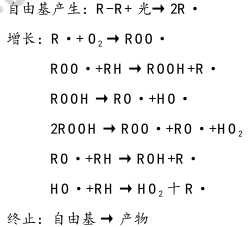
产物光分解和光氧化作用导致有机涂层分子链降解。有机涂层结构发生变化后引起有机涂层性能发生变化,即有机涂层在紫外线作用下发生了老化。
太阳光中主要由可见光、红外光和紫外线组成,其中可见光约占 53% ,红外光约占 44% ,少量的紫外线约占 3% 。虽然紫外线占很小的比例,然而它对聚合物有巨大的破坏作用。紫外线具有能量为 314 ~ 419KJ/m ol,而大部分聚合物自动氧化活化能约为 42 ~ 167KJ/m ol,各种化学键离解能为 167 ~ 418KJ/m ol。例如在紫外光区中300nm 的光能量相当于 399KJ/m ol,而键的离解能只有349KJ/m ol,所以 300nm 紫外线完全可以使链分解。因此到达地面的太阳光所含紫外线的能量足以破坏聚合物的化学键,引发自动氧化反应造成老化分解。
紫外线对有机涂层降解过程分为光物理过程和光化学过程。(1)光物理过程。聚合物分子吸收紫外光量子,成为激发态分子,这为聚合物分子发生光化学反应提供了可能性,但不是每个激发态分子都能促成双分子之间的化学反应 (即导致聚合物降解 )。这些分子可以通过发光 (荧光、磷光 )、发热,以及能量传递等过程转化大部分激发能。这就是一个光物理过程。
(2) Photochemical process. When the polymer molecules are in the excited state, some excited state molecules undergo photochemical reactions. Photochemical reactions still cause molecular chains to degrade through homolysis or recombination in the form of free radical reactions. Photodecomposition and photooxidation finally lead to the breakage of the main chain of the organic coating, the appearance of peroxides and the generation of hydrophilic small molecules. Changes in the structure of the organic coating cause changes in the properties of the organic coating, that is, the organic coating is aged under the action of ultraviolet rays.
In order to study the aging of organic coatings, scientists have always hoped to use different experimental methods to study the aging behavior of outdoor atmospheric coatings or to indirectly study the aging behavior of organic coatings by simulating aging factors such as ultraviolet rays, temperature, humidity, and polluted gases in the outdoor atmosphere. Aging behavior of organic coatings to study the aging mechanism of coatings. The outstanding disadvantage of the outdoor exposure test method is that the test period is long, so there is an artificial accelerated aging test that simulates the outdoor natural environment (ultraviolet light, temperature, humidity, etc.). For example, the experimental method of simulating a single aging factor (such as ultraviolet rays, humidity, temperature, etc.).
In the simulated ultraviolet test method, the test sample is exposed to a light source with a known spectral power distribution and a corresponding humidity and temperature environment under certain conditions, and the coating is aged after a period of time. Commonly used light sources are carbon arc lamps, ultraviolet lamps, xenon lamps, and high pressure mercury lamps. Among the light sources, the xenon lamp is considered to be the light source that best matches the sunlight.
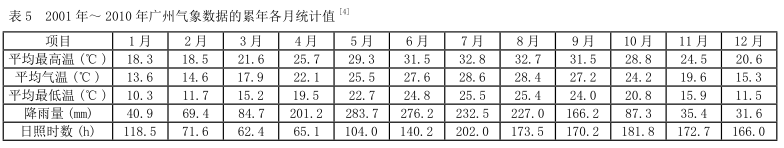
The Guangzhou test station is located at 23N, 113E. We have monitored the main outdoor environmental factors of the Guangzhou test station, and its climate characteristics are shown in Table 5. It can be seen from Table 5 that the annual average temperature in Guangzhou is 21.9°C, the annual average precipitation is 1696.5mm, the annual average relative humidity is 77%, and the annual average sunshine hours are more than 1800 hours, which belongs to the typical subtropical monsoon climate. Guangzhou has strong solar radiation, high temperature, and large precipitation. These continuous strong radiation, high temperature, and high humidity factors all accelerate the aging of organic coatings. Therefore, the xenon arc light aging used in this paper is more in line with the aging mechanism of the coating, and has better acceleration than the Guangzhou outdoor atmospheric exposure test.
4 Conclusion
(1) After 36 months of natural exposure outdoors in Guangzhou and 60 days of laboratory xenon arc light aging test, the color of the sample changed to varying degrees, and there were obvious chalking phenomena;
(2) The aging speed of 1# and 2# samples is slower than that of 3# samples, showing more stable performance;
(3) Laboratory xenon arc light aging test has high acceleration, the acceleration factor for 1# and 2# samples is 9, and the acceleration factor for 3# sample is 6.
