Definition of VOCs
The academic definition of VOCs: refers to organic chemical substances with a vapor pressure above 0.1mmHg (13.3Pa) and a boiling point below 260°C (500°F) under normal conditions (20°C, 101.3kPa).
Characteristics of VOCs
●All contain carbon elements, and also contain non-metallic elements such as H, O, N, P, S and halogens.
● Low melting point, easy to decompose, easy to volatilize, can participate in atmospheric photochemical reactions, and produce photochemical smog under sunlight.
●At room temperature, most of them are colorless liquids with irritating or special odor.
● Most of them are insoluble or hardly soluble in water, but easily soluble in organic solvents.
● There are millions of species, most of which are flammable and explosive, and some are poisonous or even highly toxic.
● Relative vapor density is heavier than air.
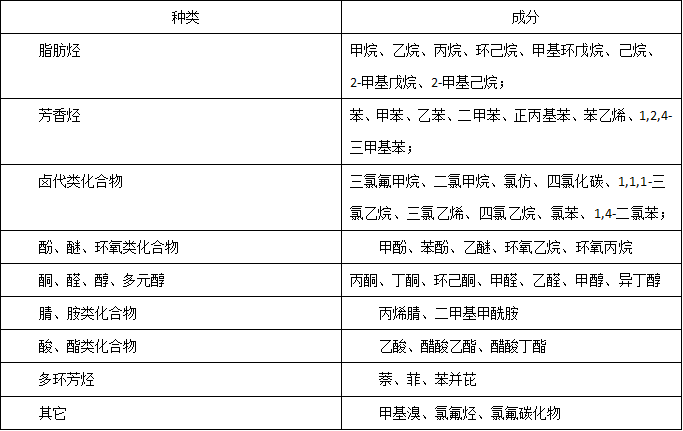
Classification of VOCs
According to their chemical structure, VOCs can be divided into: hydrocarbons (alkanes, olefins and aromatics), ketones, esters, alcohols, phenols, aldehydes, amines, nitriles (cyanides), etc.
Common VOCs types and components are shown in the table
Sources of VOCs
The research on the emission source of VOCs and its pollutant emission is the fundamental to control VOCs in the atmosphere, and the sources of VOCs gas are very extensive. Typical VOCs emission sources can be divided into two types: man-made emission sources (including stationary sources and mobile sources) and natural emission sources (including biological sources and non-biological sources). Production process, product consumption behavior and motor vehicle exhaust. Through analysis and summary, VOCs mainly come from the following aspects:
(1) Process tail gas discharged from petrochemical plants, such as petroleum refining process, petrochemical oxidation process, petrochemical storage tank production process;
(2) A large amount of VOCs gas may be produced during the mining, storage and transportation of oil, coal, natural gas, etc.;
(3) Incomplete combustion products of coal, petroleum, petroleum products, natural gas, wood, and tobacco combustion, flue gas generated during waste incineration, and incompletely combusted hydrocarbons contained in tail gas emitted by motor vehicles;
(4) Interior decoration and decoration materials such as paints, spray paints and their solvents, wood preservatives, paints, plywood, etc. can release benzene, toluene, xylene, formaldehyde, phenols and other volatile organic substances at room temperature;
(5) Volatile organic substances such as phenols, ethers, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons can be produced during the processing and use of cosmetics used in daily life, organic pesticides, deodorants, disinfectants, preservatives, and various detergents;
(6) Various synthetic materials, organic adhesives and other organic products are oxidized and cracked when exposed to high temperature, which can produce some low-molecular organic pollutants;
(7) Some organic pollutants are produced during the oxidation and decomposition of starch, fat, protein, cellulose, sugar, etc.
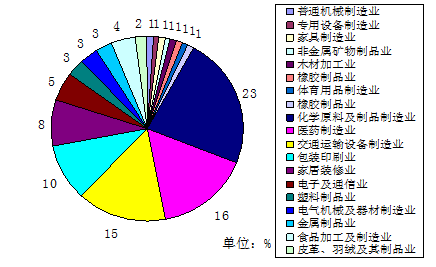
In addition, according to the survey results, the industry distribution of industrial VOCs emission sources in my country is shown in the figure
The hazards of VOCs
There are many kinds of VOCs, and their harm to human health and living environment mainly reflects the following aspects:
(1) Most VOCs have irritating odor or odor, which can cause people's sensory discomfort and seriously reduce people's quality of life. Malodorous gas refers to all gaseous substances that stimulate the olfactory organs and cause people's unpleasantness.
(2) VOCs are complex in composition, have special odor and have the characteristics of penetration, volatilization and fat solubility, which can cause many discomfort symptoms in the human body. It also has toxic, irritating, teratogenic and carcinogenic effects, especially benzene, toluene, xylene, and formaldehyde are very harmful to human health. Long-term exposure will cause people to suffer from anemia and leukemia. In addition, VOCs gas can also cause lesions in the respiratory tract, kidney, lung, liver, nervous system, digestive system and hematopoietic system. As the concentration of VOCs increases, the human body will experience symptoms such as nausea, headache, convulsions, and coma.
(3) VOCs are mostly photochemically reactive. Under sunlight, VOCs will chemically react with NOx in the atmosphere to form secondary pollutants (such as: ozone, etc.) or intermediate products with strong chemical activity (such as: free radicals, etc. ), thereby increasing the surface concentration of smog and ozone, which will endanger human life, and also endanger the growth of crops, and even lead to the death of crops. The smog caused by photochemical reactions, in addition to reducing visibility, produces ozone, peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN), peroxybenzoyl nitrate (PBN), aldehydes and other substances that can irritate human eyes and breathing system, endangering people's health, London, Tokyo and other cities have successively experienced photochemical smog pollution incidents.
(4) Certain VOCs are flammable, such as benzene, toluene, acetone, dimethylamine, and thiohydrocarbons. When these substances are discharged at high concentrations, if they encounter static sparks or other ignition sources, they are likely to cause fires. In recent years, fire and explosion accidents caused by VOCs have occurred frequently, especially in petrochemical enterprises.
(5) Some VOCs can destroy the ozone layer, such as chlorofluorocarbons. When it is exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun, it can undergo a photochemical reaction to generate chlorine atoms, thereby catalytically destroying the ozone in the ozone layer. The decrease in the amount of ozone and the destruction of the ozone layer increases the amount of ultraviolet radiation reaching the ground. Ultraviolet rays are harmful to human skin, eyes and immune system.
VOCS is ubiquitous in daily life, work, operation and other environments, so the detection and management of VOCS should be strengthened and popularized. For detecting the concentration of VOCS , you can use a VOCS Detector, such as Shenzhen Wuyanjie Technology Needle VOCS Detector .









